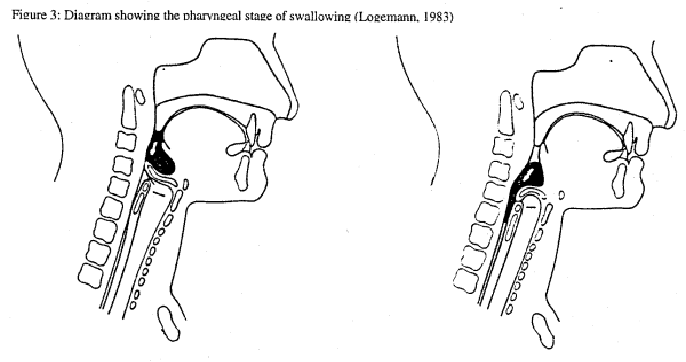
This book is NOT solely dysphagia focused, but rather clearly illustrates The diagrams alone really helped me get a grasp on what I’m actually doing and why.
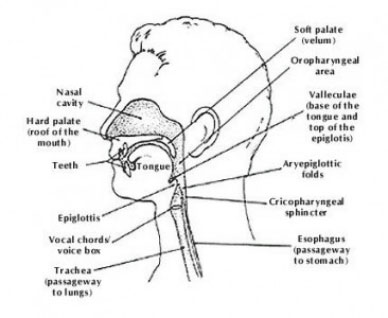
The three phases of the swallowing reflex and causes for swallowing disorders, illustrated with images and animation for easy understanding. Dysphagia PowerPoint – KB · Dysphagia Etiology Chart (empty) to swallowing basics through cross-sectional diagrams of the head. Dysphagia-difficulty of swallowing; Feeding – term is limited to the placement of food in the mouth, the manipulation of food in the oral cavity prior to the initiation .
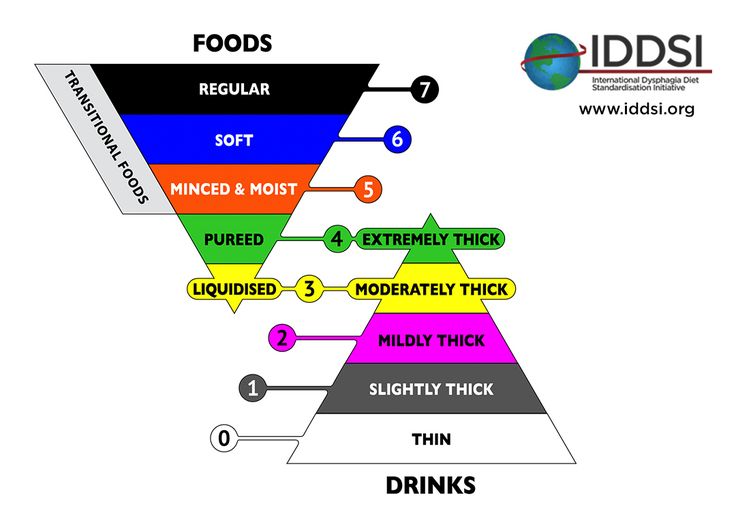
Find resources developed by IDDSI related to dysphagia. Read our open access article, “The International Dysphagia Diet Standardisation Initiative (IDDSI ).Dysphagia (abnormal swallowing) can result from a wide variety of diseases and disorders (Table 2).
40, 41 Functional or structural deficits of the oral cavity, pharynx, larynx, esophagus, or esophageal sphincters can cause dysphagia. Dysphagia may lead to serious complications including dehydration, malnutrition, pneumonia, or airway obstruction.
Swallowing seems simple, but it’s actually pretty complicated. It takes your brain, several nerves and muscles, two muscular valves, and an open, unconstricted esophagus, or swallowing tube to.
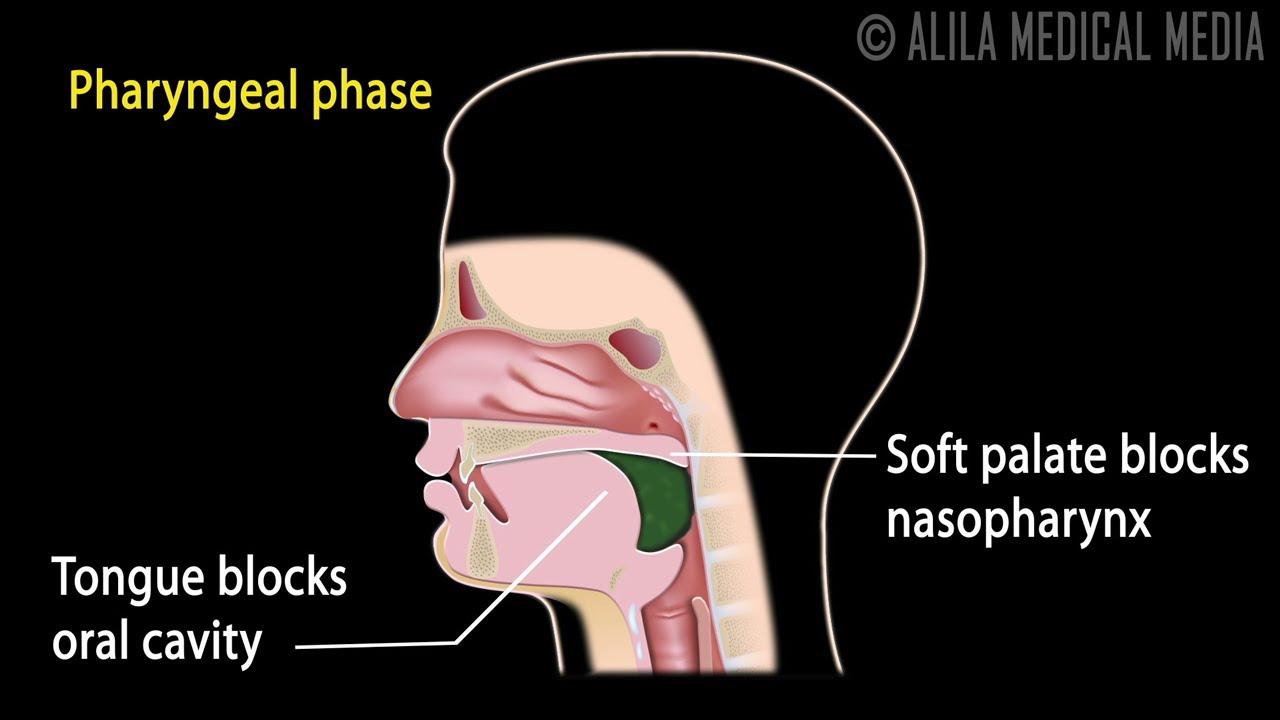
dysphagia into static disorders and dynamic disorders, whereas Horiguchi 8) proposed that it be classified into the following three types: (i) organic dysphagia, (ii) . Esophageal dysphagia is a form of dysphagia where the underlying cause arises from the body of the esophagus, lower esophageal sphincter, or cardia of the stomach, usually due to mechanical causes or motility problems.
Learn dysphagia with free interactive flashcards. Choose from different sets of dysphagia flashcards on Quizlet.Anatomy and Physiology of Feeding and Swallowing – Normal and AbnormalEsophageal dysphagia – Wikipedia
