
If you’re in need of an ABS brake line diagram for your 2003 Chevy Tahoe, you’ve come to the right place. The anti-lock braking system (ABS) is a safety feature that prevents the wheels from locking up during sudden stops or braking on slippery surfaces. It is crucial for the proper functioning of your vehicle’s braking system, and understanding its layout can help you diagnose and fix any issues that may arise.
In a 2003 Chevy Tahoe, the ABS brake line diagram shows the path of the brake fluid through the system. Starting from the brake master cylinder, the fluid travels through the ABS control module, which is responsible for monitoring the speed of each wheel. From there, the fluid is directed to each brake caliper or wheel cylinder, depending on the type of braking system your Tahoe has.
The ABS brake line diagram also includes important components such as the brake lines, brake hoses, and brake pedal. These components work together to ensure that the braking force is evenly distributed to all four wheels, maximizing stopping power and control. If any of these components become damaged or worn out, it can affect the performance of the ABS system and compromise your safety on the road.
By referring to a 2003 Chevy Tahoe ABS brake line diagram, you can easily locate and identify the various components of the ABS system. This can be helpful when troubleshooting issues, performing maintenance, or making repairs. Whether you’re a DIY enthusiast or a professional mechanic, having access to a detailed diagram can save you time and help ensure that the job is done correctly.
In conclusion, the ABS brake line diagram is a valuable resource for anyone working on their 2003 Chevy Tahoe’s braking system. It provides a visual representation of how the brake fluid flows through the system, allowing for easier troubleshooting and repair. By understanding the layout and components of the ABS system, you can ensure that your Tahoe’s brakes are operating at their best and keeping you safe on the road.
Understanding the ABS Brake Line System of 2003 Chevy Tahoe
The ABS brake line system in a 2003 Chevy Tahoe is a crucial component that helps to ensure safe and efficient braking. This system utilizes a network of brake lines, valves, sensors, and the ABS control module to actively monitor and manage the braking process. By understanding how the ABS brake line system works, you can better appreciate its importance and take necessary actions to maintain its functionality.
Components of the ABS brake line system:
- Brake lines: These are metal tubing that carries brake fluid from the master cylinder to the calipers or wheel cylinders.
- Valves: The system includes a combination valve, which distributes the brake fluid to the front and rear wheels, as well as individual wheel valves that control the pressure to each wheel.
- Sensors: The system is equipped with wheel speed sensors that measure the rotational speed of each wheel. These sensors provide crucial data to the ABS control module.
- ABS control module: This module is the brain of the system. It receives input from the wheel speed sensors and makes decisions to prevent wheel lock-up during braking. It accomplishes this by modulating the brake pressure to each wheel.
How the ABS brake line system works:
When you apply the brakes, the ABS control module constantly monitors the rotational speed of each wheel using the wheel speed sensors. If the module detects a wheel lock-up or a significant difference in rotational speed between wheels, it activates the appropriate valves to modulate brake pressure. By adjusting the brake pressure to the specific wheel, the system prevents wheel lock-up and allows the driver to maintain control of the vehicle.
Maintenance and troubleshooting:
To ensure the proper functioning of the ABS brake line system, regular maintenance and inspections are necessary. This includes checking for leaks in the brake lines, ensuring proper brake fluid levels, and performing diagnostic tests to detect any issues with the system. If you experience any abnormal brake behavior, such as pulsating brake pedal or ABS warning lights, it is essential to have the system inspected by a qualified technician. They can diagnose and repair any potential problems and ensure your 2003 Chevy Tahoe’s ABS brake line system is functioning optimally.
Overview of the ABS Brake System
The ABS (Anti-lock Braking System) is an essential component of modern vehicles, including the 2003 Chevy Tahoe. It is designed to enhance the safety and control of the vehicle during braking by preventing the wheels from locking up. In this way, it allows the driver to maintain steering control and avoid skidding, especially in emergency situations.
The ABS brake system consists of several key components that work together to ensure effective braking performance. These include the ABS control module, wheel speed sensors, hydraulic control unit, and brake lines. The control module is the brain of the system, continuously monitoring the speed of each wheel through the sensors.
- The wheel speed sensors are typically located at each wheel or in the differential and provide information about the rotational speed of the wheels.
- The hydraulic control unit is responsible for regulating the brake pressure on each wheel individually, based on the input received from the control module.
- The brake lines in the system are responsible for transmitting hydraulic fluid from the master cylinder to each wheel, allowing the control module and hydraulic control unit to regulate the brake pressure.
