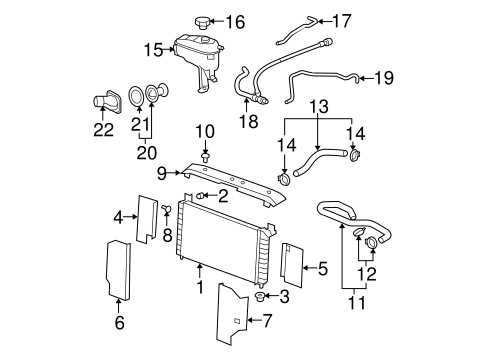
Understanding the cooling system of your 2000 Chevy Cavalier is essential to keeping your engine running smoothly and preventing overheating. The radiator, located at the front of the engine, plays a crucial role in maintaining the proper operating temperature of your vehicle. In this article, we will discuss the radiator diagram for a 2000 Chevy Cavalier, providing you with a better understanding of how the cooling system works.
The radiator diagram for a 2000 Chevy Cavalier consists of several key components. The main component is the radiator itself, which is a heat exchanger designed to remove heat from the engine coolant. Coolant, also known as antifreeze, circulates through the engine, absorbing heat and carrying it to the radiator. The radiator has a series of tubes and fins that help dissipate the heat from the coolant, allowing it to cool down before it is recirculated back into the engine.
Connected to the radiator are two hoses, known as the upper and lower radiator hoses. The upper hose carries coolant from the engine to the radiator, while the lower hose returns cooled coolant back to the engine. These hoses are typically made of rubber and are reinforced with fabric or wire to withstand high temperatures and pressure. It is important to inspect these hoses regularly for any signs of wear or leaks, as they can cause coolant loss and lead to engine overheating.
In addition to the radiator and hoses, the cooling system of a 2000 Chevy Cavalier also includes a thermostat, water pump, and a fan. The thermostat regulates the flow of coolant through the engine, opening and closing as needed to maintain the optimal temperature. The water pump circulates the coolant throughout the system, ensuring that it reaches all parts of the engine. The fan, either mechanical or electric, helps dissipate heat from the radiator when the vehicle is stationary or at low speeds.
In conclusion, understanding the radiator diagram for a 2000 Chevy Cavalier is crucial for maintaining the proper functioning of the cooling system. Regular inspection and maintenance of the radiator, hoses, thermostat, water pump, and fan are essential to prevent overheating and potential engine damage. By being familiar with how these components work together, you can ensure the longevity and performance of your vehicle.
Understanding the Cooling System of a 2000 Chevy Cavalier
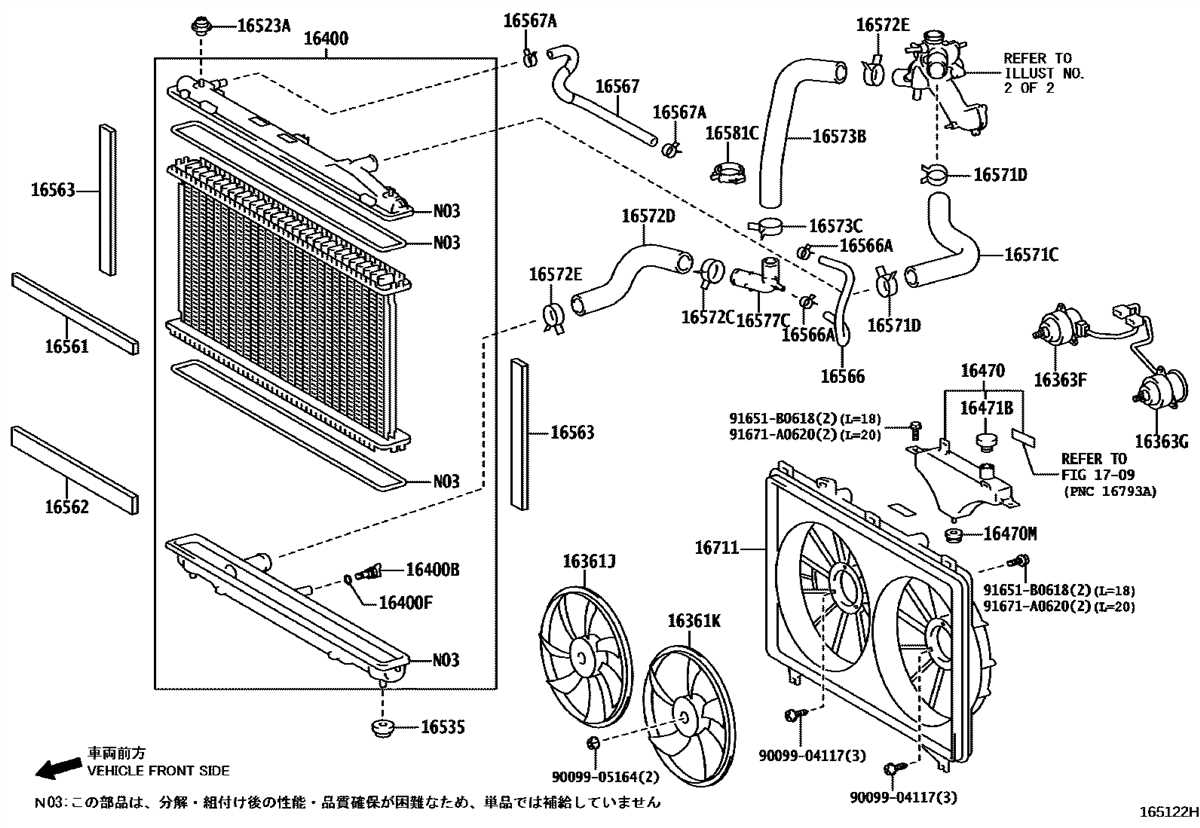
The cooling system is an essential component of any vehicle, including the 2000 Chevy Cavalier. It plays a crucial role in maintaining optimal engine temperature and preventing overheating. Understanding the cooling system of your 2000 Chevy Cavalier can help you identify potential issues and perform regular maintenance to keep your vehicle running smoothly.
