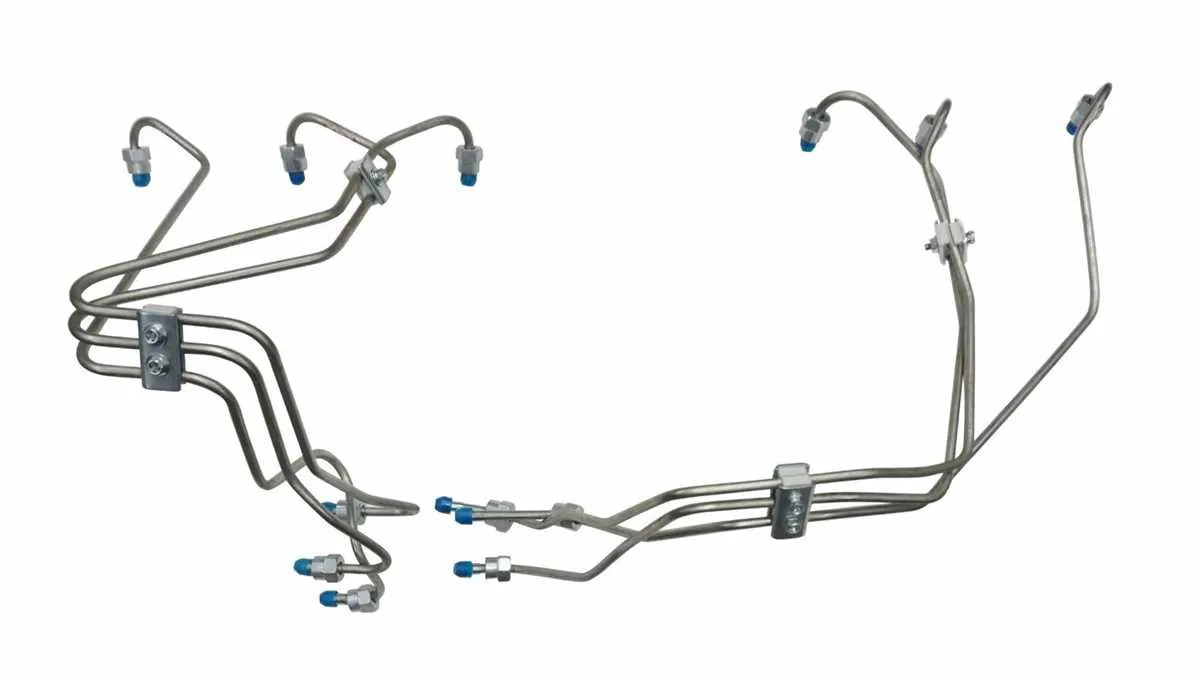
For effective maintenance and troubleshooting of your engine’s fuel system, it’s crucial to follow the correct routing and connections of all components. The fuel delivery system in the 5.9L engine is comprised of several critical parts that ensure proper fuel pressure and flow throughout the engine. Identifying the correct positioning of each component helps in diagnosing performance issues, ensuring longevity and efficiency.
Start by checking the fuel supply path: The primary components involved include the lift pump, fuel filter, high-pressure lines, and injectors. Each part must be securely connected to avoid leaks, and all hoses should be routed without any sharp bends to prevent flow restrictions. When dealing with fuel issues, always begin by confirming that there are no blockages or cracks in the supply and return pathways.
Ensure proper routing of return lines: The return system plays an essential role in maintaining the right pressure levels. Incorrect routing can lead to excess heat, leading to degradation of components over time. Check the pressure regulator, which manages the fuel return flow, and ensure it is set to factory specifications.
Lastly, always refer to the manufacturer’s technical resources for any revisions to the setup. A precise understanding of the flow directions and interconnectivity between components is necessary for accurate diagnostics and repairs.
Fuel System Layout and Connections
To ensure proper operation of the injection system, it is crucial to follow the exact routing for the delivery hoses. Begin by confirming that each hose is securely attached to the respective ports without any kinks. The main supply hose should connect directly to the high-pressure pump, with no obstructions along the route.
Primary connections from the fuel tank to the filter assembly should be tightly sealed. Inspect the connection points for wear or leaks, especially where the hoses meet the pump and injector unit. Use high-quality clamps to prevent any fuel leakage from these crucial points.
The return lines must be installed in the correct orientation to ensure proper circulation. These lines must be routed to avoid contact with hot surfaces to prevent any potential damage. Any signs of wear on these lines should prompt immediate replacement to avoid the risk of system failure.
For maintaining the integrity of the system, check the clamps regularly. Ensure that they are tight and that there is no movement that could cause the lines to come loose. Inadequate clamp pressure could result in fuel leakage and reduced performance of the injectors.
Cleanliness during installation is key. Even small particles or contaminants can cause severe clogging or damage to the injection system. Prior to installation, ensure all hoses and connections are free from dirt and debris.
Lastly, verify that the fuel pump operates within the recommended pressure range. Any drop in pressure could indicate a blockage or leak in the system, requiring further inspection of each segment of the delivery route.
Understanding the Fuel Line Routing on the 12v 5.9 Cummins Engine
Ensure proper installation by following the correct routing of the high-pressure delivery pipes. Any deviation can lead to leaks, loss of performance, or engine damage. Begin with the primary fuel pump, ensuring the inlet pipe is securely connected to the filter housing. The pressure lines should follow a direct path to the injection pump, avoiding sharp bends that could cause restriction or damage.
Key Tips:
- Always use the manufacturer’s recommended hose for fuel distribution. Avoid substitutes that might not handle the necessary pressure or chemical composition.
