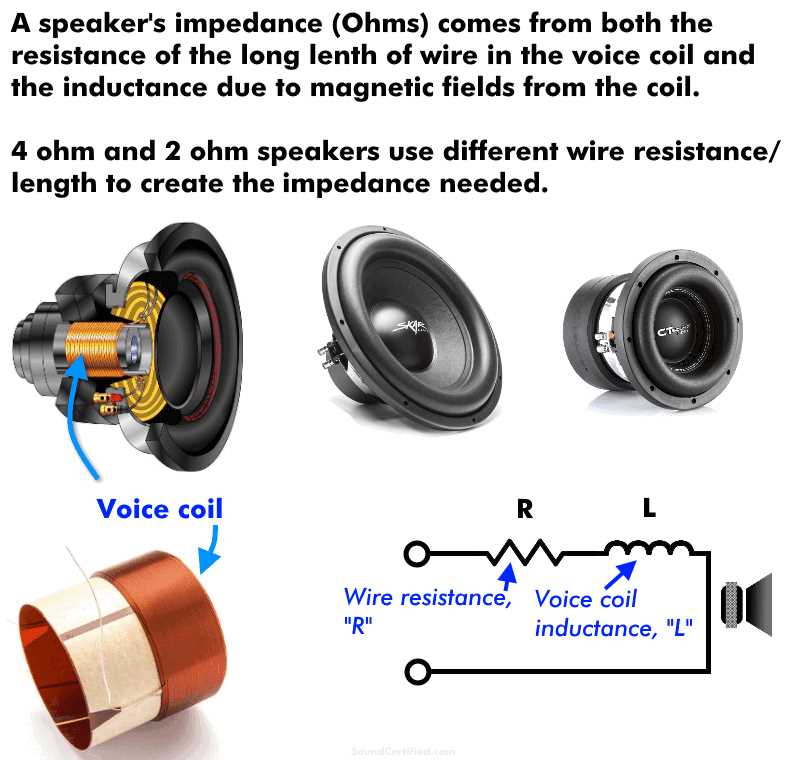
When it comes to audio systems, the impedance of the speakers plays a crucial role in determining the overall sound quality. The impedance, measured in ohms, represents the amount of electrical resistance that the speaker presents to the amplifier. While speakers usually come in 4 ohms or 8 ohms, it is possible to wire two 4-ohm speakers in a way that creates a 2-ohm load.
Before proceeding, it is important to be aware of the risks involved in wiring speakers to a lower impedance than recommended by the amplifier. Lowering the impedance of the speaker load puts additional stress on the amplifier, which can result in overheating or even damage to the amplifier. Therefore, it is crucial to ensure that the amplifier is capable of handling a 2-ohm load before attempting this wiring configuration.
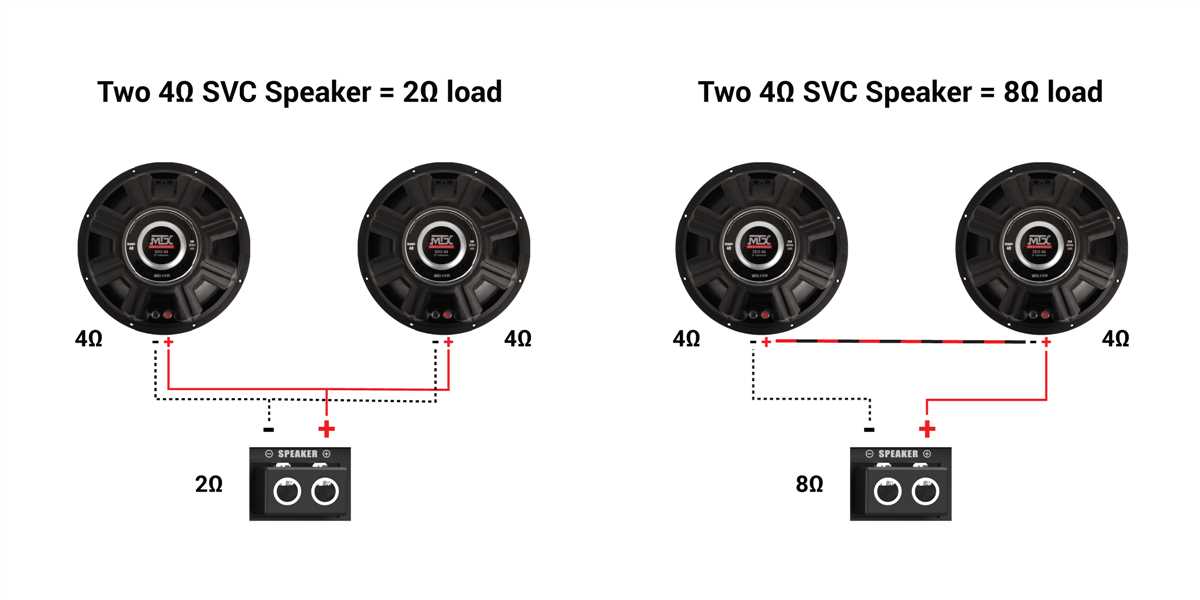
One way to wire two 4-ohm speakers to create a 2-ohm load is to connect the two speaker’s positive terminals together and the negative terminals together. This configuration, known as parallel wiring, divides the total impedance by the number of speakers, resulting in a lower overall impedance. However, it is essential to use caution and follow the speaker manufacturer’s guidelines to avoid damaging the speakers or the amplifier.
In conclusion, while it is possible to wire 4-ohm speakers to create a 2-ohm load, it is important to proceed with caution and ensure that the amplifier can handle the lower impedance. Wiring speakers incorrectly can lead to overheating and damage to the amplifier or speakers, so it is always best to consult the manufacturer’s guidelines and seek professional advice if unsure. Proper wiring and choosing the right amplifier will result in optimal sound quality and avoid any potential damage.
Understanding Speaker Impedance: Wiring 4 Ohm Speakers to 2 Ohm
The impedance of a speaker is an important factor to consider when setting up a sound system. It refers to the resistance the speaker presents to the electrical current flowing through it. Measured in ohms, impedance plays a crucial role in determining the overall performance and compatibility of the speakers with the amplifier or receiver. One common question that arises is whether it is possible to wire 4 ohm speakers to create a 2 ohm load.
