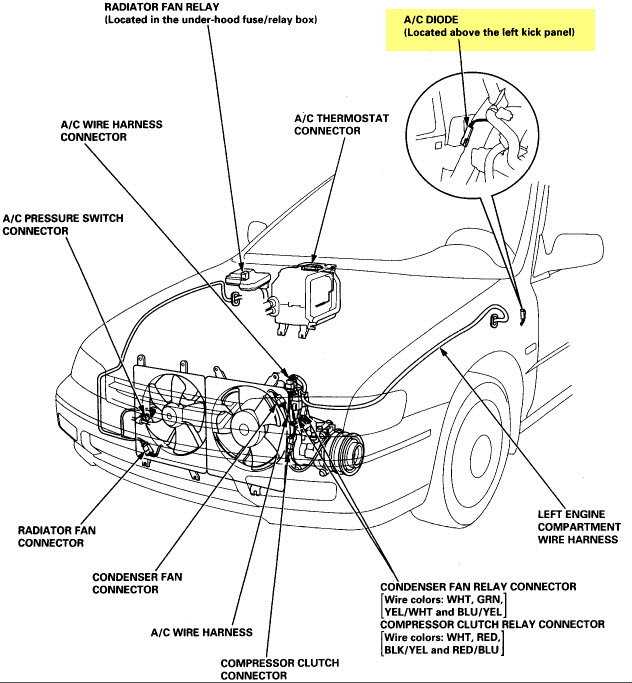
The 1996 Honda Accord is a beloved vehicle known for its reliability and performance. One crucial aspect of this car that many owners and enthusiasts are interested in is the engine. Understanding the engine of the 1996 Honda Accord can help with maintenance, troubleshooting, and modifications. In this article, we will provide a detailed overview of the engine diagram for the 1996 Honda Accord, highlighting its various components and their functions.
The engine diagram of the 1996 Honda Accord showcases a four-cylinder inline engine layout. This design has been a staple of Honda engines for many years and is known for its efficiency and smooth operation. The engine is located in the front of the vehicle and is connected to the transmission, which delivers power to the wheels.
One of the essential components of the engine is the engine block. It serves as the foundation of the engine, housing several critical parts such as the pistons, connecting rods, and crankshaft. The engine block is made of cast iron or aluminum and plays a crucial role in maintaining the engine’s stability and structural integrity.
Other key components of the engine include the cylinder head, camshaft, valves, and fuel injectors. The cylinder head sits on top of the engine block and houses the combustion chamber. The camshaft control the opening and closing of the valves, allowing the air-fuel mixture to enter the combustion chamber and the exhaust gases to exit. The valves play a vital role in regulating the flow of air and fuel during the combustion process, while the fuel injectors deliver the fuel into the combustion chamber.