- Check for correct alignment before tightening. Misaligned connections can result in premature wear and increased risk of leaks.
- Make sure to clean all connections before installation to prevent debris from entering the system, which could clog injectors or damage sensitive components.
Position the return pipe away from high-pressure lines to prevent backflow and ensure smooth operation. The return flow should direct into the tank without restriction. Secure each connection tightly to prevent loosening from engine vibrations.
Never ignore the condition of the seals and washers at the connection points. Damaged seals can cause leaks, leading to fire hazards and efficiency loss.
Use clamps to hold pipes securely, but avoid over-tightening, as this can crush the tubing and lead to leaks. Always inspect for potential wear points, especially near engine components that experience higher heat levels.
Identifying Key Components in the Fuel System
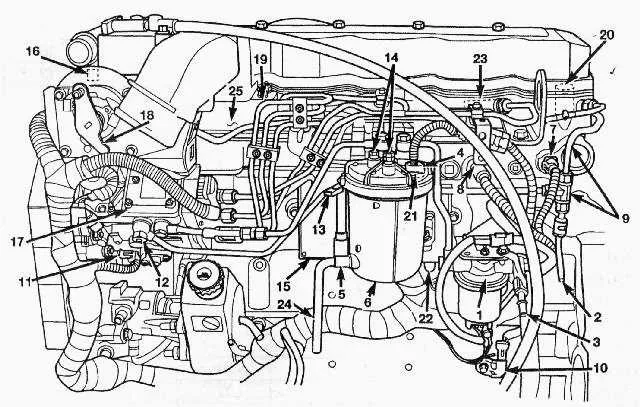
Start by locating the primary filter housing, which plays a crucial role in removing debris and contaminants before the liquid reaches the injectors. Ensure it’s securely mounted and check for any signs of leakage. The fuel pump, typically mounted near the engine block, is responsible for maintaining proper pressure. Inspect it for wear, cracks, or any irregularities in fuel flow.
The injector lines are responsible for delivering pressurized liquid directly to the engine’s combustion chambers. Trace each line for visible cracks, kinks, or bends that could cause issues with pressure regulation. These lines should be tightly secured, avoiding any potential for vibration-induced wear.
Next, focus on the pressure regulator, which manages the force exerted by the fuel system to maintain consistent flow to the injectors. Ensure the regulator is functioning correctly to prevent pressure surges or drops, which could impair engine performance.
Finally, check the connections to the return line. Any obstruction or leakage here could result in poor engine performance or misfires. Use a fuel pressure gauge to verify that all components are performing within the manufacturer’s specifications.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting Tips for Fuel System Setup
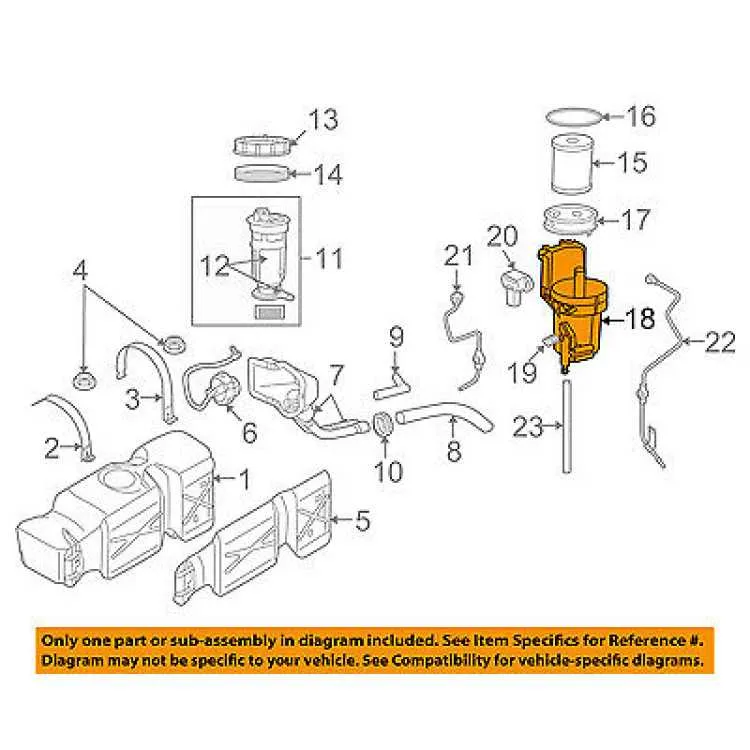
When dealing with the delivery system setup, the most frequent issues arise from blockages, leaks, and air infiltration. Address these areas promptly to maintain optimal engine performance.
- Clogged Components: Inspect the filters and check valves for debris or buildup. Replace filters every 10,000 miles or as recommended by the manufacturer. Clogged components can restrict flow and damage the system.
- Leaks: Leaks in the hoses or connections are a common issue. Always ensure that all fittings are properly torqued. If fuel is leaking from a connector, replace the O-ring seals immediately. Inspect for visible cracks in rubber or plastic components.
- Air in the System: Air can enter the delivery system during fuel changes or when seals are not correctly seated. Bleed the system thoroughly to remove any trapped air. Check the supply tank for any signs of contamination that could cause air bubbles.
- Improper Pressure: If the engine is not starting or running roughly, it may indicate an issue with fuel pressure. Use a pressure gauge to check if the pressure matches the manufacturer’s specifications. Adjust the regulator or replace a faulty pump if needed.
- Inconsistent Flow: Unstable engine performance can be linked to inconsistent fuel flow. Check all hoses for kinks or damage. Replace any sections of hose that show signs of wear or damage.
Ensure that all parts of the system are in good condition and that the connections are secure. Perform regular maintenance to avoid prolonged downtime or performance issues.