The cooling system of a 2000 Chevy Cavalier consists of several key components, including the radiator, water pump, thermostat, and coolant reservoir. These components work together to circulate coolant throughout the engine, dissipating excess heat and maintaining a consistent temperature. The radiator serves as the main heat exchanger, cooling the coolant as it passes through its fins and transferring the heat to the surrounding air.
The coolant pump, driven by the engine’s serpentine belt, circulates the coolant through the engine and radiator. It ensures that the coolant flows at a constant rate, promoting efficient heat transfer and preventing overheating. The thermostat, located between the engine and the radiator, regulates the coolant flow based on the engine temperature. It opens and closes to maintain the ideal operating temperature, allowing the coolant to flow through the engine when needed.
Regular maintenance of the cooling system is crucial to ensure its proper functioning. This includes checking the coolant level regularly and topping it up if necessary. It is also important to inspect the radiator for any leaks or damage and clean the fins to maintain proper airflow. Additionally, the coolant should be flushed and replaced according to the manufacturer’s recommendations to prevent corrosion and the build-up of deposits.
In conclusion, understanding the cooling system of a 2000 Chevy Cavalier is essential for proper vehicle maintenance. The radiator, water pump, thermostat, and coolant reservoir all play crucial roles in keeping the engine temperature within optimal range. Regular maintenance, including checking coolant levels, inspecting the radiator, and flushing the coolant, is necessary to ensure the efficient functioning of the cooling system.
The Function of the Radiator
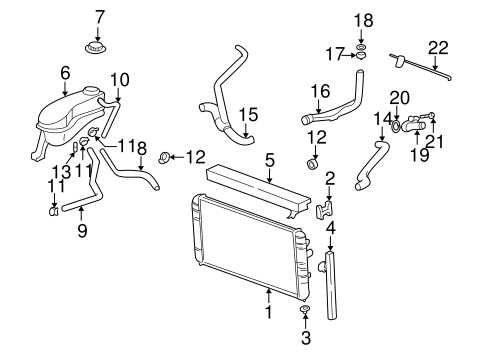
The radiator is an essential component of a vehicle’s cooling system. It plays a crucial role in regulating the temperature of the engine by dissipating heat generated during the combustion process.
The radiator is typically located at the front of the vehicle, behind the grille, where it is exposed to airflow while the vehicle is in motion. Its main purpose is to transfer heat from the coolant circulating through the engine to the surrounding air, thus cooling down the engine and preventing it from overheating.
The radiator consists of a network of tubes and fins, which provide a large surface area for heat exchange. The hot coolant from the engine enters the radiator through an inlet, where it flows through the tubes. As the coolant passes through the tubes, the fins help to increase the contact area with the surrounding air, allowing for efficient heat transfer. The cooled coolant then exits the radiator and returns to the engine to continue the cooling process.