1996 Honda Accord Engine Diagram
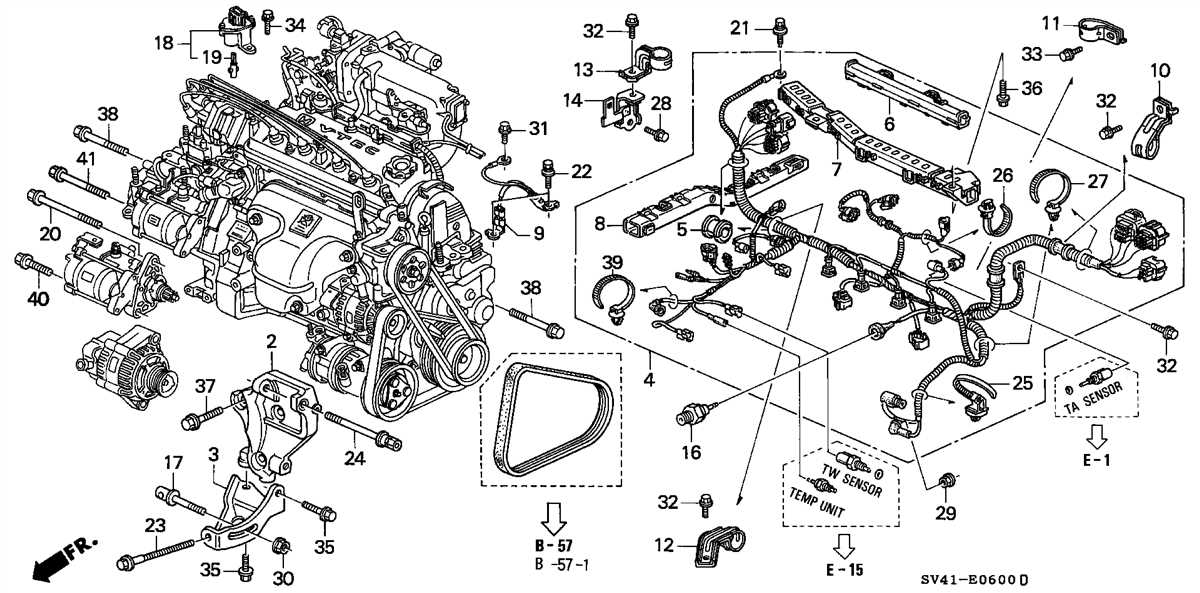
The 1996 Honda Accord is equipped with a four-cylinder engine that offers a balanced combination of power and fuel efficiency. Understanding the engine diagram can help you better understand the various components and how they work together to power your Accord.
Main Components
The main components of the 1996 Honda Accord’s engine include the cylinder block, cylinder head, pistons, valves, crankshaft, and camshaft. The cylinder block houses the cylinders where the combustion process takes place. The cylinder head sits on top of the block and contains the valves and spark plugs. The pistons move up and down within the cylinders to generate power, while the valves control the flow of air and fuel into and out of the combustion chambers. The crankshaft converts the up-and-down motion of the pistons into rotational motion, which is then transferred to the transmission.
Fuel and Air Delivery
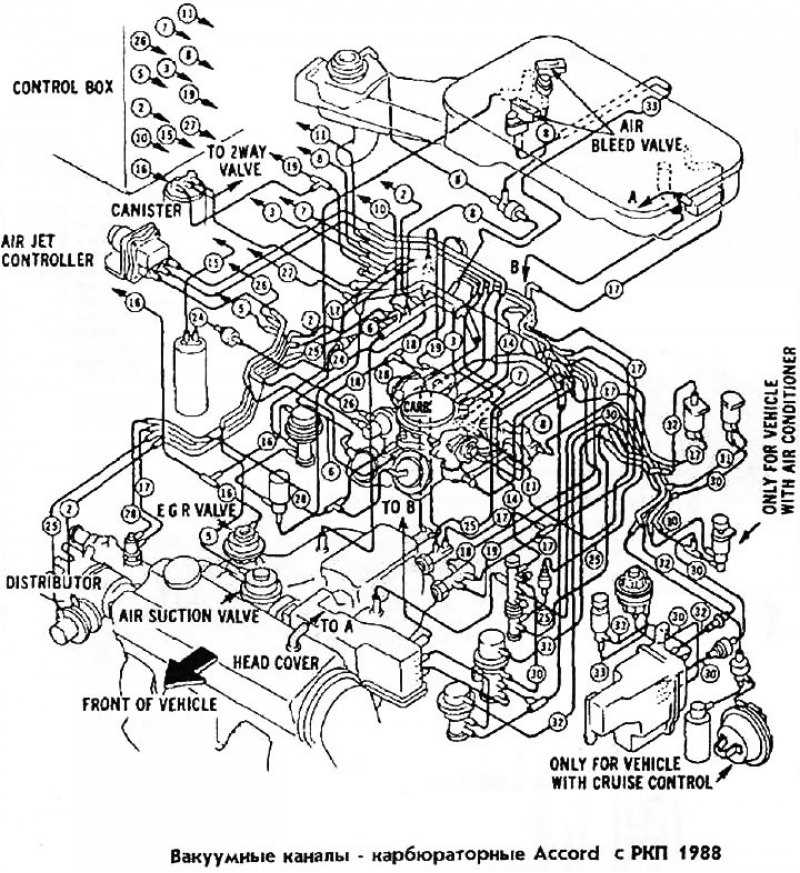
To understand how fuel and air are delivered to the engine, it’s important to look at the fuel system and intake system. The fuel system consists of the fuel tank, fuel pump, fuel filter, and fuel injectors. The fuel pump delivers fuel from the tank to the injectors, where it is sprayed into the combustion chambers. The intake system, on the other hand, brings in clean air for combustion. It includes the air filter, throttle body, and intake manifold. The throttle body regulates the amount of air entering the engine, while the intake manifold distributes the air evenly to all the cylinders.
