Locate the primary electrical panel under the dashboard on the driver’s side for quick access. The unit contains labeled slots corresponding to circuits controlling headlights, horn, fuel pump, and interior lighting. Each slot has a specific amperage rating clearly marked to ensure correct replacements.
Inspect blown elements by identifying the damaged connector inside the power distribution center. Refer to the owner’s guide to match circuit functions with their positions in the layout. This helps avoid replacing the wrong component and reduces troubleshooting time.
Use a multimeter to verify continuity across the circuit connectors when symptoms such as non-working indicators or faulty ignition occur. Proper understanding of the panel’s structure is crucial for maintaining electrical integrity and preventing further damage.
Electrical Panel Layout for the 1996 Truck Model

Locate the primary electrical control unit under the dashboard on the driver’s side for easy access. The secondary panel sits in the engine compartment near the battery.
- Driver’s Cabin Panel: Houses circuits for interior lighting, instrument cluster, and power accessories.
- Engine Bay Unit: Protects the ignition system, cooling fans, headlights, and horn.
Each slot is clearly numbered and labeled to match specific functions:
- Slot 1: Headlight low beam
- Slot 2: Headlight high beam
- Slot 3: Fuel pump
- Slot 4: Cooling fan
- Slot 5: Horn
- Slot 6: Power windows
- Slot 7: Radio and audio system
- Slot 8: Interior lights
Refer to the inside cover of each panel for a detailed function guide. Use a multimeter to test individual circuits if any electrical component malfunctions. Replace the fuse with the exact amperage rating printed on the panel to avoid damage.
Locating the Electrical Panel in a ’96 Pickup Truck

Find the primary power distribution panel beneath the dashboard on the driver’s side. It is typically mounted near the steering column, either attached to the lower dash or the side panel next to the footwell.
Open the panel cover by pulling the plastic latch or clips to reveal the array of miniature circuit protectors. This access point controls most of the vehicle’s electrical circuits.
Additionally, check under the hood near the battery or firewall for a secondary protective unit housing larger circuit protectors and relays responsible for major systems.
Use the owner’s manual or service guide for exact locations and labels on the protective units to ensure correct identification and maintenance.
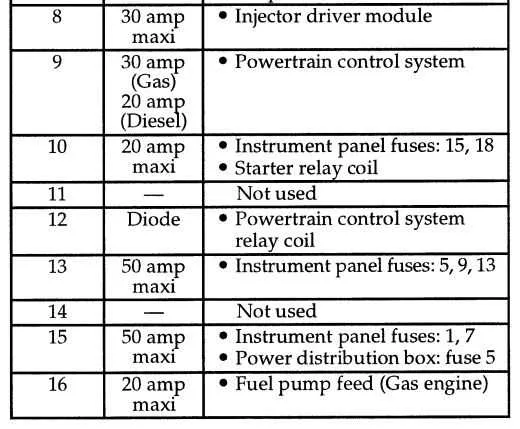
Identifying and Understanding Each Fuse Function

To ensure proper operation of the vehicle’s electrical system, it’s crucial to understand the role of each safety component in the distribution panel. Begin by checking the location and labeling of each section within the panel for easy identification. Each slot corresponds to a specific circuit that powers individual systems, such as lighting, engine components, or accessories.
Start by focusing on high-priority circuits like the ignition system, air conditioning, and braking mechanisms. For these, always verify that the component is rated appropriately for the vehicle’s electrical load. If you notice any inconsistencies with power delivery or operational issues, inspect the related protective parts for signs of wear or damage.
Each section of the panel typically includes a color code or number that denotes the amperage, which is essential for troubleshooting. Keep a reference chart of these color codes and amperages to replace damaged ones with the correct type. Regularly inspecting the protection elements for signs of corrosion or dirt buildup can prevent disruptions.
If a specific function, such as interior lighting or audio system, is malfunctioning, check the related sections in the electrical diagram to trace potential short circuits or overcurrent issues. Always ensure that replacements match the specifications recommended by the manufacturer to maintain the system’s reliability and avoid further electrical problems.
Finally, periodic maintenance and visual inspections can help detect issues before they escalate. When replacing components, choose parts with equal or higher ratings, but never exceed the recommended limits to avoid system overloads.
Steps to Safely Replace a Fuse in the 1996 Ford F150
1. Begin by turning off the ignition and removing the key. Ensure the vehicle is not running to avoid electrical hazards.
2. Locate the fuse panel inside the cabin, typically beneath the dashboard on the driver’s side, near the footwell. If necessary, consult the owner’s manual to find the exact location of the fuse assembly.
3. Identify the faulty component by referring to the label or legend on the panel cover. If unavailable, use a multimeter to test the circuit for continuity.
4. Use a fuse puller or needle-nose pliers to remove the blown fuse. Be gentle to avoid damaging the surrounding components.
5. Verify the replacement fuse matches the required amperage rating. Using a fuse with an incorrect rating can damage the electrical system.
6. Insert the new fuse carefully into the appropriate slot, ensuring it is seated firmly. Do not force it into place.
7. Test the system by turning the ignition back on. If the electrical issue persists, check for underlying wiring issues.
8. Close the fuse panel securely and store any tools used for easy access in the future.