When it comes to wiring speakers, it is generally recommended to match the impedance of the speakers to the amplifier or receiver. However, in some cases, it is possible to wire 4 ohm speakers in a way that results in a 2 ohm load. This can be done by connecting two 4 ohm speakers in parallel, effectively cutting the impedance in half. It is important to note that not all amplifiers or receivers are designed to handle a 2 ohm load, so it is essential to check the specifications of the audio equipment before attempting this kind of wiring.
Wiring 4 ohm speakers to create a 2 ohm load can have some advantages and disadvantages. One advantage is that it can potentially increase the power output of the amplifier, as lower impedance allows for greater electrical current flow. This can result in louder and more dynamic sound. However, it is important to be cautious as this can also put more strain on the amplifier and may lead to overheating or reduced lifespan of the equipment.
Another disadvantage of wiring 4 ohm speakers to 2 ohm is that it may not be compatible with all amplifiers or receivers. Most audio equipment is designed to work with specific impedance ranges, and deviating from these ranges can lead to distortion, reduced sound quality, or even damage to the equipment. It is crucial to consult the manufacturer’s guidelines or seek professional advice before attempting any unconventional wiring configurations.
In conclusion, wiring 4 ohm speakers to create a 2 ohm load is possible in some cases, but it is important to consider the compatibility and specifications of the amplifier or receiver. While it can potentially increase power output and enhance sound, it may also strain the equipment and reduce its lifespan. Understanding speaker impedance and consulting professional advice can help ensure a safe and optimal setup for your sound system.
What is Speaker Impedance?
Speaker impedance refers to the opposition the speaker presents to the flow of electrical current. It is measured in ohms and is an important factor in determining the compatibility and performance of audio systems.
