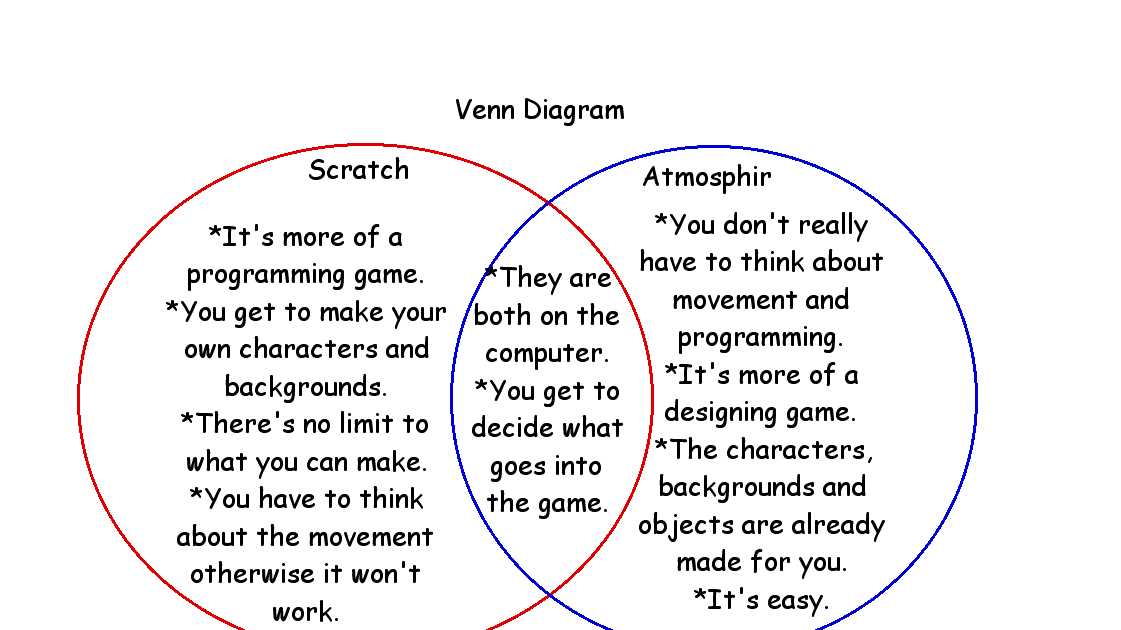
A Venn diagram is a diagram that shows all possible logical relations between a finite collection of different sets. It is a graphical representation of sets. Invented by John Venn, a logician and philosopher, the Venn diagram is widely used in various fields, including mathematics, statistics, and computer science.
The Venn diagram consists of multiple circles or ellipses that represent different sets. Each set is depicted as a separate circle, and the overlapping areas between the circles represent the common elements or relations between the sets. The Venn diagram allows individuals to visually analyze and understand the relationships between different sets, making it a valuable tool for organizing and presenting complex information.
One common question that often arises when using Venn diagrams is how to determine the number of elements in certain regions or combinations of sets. This question can be solved by applying basic set theory principles and counting techniques. By understanding the concepts of union, intersection, and complement, individuals can accurately calculate the number of elements in specific regions of a Venn diagram.
Overall, Venn diagrams offer a visual and intuitive way to represent and analyze the relationships between sets. Understanding how to interpret and use Venn diagrams effectively can greatly enhance one’s ability to solve problems and make logical conclusions in various fields of study and professions.
What is a Venn Diagram?