Ignition and Exhaust
The ignition system is responsible for creating the spark that ignites the fuel-air mixture in the combustion chambers. It consists of spark plugs, ignition coils, and an ignition module. The exhaust system, on the other hand, helps remove the burnt gases from the engine. It includes the exhaust manifold, catalytic converter, and muffler. The exhaust manifold collects the gases from each cylinder and directs them towards the catalytic converter, which reduces harmful emissions. The muffler then reduces the noise produced by the exhaust gases.
Understanding the engine diagram of your 1996 Honda Accord can help you know the various components and their functions. This knowledge can be useful for troubleshooting and performing maintenance tasks on your Accord’s engine.
Understanding the Components of a 1996 Honda Accord Engine
The 1996 Honda Accord is a reliable and popular car model known for its efficient engine performance. To have a better understanding of the components that make up the engine, here is a breakdown of the key parts:
1. Engine Block
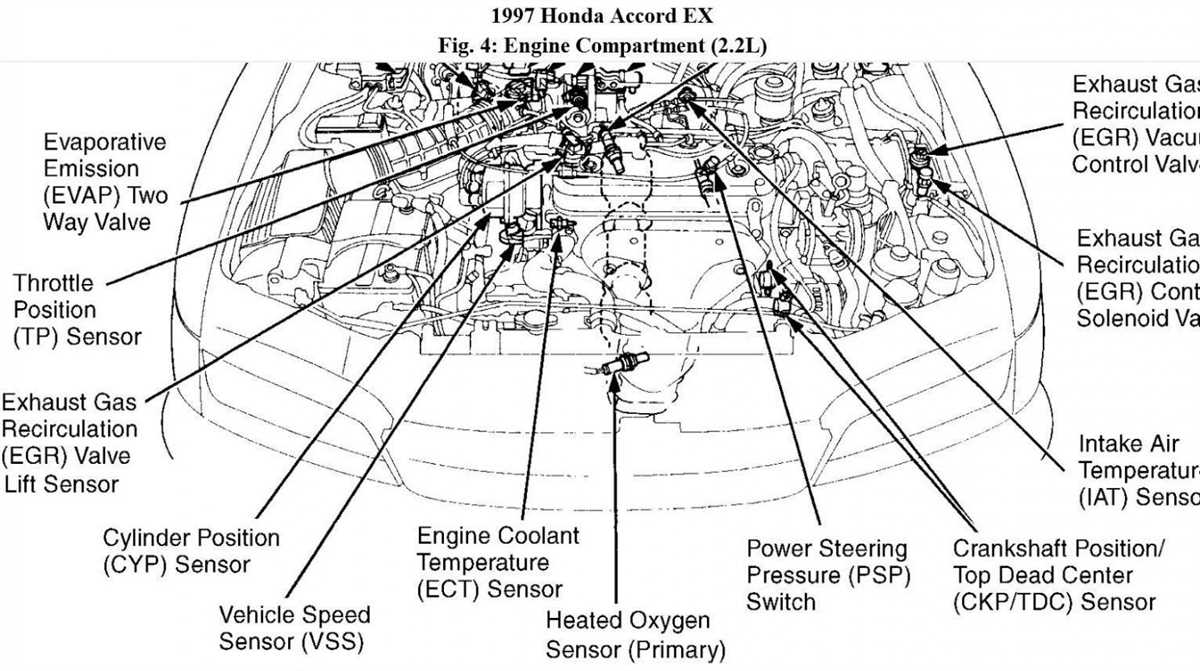
The engine block is the main housing for all the internal components of the engine. It provides support and stability to the moving parts and contains the cylinders and crankshaft. In the 1996 Honda Accord, the engine block is typically made of cast iron or aluminum alloy.