The impedance of a speaker is determined by its design and construction, including the type and number of voice coils, magnets, and other components. It can vary depending on the frequency of the audio signal being produced, with some speakers having a higher impedance at certain frequencies.
When connecting speakers to an audio amplifier or receiver, it is important to match the impedance of the speakers to the rated impedance of the amplifier. This ensures that the amplifier can effectively drive the speakers and prevents any potential damage to the amplifier or distortion in the audio signal.
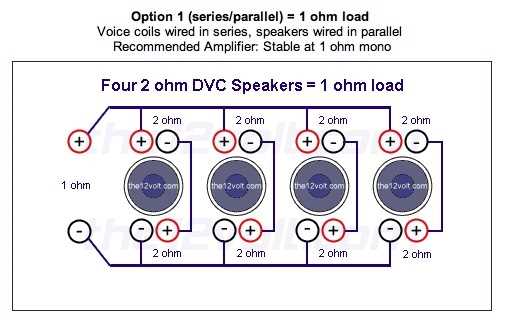
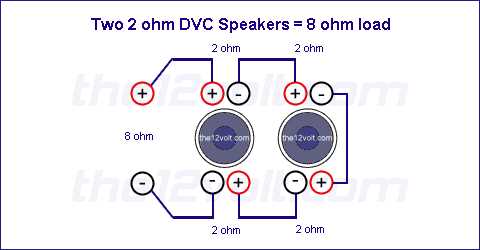
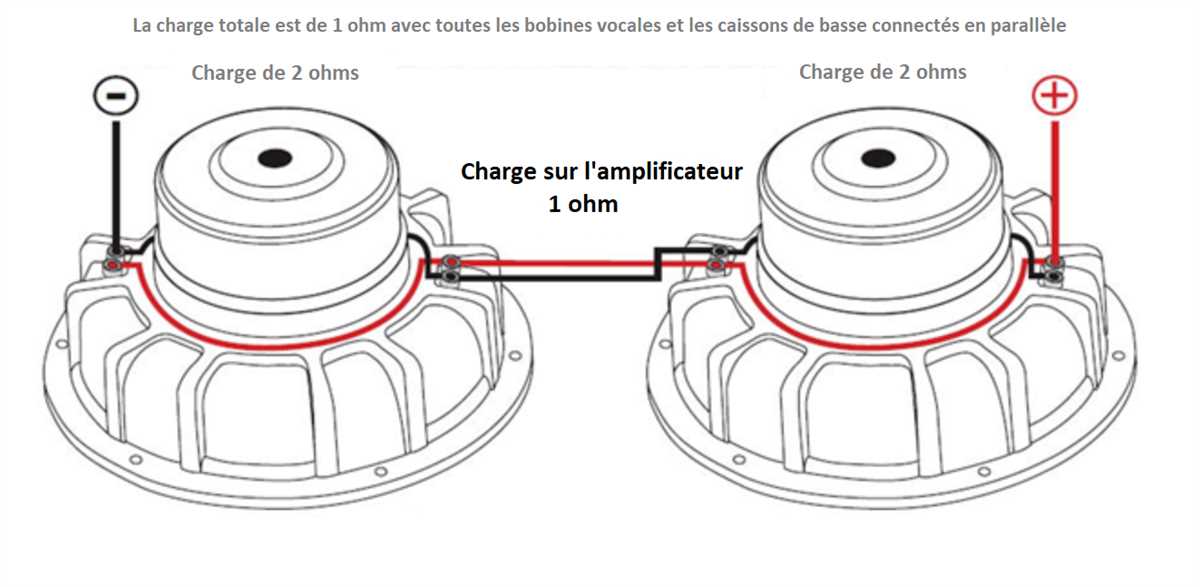
There are also situations where it is possible to wire multiple speakers together to achieve a desired impedance. For example, wiring two 4 ohm speakers in parallel will result in a 2 ohm load, while wiring them in series will result in an 8 ohm load. It is important to consider these factors when designing and building audio systems in order to achieve the desired performance and compatibility.