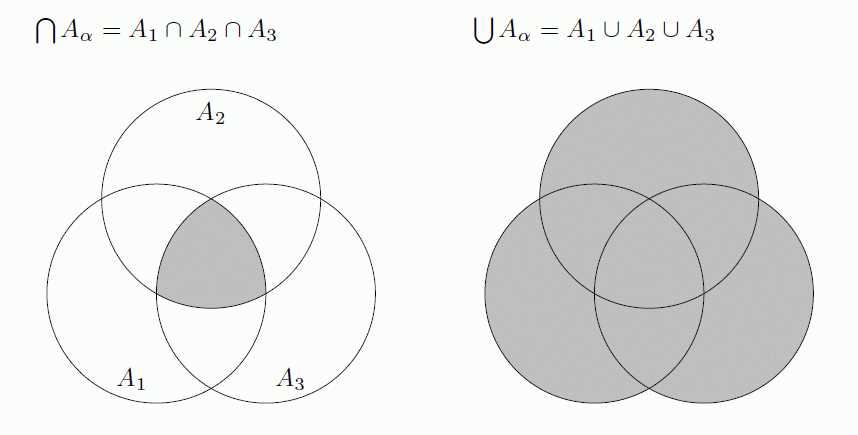
A Venn diagram is a graphical representation of sets, often used to visualize relationships between different items or concepts. It consists of overlapping circles or ellipses, each representing a set, and the overlapping areas indicating the intersection of those sets.
Invented by the mathematician John Venn in the late 19th century, Venn diagrams are widely used in various fields, including mathematics, logic, statistics, and computer science. They provide a visual way to understand the relationships between different sets and their elements.
In a Venn diagram, each circle or ellipse represents a set. The items or elements of a set are represented by points or objects inside the circles. The overlapping areas of the circles show the common elements shared by the sets. For example, if we have two sets A and B, the overlapping area represents the elements that belong to both sets.
Venn diagrams can also be used to show the relationships between more than two sets. In such cases, additional circles or ellipses are added, and the overlapping areas indicate the intersections between multiple sets. This allows for a clearer understanding of the relationships and overlaps between different sets.
Overall, Venn diagrams are a powerful tool for visualizing and understanding the relationships between sets and their elements. They provide a simple and intuitive way to analyze and compare different sets, making them valuable in various fields of study and analysis.
How to Create a Venn Diagram
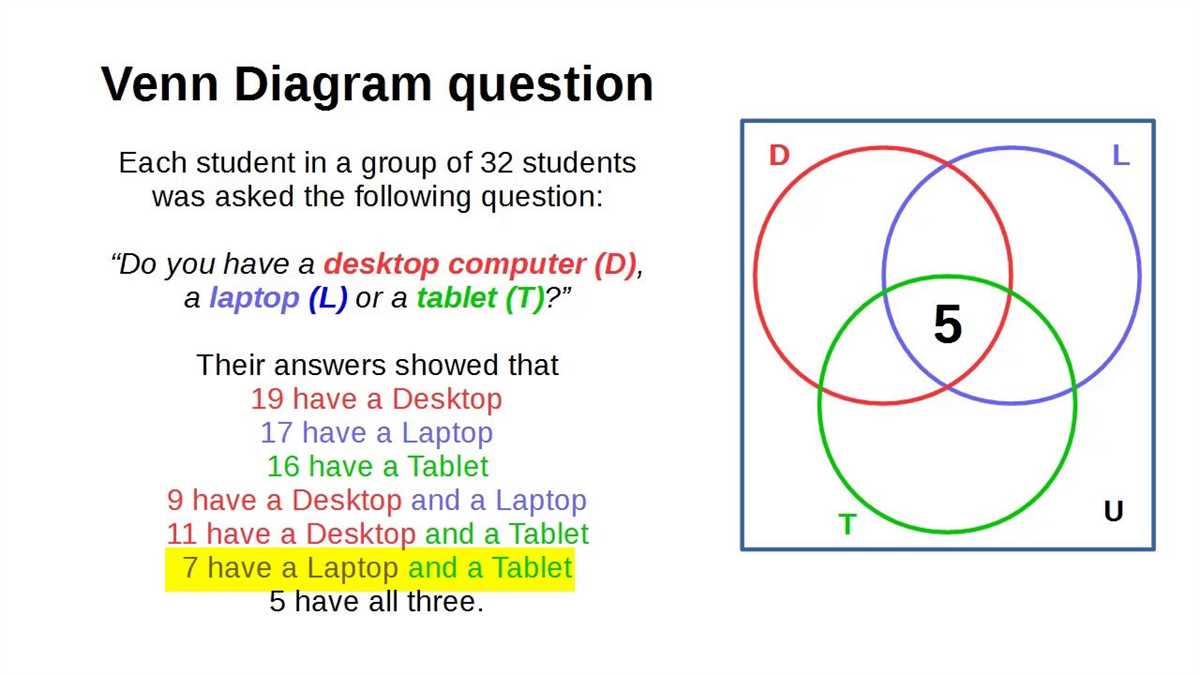
Creating a Venn diagram is a useful way to visually represent the relationships between different sets of data. It can help illustrate commonalities and differences between multiple categories or groups. Here are a few steps to guide you in creating a Venn diagram:
- Identify the sets: Start by determining the different sets or categories you want to include in your Venn diagram. These can be anything from colors, animals, or even concepts like “dogs” and “cats.”
