To optimize the sound and versatility of your guitar, a dual pickup configuration can provide a significant improvement. Start by connecting the two magnetic pickups to the appropriate switches and pots. This allows you to easily blend both units for a rich tonal variety, or toggle between them for specific sounds.
The key to mastering this setup is the selection of the right components and proper wiring. Ensure that the pickups are installed in the correct order relative to the tone and volume pots. This setup often involves using a 3-way switch for toggling between the neck and bridge pickups, with a middle position for both active simultaneously. Pay attention to the grounding and signal paths to avoid unwanted noise or interference.
For those looking to modify their instrument further, adding a phase switch or coil splitting can offer additional tonal options. Using a dedicated tone pot for each pickup lets you customize the high frequencies for each unit individually, making your guitar more responsive to different playing styles.
Important consideration: Always double-check your connections and use high-quality components to ensure reliable performance over time. Incorrect wiring can lead to poor output or even damage to your gear.
Ultimately, understanding the interaction between the pickups, switches, and pots allows you to fine-tune your instrument to achieve a wide range of sounds. Whether you’re playing clean jazz or heavy rock, this modification gives you full control over your tone.
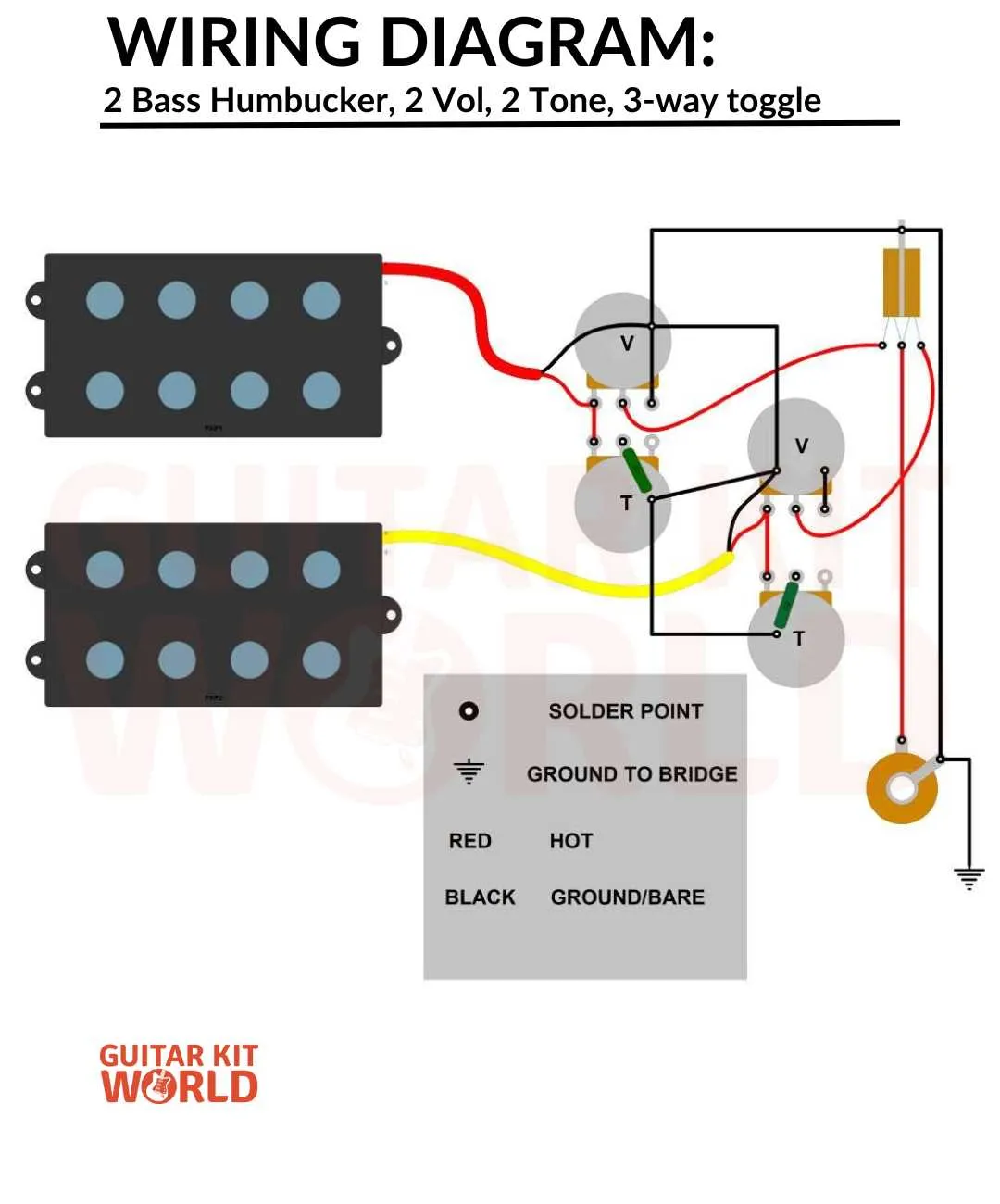
2 Pickup Configuration Guide
To wire two pickups in parallel with a 3-way switch, connect both hot leads to the switch terminals. The first pickup’s hot wire goes to the first switch terminal, and the second pickup’s hot lead goes to the second terminal. The common ground wire connects both pickups to the ground terminal of the switch. The output of the switch is connected to the volume pot. The two pickups can be set to series or parallel depending on the desired tone.