2. Pistons
The pistons are cylindrical components that move up and down within the cylinders of the engine block. They are connected to the crankshaft and play a crucial role in converting the combustion energy into rotational motion. The 1996 Honda Accord engine usually has four pistons.
3. Cylinder Head
The cylinder head sits on top of the engine block and contains the valves, spark plugs, and camshafts. The valves regulate the flow of air and fuel into the engine cylinders, while the spark plugs ignite the air-fuel mixture for combustion. The camshafts control the opening and closing of the valves.
4. Crankshaft
The crankshaft is responsible for converting the linear motion of the pistons into rotational motion, which ultimately drives the wheels. It is connected to the pistons via connecting rods and transfers the energy generated during combustion to the transmission and wheels of the car.
5. Timing Belt/Chain
The timing belt or chain ensures the synchronized movement of the camshaft and crankshaft. It controls the timing of valve operation and ignition, enabling the engine to run smoothly. Regular maintenance and replacement of the timing belt/chain are essential to prevent engine damage.
6. Intake and Exhaust Manifolds
The intake manifold delivers air and fuel mixture to the cylinders, while the exhaust manifold collects and redirects the exhaust gases out of the engine. These manifolds are crucial for proper air and fuel circulation and efficient engine performance.
Understanding these key components of a 1996 Honda Accord engine can help car owners have a better understanding of how their engine works and enables them to make informed decisions regarding maintenance and repairs.
Exploring the Engine Block and Cylinder Head

The engine block is the main structure of the engine and is typically made of cast iron or aluminum. It houses the cylinders, pistons, and other essential components. The cylinder head, on the other hand, is a separate component that is bolted onto the top of the engine block. The cylinder head contains the valves, spark plugs, and fuel injectors. Both the engine block and the cylinder head play crucial roles in the overall performance of the engine.
The engine block is responsible for housing the cylinders, which are the chambers where the combustion process takes place. Each cylinder contains a piston that moves up and down, converting the energy from the combustion into mechanical motion. The engine block also houses the crankshaft, which converts the linear motion of the pistons into rotational motion that drives the wheels of the vehicle. Additionally, the engine block contains various passages and channels for coolant, oil, and air flow, ensuring proper cooling and lubrication of the engine.
The Cylinder Head
The cylinder head sits on top of the engine block and forms the top of the combustion chamber. It houses the intake and exhaust valves, which control the flow of air and fuel into the cylinders and the expulsion of exhaust gases. The cylinder head also contains the spark plugs, which ignite the air-fuel mixture for combustion, and the fuel injectors, which deliver fuel into the intake ports. It is crucial for the cylinder head to have a tight seal with the engine block to prevent leakage of combustion gases and coolant, as well as to maintain optimal compression and power output.
In summary, the engine block and cylinder head are essential components of the engine. The engine block houses the cylinders, pistons, and crankshaft, while the cylinder head contains the valves, spark plugs, and fuel injectors. Together, they ensure proper combustion, cooling, and lubrication, and contribute to the overall performance and efficiency of the engine. Understanding the layout and components of the engine block and cylinder head can help in diagnosing and maintaining the engine of a 1996 Honda Accord or any other vehicle.
Examining the Intake and Exhaust Systems
The intake and exhaust systems in a 1996 Honda Accord play crucial roles in the proper functioning of the engine, ensuring optimal performance and efficiency. Let’s take a closer look at these systems and how they work together to provide the necessary air and fuel mixture and release exhaust gases.
Intake System
The intake system of the 1996 Honda Accord consists of several components, including the air filter, intake manifold, throttle body, and intake valves. Its primary function is to bring in the necessary air for combustion and mix it with fuel to create a combustible mixture. The air filter ensures that only clean air enters the system, preventing debris and particles from entering the engine. The intake manifold distributes the air evenly to each cylinder, while the throttle body controls the amount of air entering the engine. The intake valves open and close to let the air-fuel mixture enter the combustion chamber.