In conclusion, speaker impedance is an important factor to consider in audio systems. Matching the impedance of speakers to amplifiers and understanding the effects of wiring multiple speakers together can help ensure optimal performance and compatibility in audio setups.
The Importance of Matching Impedance
When it comes to wiring speakers, one important consideration is matching the speaker’s impedance. Impedance is the measure of opposition to the flow of electrical current, and it is typically measured in ohms. It is crucial to match the impedance of your speakers to the amplifier or audio source you are using in order to ensure optimal performance and avoid potential damage.
Matching the impedance is important because it affects the power transfer between the amplifier and the speakers. If the impedance of the speakers is too low compared to the amplifier, it can cause the amplifier to deliver more power than it is designed to handle. This can result in overheating, distortion, or even damage to the amplifier. On the other hand, if the impedance of the speakers is too high, it can lead to inefficient power transfer, resulting in lower volume levels and potentially damaging the amplifier as well.
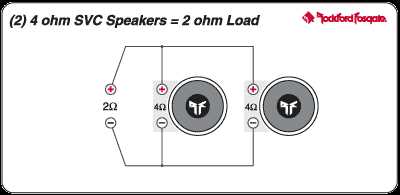
When wiring 4 ohm speakers to a 2 ohm load, it is important to understand the impact on the overall impedance. Connecting two 4 ohm speakers in parallel will result in a 2 ohm load, which can be problematic if the amplifier is not capable of handling such low impedance. It is recommended to check the specifications of both the speakers and the amplifier to ensure compatibility and avoid any potential issues.
In conclusion, matching impedance is vital for optimal performance and safety when it comes to wiring speakers. Whether you are connecting 4 ohm speakers to a 2 ohm load or any other configuration, it is essential to consider the compatibility of both the speakers and the amplifier to avoid damage and achieve the best audio experience possible.
Wiring 4 Ohm Speakers in Series

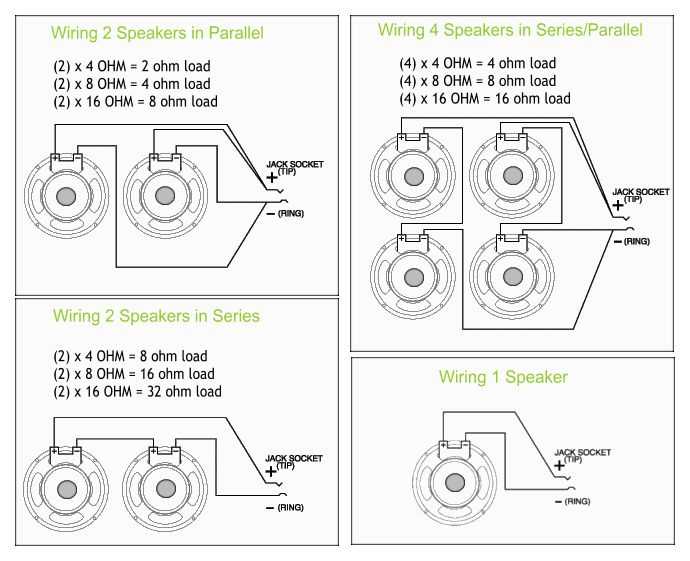
When it comes to wiring multiple speakers together, one common method is to connect them in series. This means that you will connect the positive terminal of one speaker to the negative terminal of the next speaker, and so on. By doing this, you will effectively increase the overall impedance of the speakers.
When wiring 4 Ohm speakers in series, the total impedance will be 8 Ohms. This is because when you connect speakers in series, the total impedance is the sum of the individual speaker impedances. In this case, 4 Ohms + 4 Ohms = 8 Ohms.
If you are planning to connect amplifiers or other audio equipment to these speakers, it is important to consider the impedance matching. Some amplifiers may not be compatible with a 2 Ohm load, so connecting 4 Ohm speakers in series to achieve an 8 Ohm load can be beneficial.