If you’re aiming for coil splitting, add a push-pull pot to the volume knob. This allows you to switch between a single coil and a dual-coil setup for each pickup. Ensure the two coil taps are properly wired to the switch to maintain proper signal integrity when splitting.
For a more versatile setup, use a 5-way switch to create additional tone options, like out-of-phase or parallel wiring configurations. Make sure to connect the signal from each pickup to the correct switch terminal based on your preferred combination of tones.
Understanding Parallel vs. Series Connections for Dual-Coil Pickups
For dual-coil pickups, selecting between parallel and series configurations directly affects tone and output. In a parallel setup, the two coils are connected side by side, resulting in a cleaner, brighter sound with less output. This option reduces hum and noise, but the sound may lack the depth found in a series configuration.
On the other hand, wiring the coils in series boosts the output significantly. This creates a thicker, more powerful sound with increased mids and lower frequencies. However, series connections tend to amplify any hum, especially if the coils are not perfectly hum-cancelling. The overall tone becomes warmer and more dynamic, ideal for heavier styles or when maximum output is needed.
For versatility, many setups allow switching between these two configurations. This can be achieved using a push-pull pot or a toggle switch, giving you control over whether you want a brighter, quieter tone (parallel) or a fuller, more aggressive sound (series).
When deciding which connection to use, consider the style of music you play and the tonal balance you seek. Parallel is best for clean tones and hum reduction, while series excels at delivering punch and sustain in heavier settings.
Step-by-Step Guide for Installing a 2 Pickup Circuit
Start by gathering all necessary components: two pickups, a switch, potentiometers, capacitors, and soldering tools. Ensure your guitar’s cavity has enough space for the components.
Step 1: Connect the ground wire from each pickup to the common ground of the circuit. This prevents unwanted hum and ensures proper signal flow.
Step 2: Solder the hot wire from each pickup to the corresponding terminal of the volume potentiometer. Make sure the solder joint is secure and clean to avoid signal loss.
Step 3: Connect the output terminal of the volume pot to the input of the tone pot. If you’re using a tone control, wire the tone pot’s output to the main output jack.
Step 4: Solder the capacitors to the tone control as per your preference for tonal shaping. Use a .022µF or .047µF cap for a standard setup, depending on your desired frequency response.
Step 5: Attach the selector switch to route the signal from each pickup to the output. Ensure the switch is properly wired to select each pickup individually or both together.
Step 6: Double-check all connections, making sure there are no short circuits or loose connections. Clean up any excess solder with a desoldering pump if necessary.
Step 7: Reassemble your guitar and test the setup. Play through each pickup setting to ensure the tone control works as expected and the signal is routed correctly.
Final Check: Ensure all connections are insulated properly, and the circuit is grounded to prevent electrical noise.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting in Pickup Setup

When setting up dual coil pickups, there are a few common issues you may encounter. Here are some solutions to help you resolve them effectively:
- No sound output: Check the connections to ensure all leads are properly soldered. A loose or broken connection is often the cause of this issue. Make sure the ground wire is securely attached to the metal parts of the guitar.
- Weak or distorted signal: If your signal is weak or overly distorted, inspect the tone and volume pots for possible damage or dirt accumulation. Cleaning the potentiometers or replacing faulty ones can often solve this issue.
- Unbalanced output: If one pickup sounds significantly louder or quieter than the other, ensure that the height adjustment of each coil is balanced. Adjusting the pole pieces on the pickup can also help achieve a more consistent output.
- Hum or noise: Excessive hum can result from improper grounding or interference. Ensure all grounds are properly connected and avoid routing signal wires close to power cables. Using shielded cables and grounding the shield properly can also reduce noise.
- Phase issues: When pickups are wired out of phase, the sound can become hollow or weak. If you’re hearing this, check that the hot and ground wires are correctly positioned. Reversing the connections on one of the pickups can resolve phase cancellation problems.
By carefully checking these components and making necessary adjustments, most common issues with dual coil pickup setups can be easily fixed.