Exhaust System
The exhaust system is responsible for removing the burned gases from the combustion process and expelling them safely into the environment. It consists of the exhaust manifold, catalytic converter, muffler, and tailpipe. The exhaust manifold collects the exhaust gases from each cylinder and directs them to the catalytic converter. The catalytic converter helps reduce harmful emissions by converting pollutants into less harmful substances. The muffler helps to reduce noise produced during the exhaust process, and the tailpipe directs the exhaust gases out of the vehicle.
Overall, the intake and exhaust systems of the 1996 Honda Accord work together to ensure the engine receives the proper air-fuel mixture for combustion and efficiently removes the exhaust gases from the combustion process. Regular maintenance and inspection of these systems are essential to ensure optimal performance, fuel efficiency, and comply with emission standards.
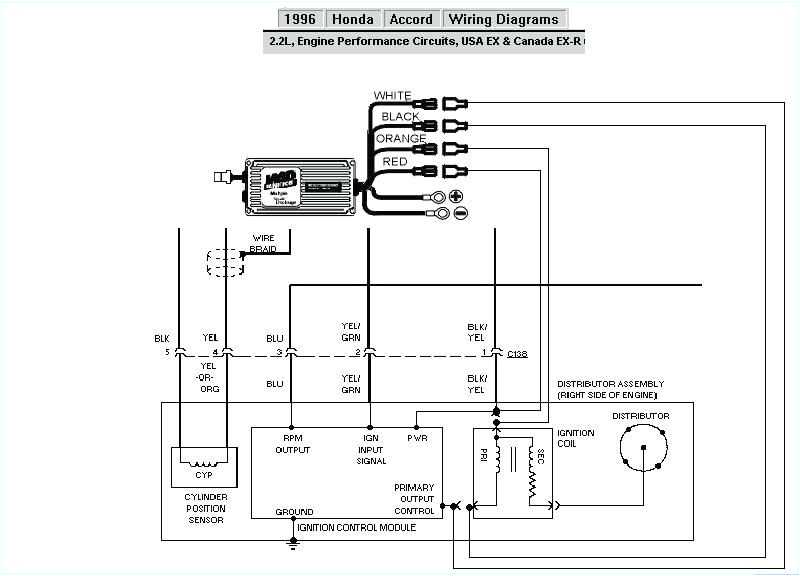
Analyzing the Fuel and Ignition Systems
The fuel and ignition systems are critical components in the operation of a 1996 Honda Accord’s engine. Understanding how these systems work and analyzing them can help diagnose and fix issues that may arise.
The fuel system is responsible for delivering the proper amount of fuel to the engine for combustion. It consists of several key components, including the fuel pump, fuel filter, fuel injectors, and the fuel pressure regulator. The fuel pump draws fuel from the tank and ensures a constant flow to the fuel injectors. The fuel filter removes any impurities from the fuel before it reaches the engine. The fuel injectors are responsible for spraying the fuel into the combustion chambers, and the fuel pressure regulator helps maintain a consistent fuel pressure throughout the system.
When analyzing the fuel system, it is essential to check for any blockages or leaks in the fuel lines, as well as ensuring that the fuel pump is functioning correctly. A fuel pressure test can also help determine if the fuel pressure regulator is functioning as it should. If there are any issues with the fuel system, such as poor fuel delivery or inconsistent fuel pressure, it may result in engine misfires, poor acceleration, or rough idle.
The ignition system, on the other hand, is responsible for creating the spark necessary for the combustion process. It consists of the ignition coil, spark plugs, distributors, and ignition module. The ignition coil converts the low voltage from the battery to high voltage required to create a spark. The spark plugs then ignite the air-fuel mixture in the combustion chambers. The distributor distributes the high voltage to the correct spark plug at the right time, and the ignition module controls the timing of the spark.
When analyzing the ignition system, it is crucial to check for any worn or fouled spark plugs, as well as ensuring that the ignition coil is producing the necessary voltage. The distributor should also be inspected for any signs of damage or wear, and the ignition module should be tested for proper operation. If there are any issues with the ignition system, such as weak or no spark, it may result in engine misfires, difficulty starting the engine, or a decrease in fuel efficiency.