It is worth noting that when wiring speakers in series, the overall power handling capacity will be lower compared to wiring them in parallel. This is because the total impedance is higher, and the amplifier will output less power to compensate for it.
In summary, wiring 4 Ohm speakers in series is a common method to increase the overall impedance of the speakers. This can be useful in situations where you want to achieve compatibility with amplifiers or other audio equipment that may not work well with a lower impedance load.
Wiring 4 Ohm Speakers in Parallel
When wiring 4 Ohm speakers in parallel, it is important to understand the concept of impedance and how it affects the overall speaker system. Impedance is the measure of opposition to alternating current flow, and in the case of speakers, it refers to the total resistance offered by all the speakers connected in a circuit. In parallel wiring, the positive terminals of the speakers are connected together, and the negative terminals are also connected together.
By wiring 4 Ohm speakers in parallel, the total impedance of the circuit is reduced. For example, if you connect two 4 Ohm speakers in parallel, the total impedance would be halved to 2 Ohms. This can be beneficial for certain amplifier setups that are designed to work with lower impedance loads, as it allows for more current to flow through the circuit.
It’s important to note that when wiring speakers in parallel, the power division between the speakers is not equal. The speaker with the lower impedance will draw more power from the amplifier than the speaker with the higher impedance. This can result in an imbalance in sound output, and it is recommended to use speakers that have the same or similar impedance ratings to ensure balanced performance.
When connecting 4 Ohm speakers in parallel, it’s also important to consider the overall power handling capability of the amplifier. Lower impedance loads can put more strain on the amplifier, and it is crucial to ensure that the amplifier is capable of safely driving the speakers at the desired volume levels without overheating or damaging the components.
In conclusion, wiring 4 Ohm speakers in parallel can be an effective way to lower the total impedance of the circuit and allow for more current flow. However, it is important to consider the power division between the speakers, ensure balanced performance, and ensure that the amplifier can handle the lower impedance load. Consulting the manufacturer’s specifications and guidelines is always recommended when wiring speakers in parallel.
Pros and Cons of Wiring 4 Ohm Speakers to 2 Ohm

Wiring 4 ohm speakers to 2 ohm can have both advantages and disadvantages. It is important to understand these pros and cons before deciding whether to proceed with this wiring configuration.
Pros
- Increased power output: One of the main advantages of wiring 4 ohm speakers to 2 ohm is that it allows for increased power output. When the impedance of the speakers is lowered, more current can flow through the system, resulting in higher volume levels and potentially more bass response.
- Potential for better sound quality: In some cases, wiring speakers for a lower impedance can lead to improved sound quality. It can provide better control over the movement of the speaker cone, resulting in tighter and more accurate bass reproduction.
- Compatibility with certain amplifiers: Some amplifiers are designed to work optimally with a 2 ohm load. By wiring 4 ohm speakers in parallel, it is possible to achieve a 2 ohm load and take full advantage of these amplifiers’ capabilities.
Cons
- Potential strain on the amplifier: Wiring 4 ohm speakers to 2 ohm can put additional strain on the amplifier, as it will need to deliver more power to drive the lower impedance load. This could potentially lead to overheating and shorten the lifespan of the amplifier.
- Increased risk of clipping: When pushing an amplifier to its limits, there is a higher risk of clipping, which occurs when the output signal exceeds the maximum voltage or current that the amplifier can deliver. Clipping can result in distortion and can potentially damage the speakers.
- Decreased reliability: Lowering the impedance of the speakers can decrease their overall reliability and longevity. The increased current flowing through the speakers may put additional stress on the voice coils, potentially leading to heat buildup and failure over time.
Overall, wiring 4 ohm speakers to 2 ohm can provide benefits such as increased power output and potential improvements in sound quality. However, it also comes with certain drawbacks, including potential strain on the amplifier and decreased reliability of the speakers. It is important to carefully consider these pros and cons and assess the capabilities of both the speakers and the amplifier before making a decision.