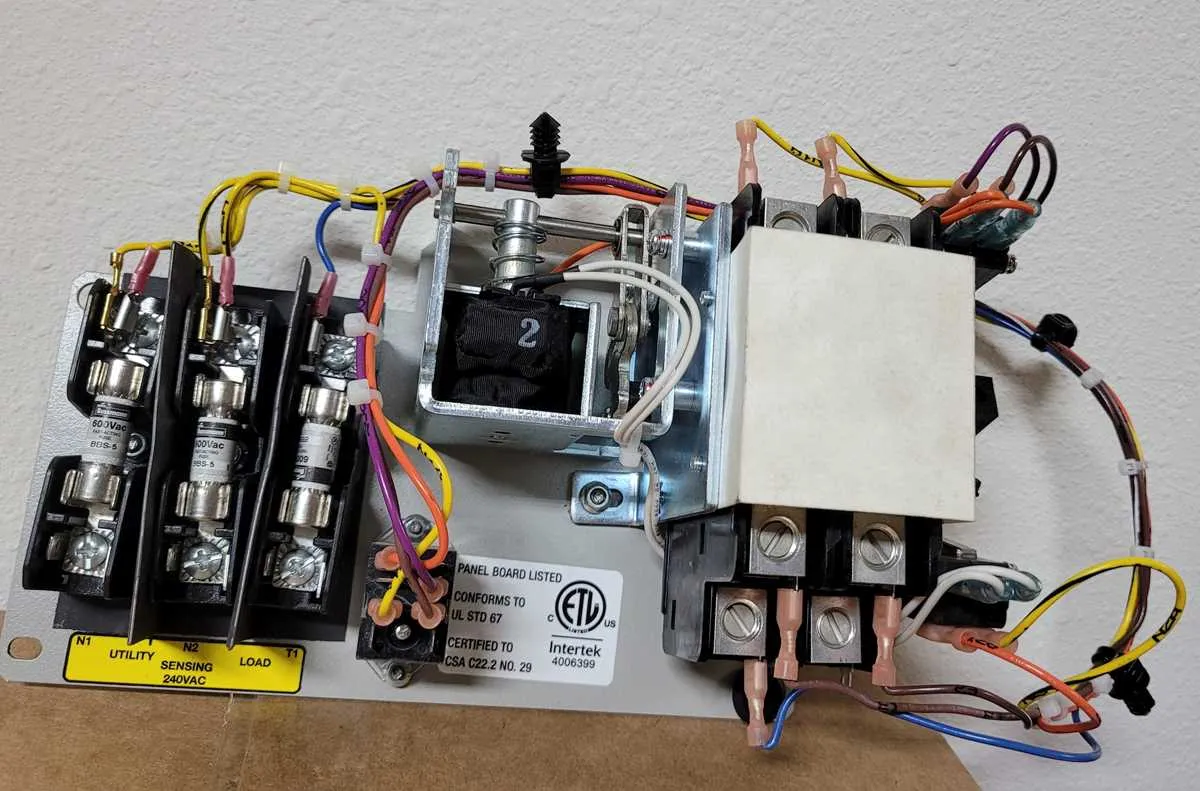
Ensure correct placement of your electrical components by following these steps closely. Begin by securely linking the generator’s output to the primary panel’s input, utilizing suitable connectors and wires rated for the load. Check that the neutral and ground connections are separated to prevent unwanted current flow.
For optimal operation, connect each phase of the generator to its corresponding breaker within the panel, ensuring that the circuit is protected against overloads. Verify the integrity of all connections with a multimeter to avoid issues caused by poor contact or incorrect wiring.
It is crucial to verify that the system complies with local electrical codes. Always consult the manual provided by the manufacturer to double-check wire gauge sizes and breaker ratings. Failure to do so could lead to subpar performance or damage to your equipment.
Electrical Connection Layout for Backup Power Systems
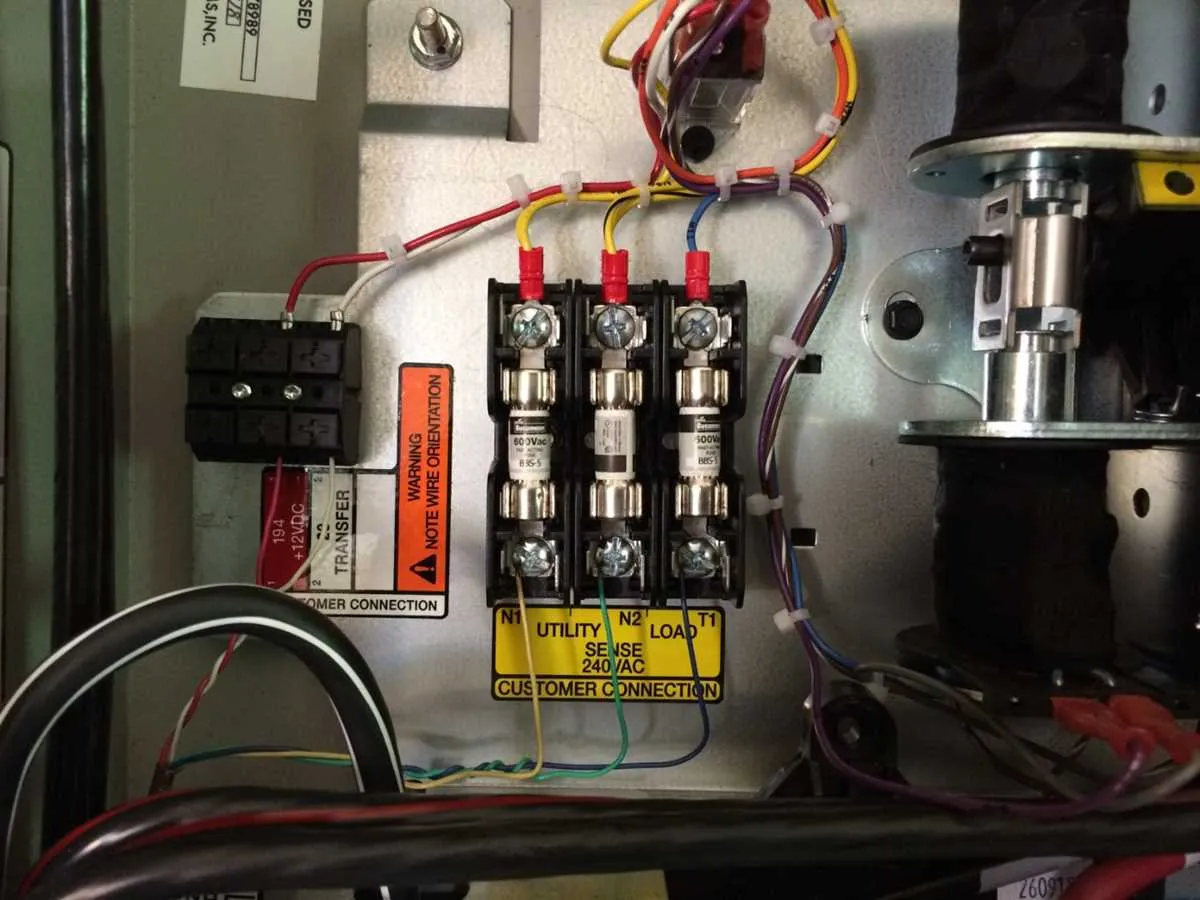
Ensure a reliable backup power setup by following the correct procedures for connecting essential components. Begin by securely wiring the main panel to the backup generator’s input. Properly identify the voltage and amperage specifications for each connection to prevent overloading or damage. Use a transfer panel to isolate the backup power source from the main grid during operation.
Establish a grounding system that meets electrical code requirements to protect both the generator and household wiring. Use appropriately rated wire gauges for each connection based on the system’s requirements. Pay close attention to the neutral and ground connections to avoid improper configurations that could lead to safety hazards.
Before initiating the connection process, verify the generator’s output is compatible with your home’s electrical system, ensuring all equipment is capable of handling the load. It is critical to use high-quality connectors and ensure all wiring is securely fastened to avoid any loose connections that may result in electrical faults.
After completing the installation, perform a thorough test to confirm functionality. Activate the generator to ensure it is correctly supplying power and that the entire system is operating within the required parameters. Regularly check for any signs of wear or damage to wiring and connections to maintain safety and reliability.
Step-by-Step Guide to Connecting a Power Control System
1. Disconnect the power supply from the main electrical panel before beginning any work. Ensure all breakers are turned off, and use a voltage tester to confirm that the system is de-energized.
2. Mount the unit securely on a solid, level surface near the electrical panel. Make sure the device is easily accessible and positioned according to manufacturer specifications.
3. Attach the main power cables to the appropriate terminals. Carefully follow the labels on the device, ensuring the live, neutral, and ground wires are connected correctly. Double-check each terminal for a secure connection.
4. Install the auxiliary circuits that will control the backup power. These should be connected to the designated terminals as per the system’s configuration. Properly match each load to the corresponding output terminal.