In conclusion, analyzing the fuel and ignition systems in a 1996 Honda Accord is crucial for diagnosing and repairing any issues that may affect the engine’s performance. By checking for blockages, leaks, and proper functioning of components in the fuel system, as well as inspecting spark plugs, ignition coil, distributor, and ignition module in the ignition system, potential problems can be identified and resolved, ensuring optimal engine performance.
Investigating the Cooling and Lubrication Systems
The cooling and lubrication systems are crucial components of the 1996 Honda Accord’s engine, working together to ensure optimal performance and prevent damage or overheating. By understanding how these systems function, drivers can maintain their vehicles properly and address any potential issues that may arise.
The cooling system of the 1996 Honda Accord consists of several key components, including the radiator, thermostat, water pump, and coolant. The radiator’s primary function is to dissipate heat from the engine, preventing it from overheating. The thermostat regulates the flow of coolant based on the engine’s temperature, ensuring it remains at an optimal operating range.
The water pump is responsible for circulating the coolant throughout the engine, ensuring it reaches all necessary areas to absorb heat and facilitate the cooling process. It is driven by a belt connected to the engine, allowing it to maintain a consistent flow of coolant at all times.
In addition to the cooling system, the lubrication system of the 1996 Honda Accord plays a vital role in ensuring the engine’s longevity and smooth operation. The lubrication system consists of the oil pump, oil filter, and various passageways that deliver oil to the engine’s moving parts.
The oil pump is powered by the engine and maintains a steady flow of oil throughout the engine, lubricating crucial components such as the pistons, bearings, and camshaft. The oil filter removes any contaminants from the oil, preventing them from causing damage to the engine.