- Draw overlapping circles: Once you have identified the sets, you can begin drawing overlapping circles to represent them. Each circle should correspond to a different set, with the overlapping areas indicating shared characteristics or elements.
- Add labels: Label each circle with the name of the set it represents. This will help clarify the information being presented in the diagram.
- Fill in the overlapping sections: Look for any elements or characteristics that are shared between the sets and fill in the corresponding overlapping sections. This will highlight the commonalities between the different categories.
- Add additional details: Depending on the complexity of your data, you can add additional details to your Venn diagram, such as numbers or percentages, to provide more specific information about the relationships between the sets.
Overall, creating a Venn diagram is a straightforward process that allows you to visually represent the relationships between different sets of data. By following these steps, you can effectively organize and present information in a clear and concise manner.
Key Components of a Venn Diagram
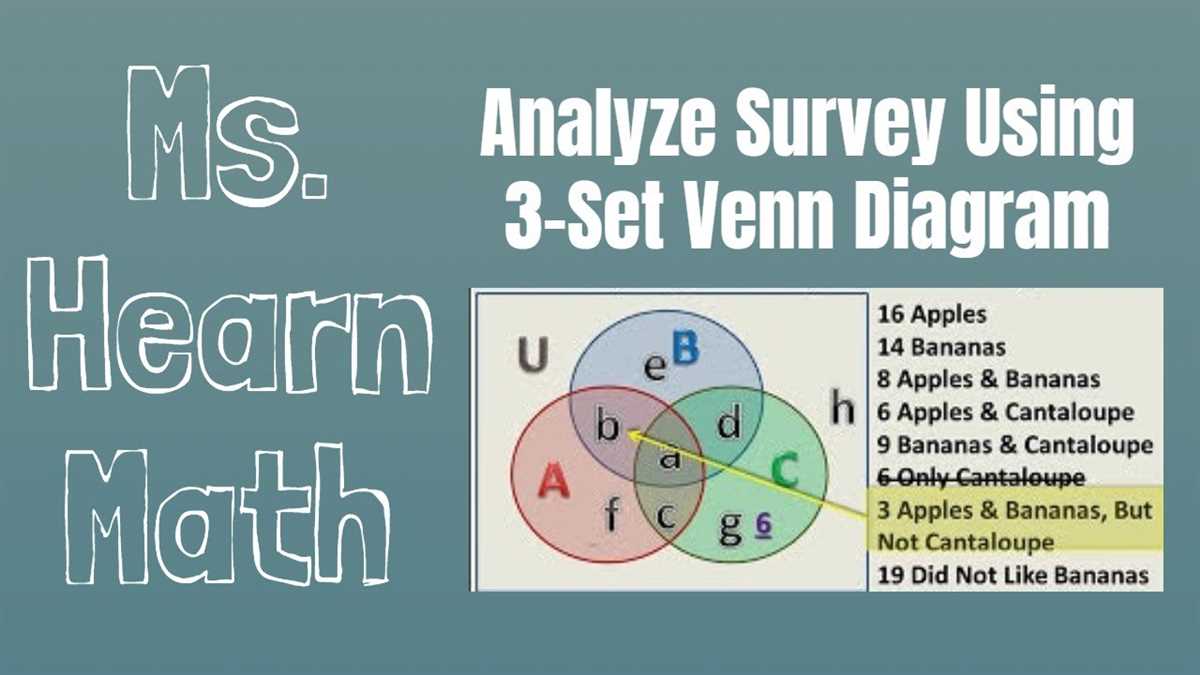
A Venn diagram is a visual representation of the relationships and intersections between different sets or groups of data. It consists of multiple overlapping circles or shapes, each representing a set or category, and the overlapping areas representing the common elements or characteristics shared between two or more sets. Venn diagrams are widely used in various fields, including mathematics, logic, statistics, and data analysis, to visualize and analyze complex relationships and patterns.