In addition to its primary function of cooling the engine, the radiator also helps maintain the optimal operating temperature for other components in the vehicle. For example, the transmission fluid may flow through a separate section of the radiator, allowing it to be cooled as well. This helps prevent overheating of the transmission and ensures proper function.
Overall, the radiator plays a critical role in maintaining the overall performance and longevity of the vehicle’s engine. Regular maintenance, such as checking for leaks or blockages, flushing and replacing coolant, and keeping the radiator clean, can help ensure its proper functioning and prevent engine damage.
Identifying the Parts of the Radiator
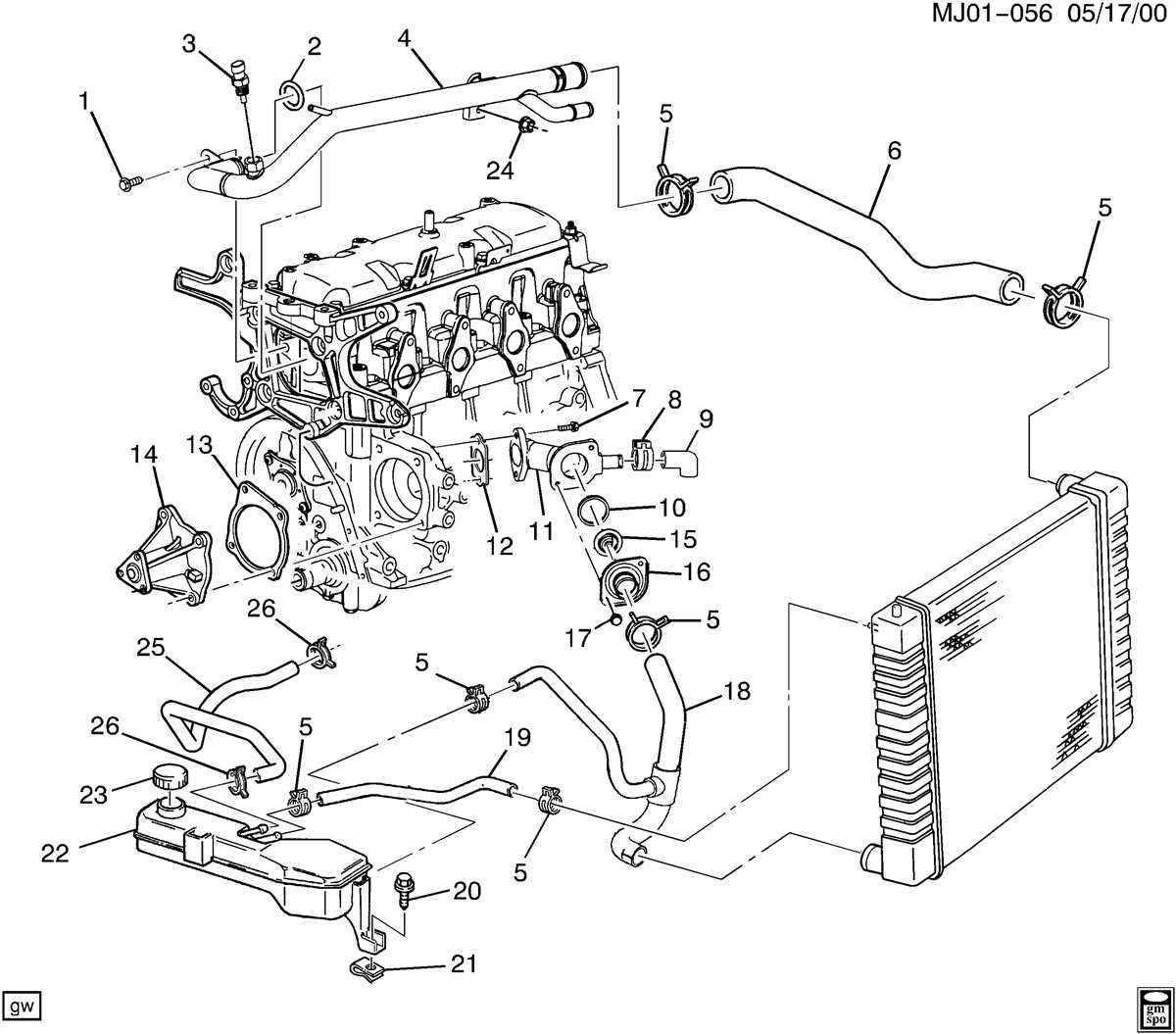
The radiator in a 2000 Chevy Cavalier plays a crucial role in keeping the engine cool and preventing overheating. Understanding the different parts of the radiator can help in diagnosing any issues and performing maintenance or repairs.