Regular maintenance is key to keeping the cooling and lubrication systems in optimal condition. Drivers should regularly check the coolant level and ensure proper mixing with water to prevent freezing or boiling. Additionally, regular oil changes and filter replacements are essential to maintain proper lubrication and prevent engine damage.
In summary,
- The cooling system consists of the radiator, thermostat, water pump, and coolant.
- The lubrication system includes the oil pump, oil filter, and oil passageways.
- Regular maintenance, such as checking coolant levels and changing oil and filters, is crucial to ensure proper functioning of these systems.
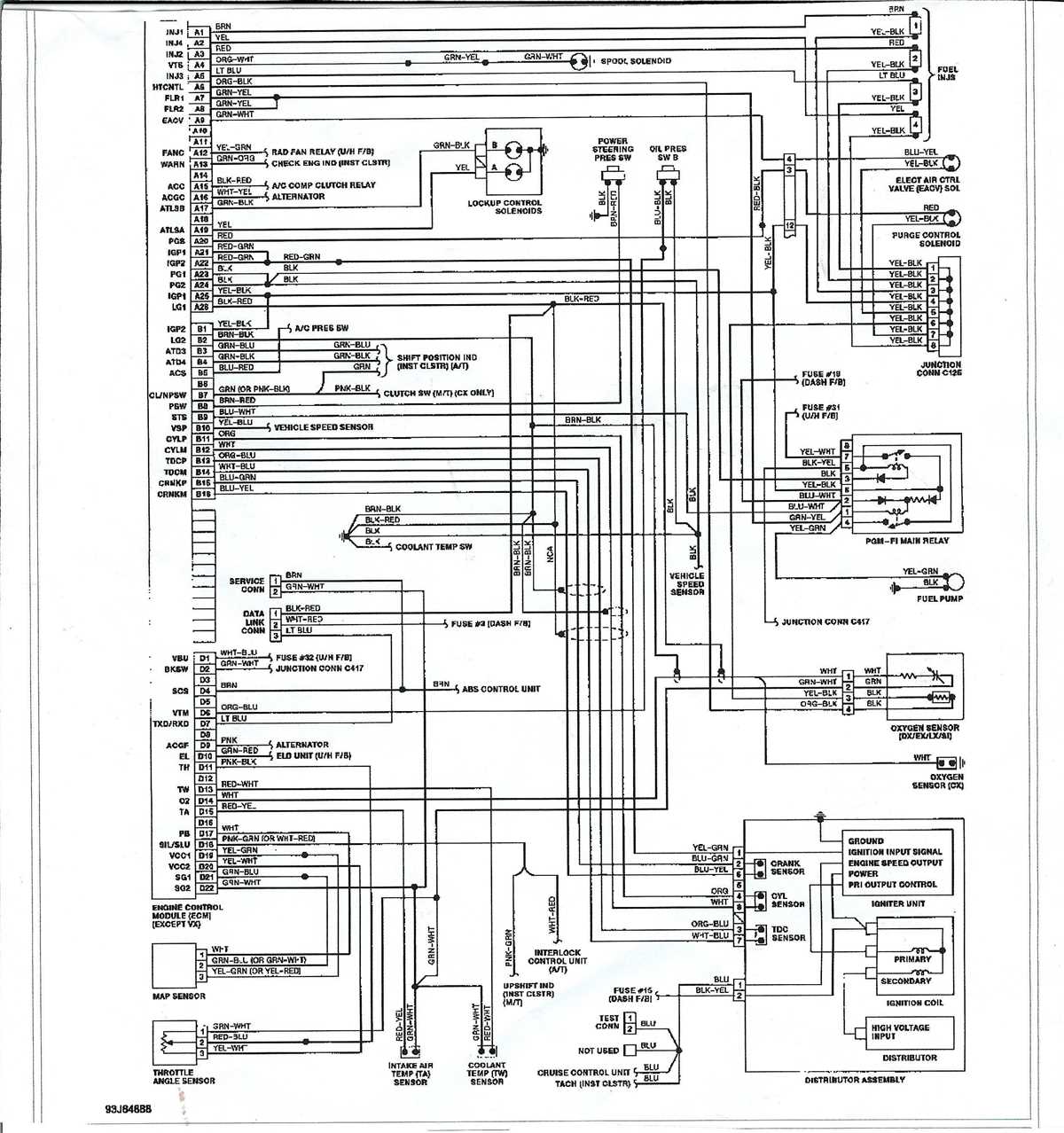
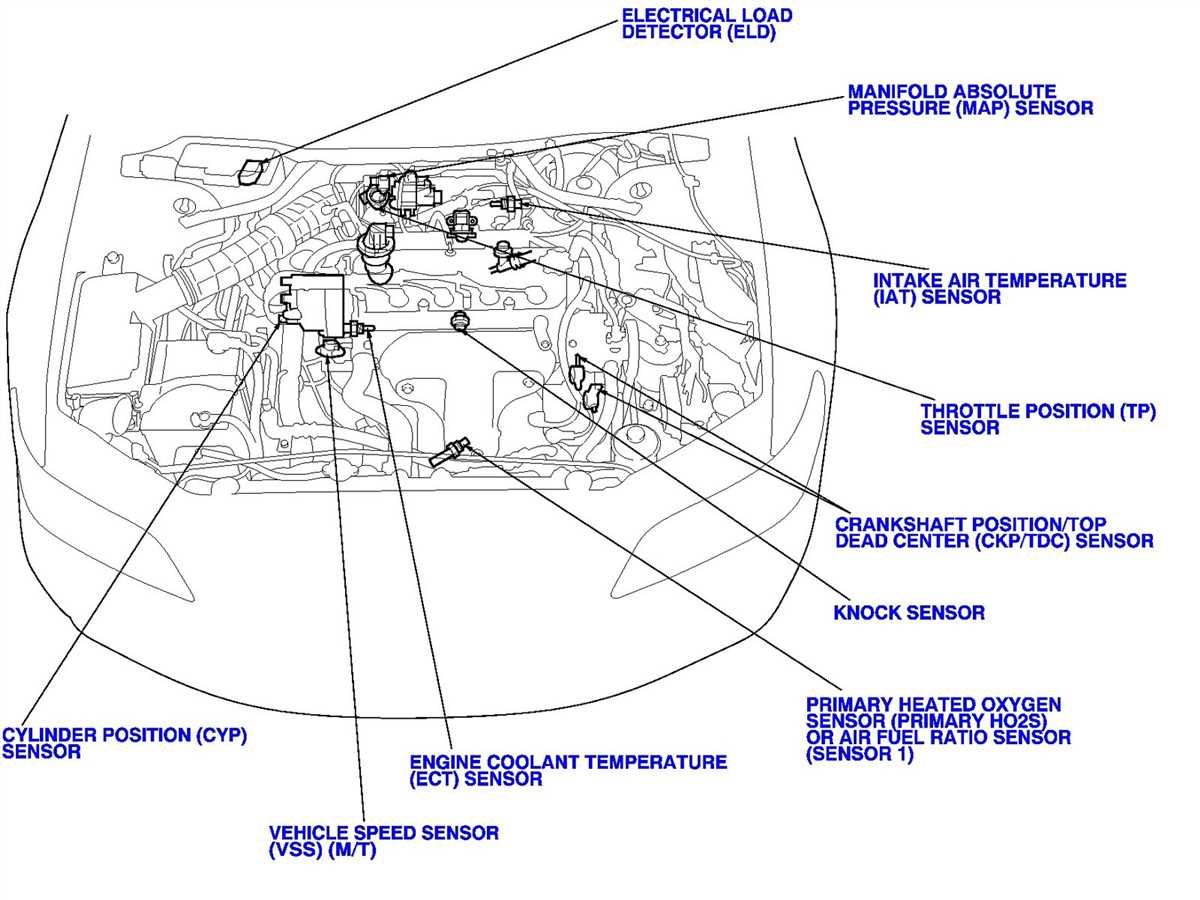
Understanding the Electrical System and Emissions Control
The electrical system and emissions control are crucial components of the 1996 Honda Accord. These systems work together to ensure the optimal performance of the vehicle and minimize its impact on the environment.
Electrical System:
The electrical system in the 1996 Honda Accord consists of various components that provide power and control to different parts of the vehicle. The key components of the electrical system include the battery, alternator, starter motor, and various wiring harnesses.
The battery serves as the primary source of power for the electrical system. It provides the initial power required to start the engine and also supplies power to the vehicle’s electrical components when the engine is not running. The alternator, on the other hand, is responsible for recharging the battery and supplying power to the electrical system while the engine is running.
The starter motor is another important component of the electrical system. It is responsible for starting the engine by turning the crankshaft. When the ignition key is turned, the starter motor engages with the flywheel and initiates the combustion process.