1. Sets: The core component of a Venn diagram is the sets or categories being compared. Each set is represented by a circle or shape, and the elements or members of that set are contained within the circle. Each circle can represent any group or category, such as animals, colors, or mathematical concepts.
2. Overlapping Areas: The overlapping areas of the circles in a Venn diagram represent the elements or characteristics that are shared by two or more sets. These areas are where the circles intersect, and they show the common elements or relationships between different groups. The size of the overlapping areas can vary depending on the number of common elements or the extent of the relationship.
3. Labels: It is essential to label each set and overlapping area in a Venn diagram to provide clarity and context. The labels can be written inside or next to the circles, indicating the name or category being represented. The overlapping areas can also be labeled to indicate the specific relationship or common elements being represented.
4. Elements or Members: The individual elements or members of each set are represented within the circles of a Venn diagram. These can be specific objects, concepts, data points, or any other relevant elements related to the category being represented. The elements can be listed within or next to each circle to provide a clear understanding of the data or information being compared.
5. Visualization: The primary purpose of a Venn diagram is to visually represent complex data or relationships in a simple and intuitive way. It allows for a quick and easy understanding of the similarities, differences, and intersections between different sets. The overlapping areas provide a visual representation of the commonalities, and the size and position of the circles can indicate the relative size or importance of each set or category.
A well-designed Venn diagram can effectively communicate complex information and relationships, making it a valuable tool in various fields and disciplines.
How to Interpret a Venn Diagram

A Venn diagram is a visual representation of relationships between different sets of data. It consists of overlapping circles (or ellipses) that represent the sets, with the overlapping regions showing the elements that are common to both sets. Understanding how to interpret a Venn diagram is key to extracting meaningful information from it.
Identify the sets: The first step in interpreting a Venn diagram is to identify the sets involved. Each circle represents a set, and the elements within each circle belong to that set. If the diagram includes more than two sets, each set will have its own distinct circle.
Analyze the overlapping regions: The overlapping regions in a Venn diagram represent the elements that are common to multiple sets. By examining these regions, you can identify the intersections between the sets and determine which elements are present in more than one set.
Read the labels: Venn diagrams often come with labels or descriptions that provide additional context for interpreting the data. These labels may indicate the names of the sets or provide specific information about the elements contained within each set. Make sure to read these labels carefully to fully understand the information presented in the diagram.
Use numerical values: In some cases, Venn diagrams may include numerical values or percentages to indicate the sizes or proportions of the sets and their intersections. These values can provide quantitative insights into the relationships between the sets and help in making more precise interpretations.
Consider the logical implications: Venn diagrams are used to illustrate logical relationships between sets, such as set inclusion or exclusion. By analyzing the diagram, you can determine if certain sets are subsets or supersets of others, and whether there are any elements that do not belong to any of the sets. This understanding can be valuable in drawing conclusions and making logical inferences.
In summary, interpreting a Venn diagram involves identifying the sets, analyzing the overlapping regions, reading the labels, using numerical values, and considering the logical implications. By following these steps, you can effectively extract meaningful information from a Venn diagram and gain insights into the relationships between different sets of data.