1. Core

The core is the main component of the radiator, where the heat exchange takes place. It is made up of small tubes and fins that allow coolant to flow through and transfer heat from the engine. The core is responsible for dissipating heat and cooling the coolant before it returns to the engine.
2. Inlet and Outlet Tanks

The radiator has two tanks, one on each side, known as the inlet and outlet tanks. The inlet tank is where the heated coolant enters the radiator, while the outlet tank is where the cooled coolant exits. These tanks provide a path for the coolant to flow through the radiator and ensure efficient cooling.
3. Pressure Cap
The pressure cap is located on the top of the radiator and is responsible for maintaining the correct pressure within the cooling system. It allows excess pressure to escape and prevents air from entering the system. The pressure cap also acts as a point of access for adding coolant to the radiator.
4. Fan and Fan Shroud
Many radiators in the 2000 Chevy Cavalier are equipped with an electric fan that helps to increase airflow through the radiator, especially at low speeds or when the vehicle is stationary. The fan is usually mounted behind the radiator and is controlled by a temperature sensor. The fan shroud directs the airflow from the fan through the radiator, optimizing cooling efficiency.
5. Coolant Hoses
There are several hoses connected to the radiator that allow for the passage of coolant between the engine and the radiator. The upper and lower hoses connect to the inlet and outlet tanks, respectively, while other hoses may be connected to the transmission cooler or heater core. It’s important to inspect these hoses regularly for any signs of leakage or damage.
Understanding the different parts of the radiator can help with troubleshooting cooling system issues and performing maintenance tasks. Regular inspection and maintenance of the radiator and its components can ensure optimal engine performance and prevent overheating.
Common Issues with the Radiator
When it comes to the radiator in a 2000 Chevy Cavalier, there are several common issues that may arise. One of the most prevalent problems is coolant leaks. Over time, the radiator can develop cracks or holes, causing coolant to leak out. This can result in overheating of the engine and potential damage if not addressed promptly. It is essential to regularly inspect the radiator for any signs of leaks, such as puddles of coolant underneath the vehicle or low coolant levels.
Another common issue with the radiator is clogging. As the coolant circulates through the radiator, debris and sediment can accumulate, obstructing the flow and reducing the cooling efficiency. This can lead to overheating and engine performance problems. Regular flushing and cleaning of the radiator can help prevent clogging and maintain optimal cooling system function. Additionally, using the correct type and concentration of coolant is crucial to prevent corrosion and buildup in the radiator.
Another issue that may occur with the radiator is a faulty radiator fan. The fan helps to cool the coolant as it passes through the radiator. If the fan fails to operate correctly, it can result in inadequate cooling, leading to overheating. It is essential to check the radiator fan regularly and ensure that it is functioning correctly. If necessary, the fan should be replaced to prevent overheating and potential engine damage.
Summary:
- Coolant leaks are a common issue with the radiator in a 2000 Chevy Cavalier, and regular inspection is necessary to detect and repair them promptly.
- Clogging of the radiator can occur over time due to debris and sediment, leading to reduced cooling efficiency. Periodic flushing and cleaning of the radiator can help prevent this issue.
- A faulty radiator fan can result in inadequate cooling and overheating. Regularly checking the fan’s operation and replacing it if necessary is crucial for maintaining proper radiator function.