The wiring harnesses in the electrical system connect all the components and ensure the proper distribution of power. These harnesses consist of various wires and connectors that transmit electrical signals to different parts of the vehicle, such as the lights, dashboard, and engine control unit.
Emissions Control:
The emissions control system in the 1996 Honda Accord is designed to reduce harmful pollutants released into the atmosphere during the combustion process. It includes various components that monitor and control the emission levels, such as the catalytic converter, oxygen sensors, and the engine control unit (ECU).
The catalytic converter is responsible for converting harmful gases, such as carbon monoxide and nitrogen oxides, into less harmful substances through a chemical reaction. It uses a catalyst to facilitate this process and reduce the emission levels from the engine.
The oxygen sensors in the emissions control system monitor the oxygen levels in the exhaust gases and provide feedback to the engine control unit. Based on this feedback, the ECU adjusts the fuel-air mixture to optimize combustion and minimize emissions.
The engine control unit (ECU) is the brain of the emissions control system. It constantly monitors various sensors and inputs to ensure the engine operates efficiently and meets emission standards. It regulates fuel injection, ignition timing, and other engine parameters to achieve optimal performance and reduce emissions.
Summary:
The electrical system and emissions control are essential aspects of the 1996 Honda Accord. The electrical system consists of components such as the battery, alternator, and starter motor, which provide power and control to various parts of the vehicle. The emissions control system, on the other hand, minimizes the release of harmful pollutants into the atmosphere and includes components like the catalytic converter, oxygen sensors, and the engine control unit. Together, these systems ensure the optimal performance of the vehicle while minimizing its impact on the environment.