Common Applications of Venn Diagrams
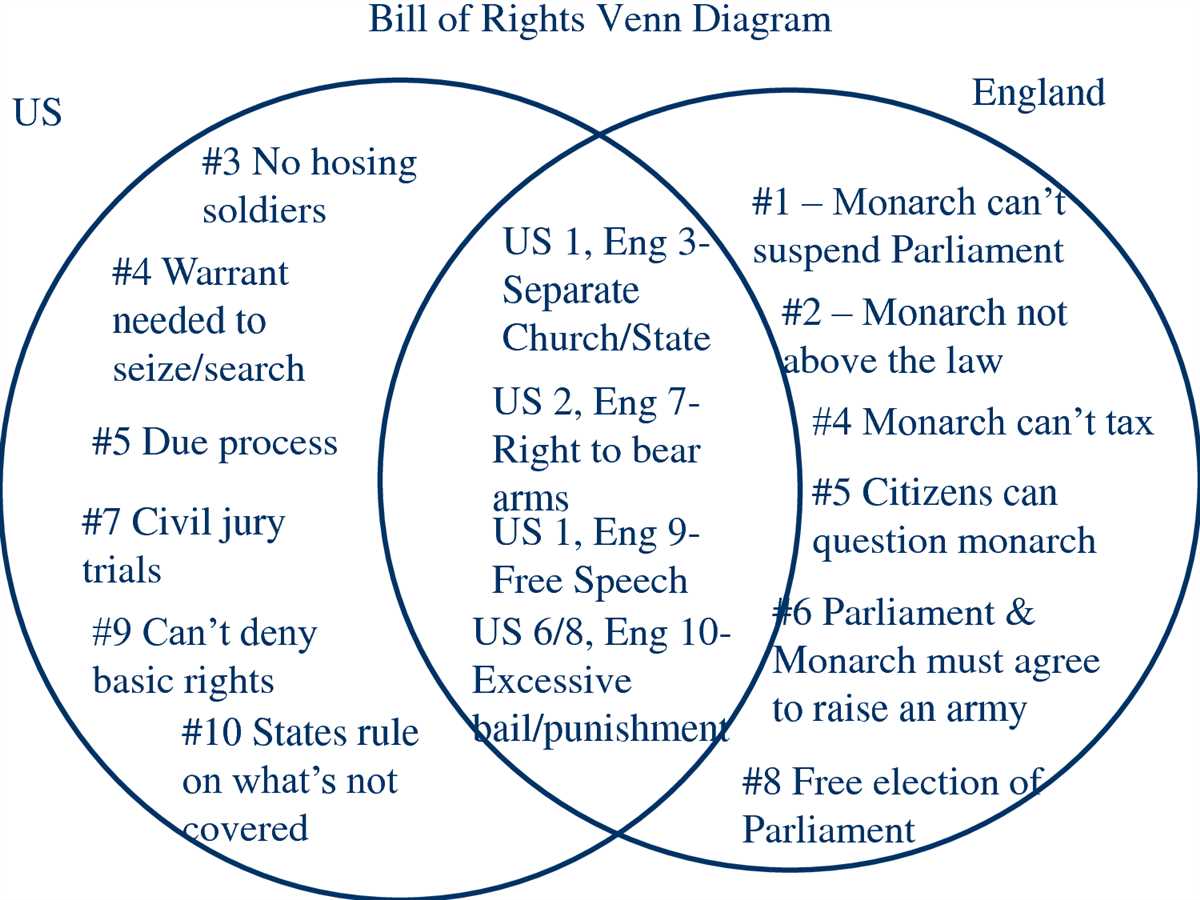
Venn diagrams are a powerful tool in visualizing the relationships between different sets or groups of objects. They are widely used in various fields, including mathematics, statistics, logic, and computer science. Here are some common applications of Venn diagrams:
- Set Theory: Venn diagrams are extensively used in set theory to illustrate the relationships between different sets. They help in understanding the concepts of union, intersection, complement, and subset.
- Data Analysis: Venn diagrams are often used in data analysis to compare and contrast different datasets. They can visually represent the similarities and differences between groups of data points, making it easier to identify patterns and trends.
- Logic: Venn diagrams are a valuable tool in logic for understanding the relationships between different propositions or statements. They can clarify the concepts of conjunction (AND), disjunction (OR), complement (NOT), and implication (IF-THEN).
- Probability: Venn diagrams are commonly used in probability theory to represent the sample space and the outcomes of different events. They can help in calculating probabilities and understanding the concepts of mutually exclusive events and conditional probability.