5. Check grounding requirements. A proper ground connection is critical for safety. Verify that the grounding wire is securely fastened to the grounding terminal and that the ground rod or other grounding method complies with local electrical codes.
6. Test the system by turning the power back on. Monitor the device closely to ensure proper functionality, with the unit switching correctly between power sources. Test each output circuit to confirm it is powered as expected.
7. Final inspection should be carried out by a licensed electrician. Ensure that all connections are tight, no wires are exposed, and that the system is functioning as intended without any issues.
Common Electrical Mistakes and How to Prevent Them
Ensure all connections are properly tightened. Loose terminals can result in overheating and electrical hazards.
- Incorrect Polarity: Always double-check that the positive and negative wires are connected correctly. Reversing them can cause short circuits or failure of critical components.
- Overloading Circuits: Avoid exceeding the rated capacity of your electrical system. Too many devices on a single circuit can lead to fires or component damage.
- Improper Grounding: A proper ground connection is essential for safety. Neglecting it can cause shocks, electrical faults, and unreliable performance.
- Neglecting Wire Gauge: Use the correct gauge for the amperage to avoid overheating. Using wires that are too thin for the current can result in insulation breakdown.
- Skipping the Inspection: After installation, inspect all connections for signs of wear, fraying, or corrosion. Regular checks ensure the longevity of your setup.
Be sure to follow proper instructions and consult a licensed electrician when in doubt to ensure safe and reliable operation.
Testing the Electrical Connections After Installation
Ensure all connections are securely tightened using a torque wrench. Verify that each terminal is properly seated and that no wires are exposed or improperly connected. It’s critical to perform continuity tests to confirm that the system is electrically sound. Use a multimeter to check each connection for potential shorts or open circuits.
Inspect the Grounding: Proper grounding is essential to prevent electrical hazards. Check that the ground wire is connected to the system’s ground bus bar and that it has a low-resistance path to earth. Use an ohmmeter to measure the resistance of the ground connection and confirm it falls within safe limits.
Test the System’s Functionality: After securing the connections, conduct a load test. Power on the system and simulate a power outage. Observe whether the system responds correctly, engaging the backup supply without delay. Ensure the system switches seamlessly between power sources and that no overheating or unusual sounds occur.
Ensure safety precautions are followed during testing. Always wear insulated gloves and use tools with insulated handles to avoid electric shock. Never perform testing while the system is under load unless it’s necessary to validate its operational capacity.