Maintaining and Troubleshooting the Radiator
Maintaining your radiator is essential to ensure that your vehicle’s engine stays cool and operates efficiently. Regular maintenance and troubleshooting can help identify any potential issues and prevent major problems before they occur. Here are some tips to help you maintain and troubleshoot your radiator:
Maintenance Tips:
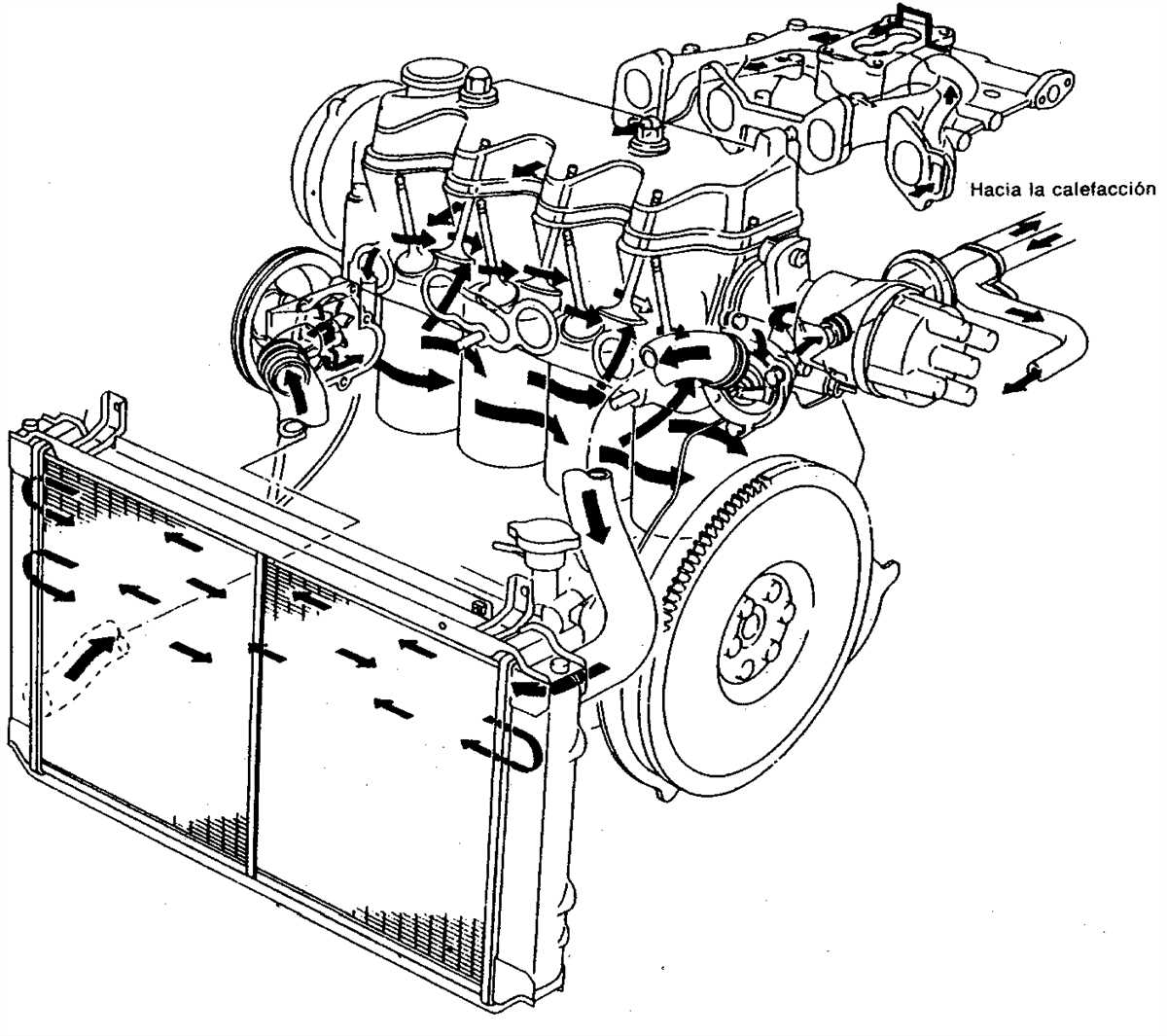
- Check the coolant level regularly and top it up if necessary. Low coolant levels can cause overheating and engine damage.
- Inspect the radiator for any signs of leaks, such as puddles or stains under the vehicle. Leaks can lead to coolant loss and overheating.
- Clean the radiator fins using compressed air or a soft brush to remove any debris or dirt that may obstruct airflow.
- Flush the radiator and replace the coolant according to the manufacturer’s recommendations. This helps remove any accumulated contaminants and ensures proper coolant performance.
- Inspect the radiator hoses for any signs of wear or damage. Replace them if necessary to prevent coolant leaks.
- Check the radiator cap for any signs of damage or corrosion. A faulty cap can cause coolant loss and overheating.
Troubleshooting Tips:
- If your engine is overheating, check the radiator for any blockages or obstructions. Clear any debris or dirt that may be preventing proper airflow.
- If you notice coolant leaks, identify the source and repair or replace the affected component. Common culprits include the radiator, hoses, and water pump.
- If your vehicle is experiencing poor heat output from the heater, it could be a sign of a clogged heater core. Flushing the heater core can often solve this issue.
- If you are consistently losing coolant without any visible leaks, you may have a head gasket issue. Consult a mechanic for further diagnosis and repairs.
By following these maintenance tips and troubleshooting techniques, you can ensure that your radiator functions optimally, keeping your engine cool and preventing any major issues. Remember to consult your vehicle’s owner manual for specific maintenance guidelines and seek professional help if needed.