- Data Visualization: Venn diagrams can be used as a visual aid to present complex information or relationships. They can make it easier for the audience to understand and interpret the data, especially when dealing with multiple datasets or categories.
- Problem Solving: Venn diagrams are often used as a problem-solving tool, particularly in organizing information and finding logical solutions. They can help in breaking down complex problems into simpler components and analyzing the relationships between different variables or factors.
In conclusion, Venn diagrams have a wide range of applications in various fields. They are versatile tools that can aid in understanding, analyzing, and visualizing complex relationships between different sets or groups of objects. Whether in mathematics, statistics, logic, or data analysis, Venn diagrams play a crucial role in simplifying and communicating complex concepts.
Tips for Using Venn Diagrams Effectively
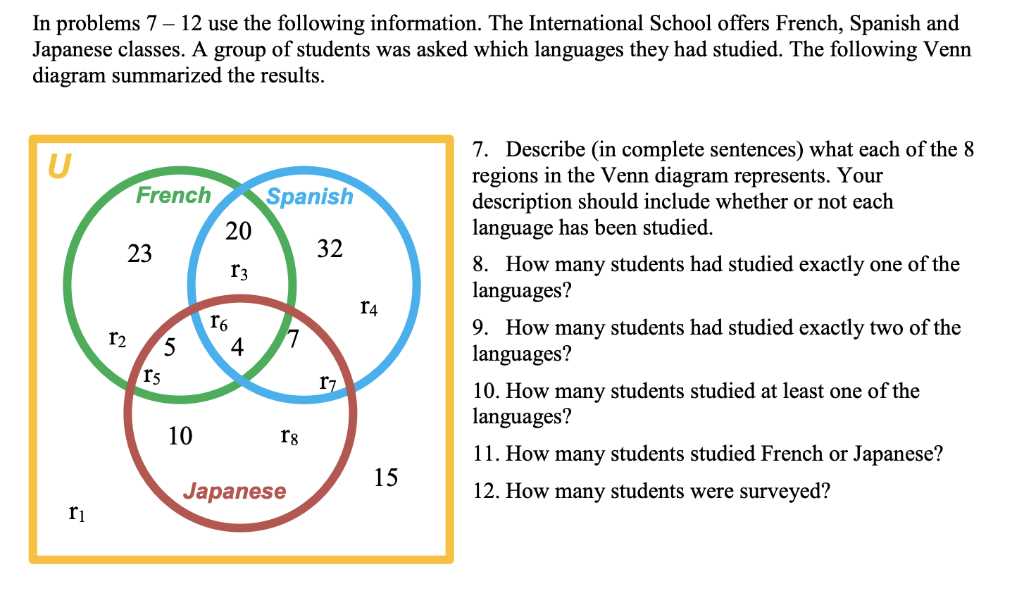
Venn diagrams are a useful tool to visually represent relationships and comparisons between different sets of data. By following these tips, you can make the most out of Venn diagrams and effectively convey your information:
- Define your sets: Before creating a Venn diagram, clearly define the sets or categories you want to compare. This will help you organize your data and avoid confusion.
- Use appropriate labels: Label each set with relevant and descriptive names. This will make it easier for your audience to understand the information presented in the diagram.
- Keep it simple: Avoid overcrowding your Venn diagram with too much information. Keep it simple and focus on highlighting the key similarities and differences between the sets.
- Use colors and shapes: Incorporate colors and shapes to differentiate the sets and make the diagram visually appealing. This can help capture the attention of your audience and make the information easier to understand.
- Use overlapping areas effectively: The overlapping areas in a Venn diagram represent the similarities between the sets. Use them to showcase the common characteristics or elements shared by the sets.
- Provide explanation and context: Along with the Venn diagram, provide a brief explanation or context to help your audience understand the significance of the data and the relationships being depicted.
- Proofread and verify: Double-check your Venn diagram for accuracy and ensure that the data represented is correct. Any errors or inaccuracies can undermine the effectiveness of your diagram.
By following these tips, you can create clear and informative Venn diagrams that effectively convey the relationships and comparisons between different sets of data.