When the driver applies the brakes, the ABS system activates, and the control module starts monitoring the wheel speeds. If it detects that any wheel is about to lock up, it rapidly modulates the brake pressure on that wheel to prevent it from skidding. This modulation is achieved through the hydraulic control unit, which adjusts the brake pressure by rapidly opening and closing the brake valves.
The result is a pulsating sensation felt by the driver, as the brake pressure is modulated to prevent wheel lock-up. This pulsation is commonly referred to as “ABS kicking in.” It is important for the driver to maintain firm and continuous pressure on the brake pedal, allowing the ABS system to do its job effectively.
In conclusion, the ABS brake system plays a crucial role in vehicle safety by preventing wheel lock-up during braking. It consists of various components that work together to ensure optimal braking performance. Understanding the functionality of the system can help drivers make informed decisions and respond appropriately in emergency situations.
Components of the ABS Brake Line System
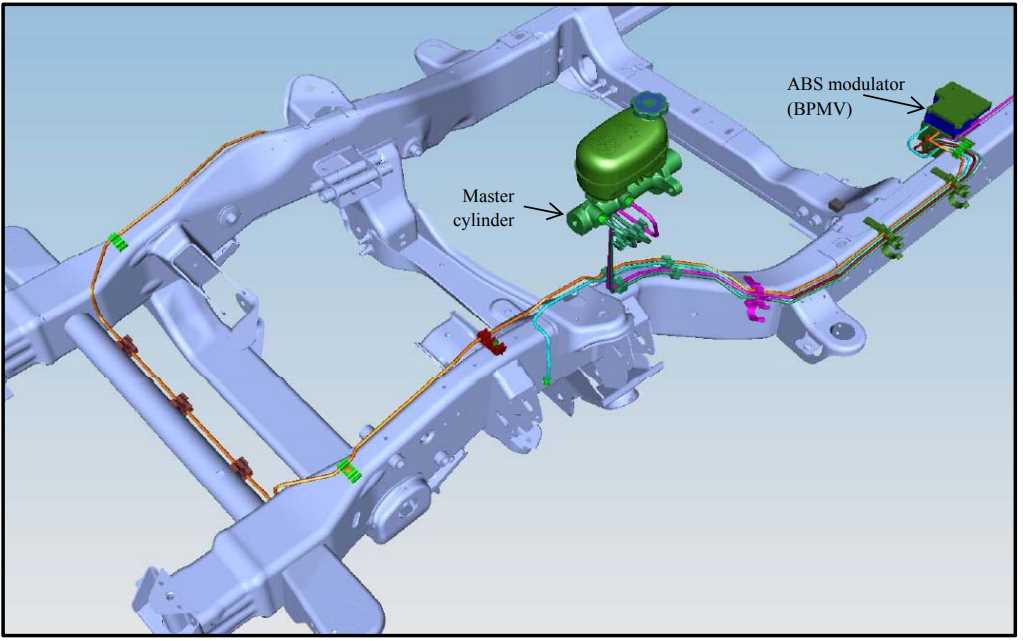
The ABS (anti-lock braking system) brake line system in a 2003 Chevy Tahoe consists of several components that work together to ensure safe and effective braking. These components include:
- ABS Control Module: This module is the brain of the ABS system and is responsible for monitoring wheel speed and controlling brake pressure during sudden stops or slippery conditions.
- Wheel Speed Sensors: There are four wheel speed sensors, one for each wheel, that measure the rotational speed of the wheels. These sensors provide important input to the ABS control module to determine if any wheel is about to lock up.
- Hydraulic Control Unit (HCU): The HCU is responsible for modulating brake pressure during ABS operation. It consists of valves and solenoids that regulate the flow of brake fluid to each wheel to prevent wheel lock-up.
- Brake Master Cylinder: The master cylinder is the main component of the braking system that generates hydraulic pressure to actuate the brakes. It provides pressurized brake fluid to the HCU and distributes it to each wheel as necessary.
- Brake Lines and Hoses: The brake lines and hoses connect the master cylinder and the HCU to the various brake calipers and wheel cylinders. These lines and hoses carry pressurized brake fluid to apply and release the brakes as commanded by the ABS control module.
- Brake Calipers and Wheel Cylinders: These components are responsible for squeezing the brake pads against the rotors or drums to create the necessary friction for stopping the vehicle. They are actuated by the pressurized brake fluid sent from the HCU.
- ABS Warning Light: The ABS warning light is located on the vehicle’s instrument cluster. It illuminates when there is a fault in the ABS system and alerts the driver to seek service.
These components work together seamlessly to ensure that the ABS system functions properly and provides maximum braking performance, especially in emergency situations or on slippery surfaces. Regular maintenance and inspection of the ABS brake line system are crucial to ensure the system’s reliability and safety.
Diagnosing ABS Brake Line Issues
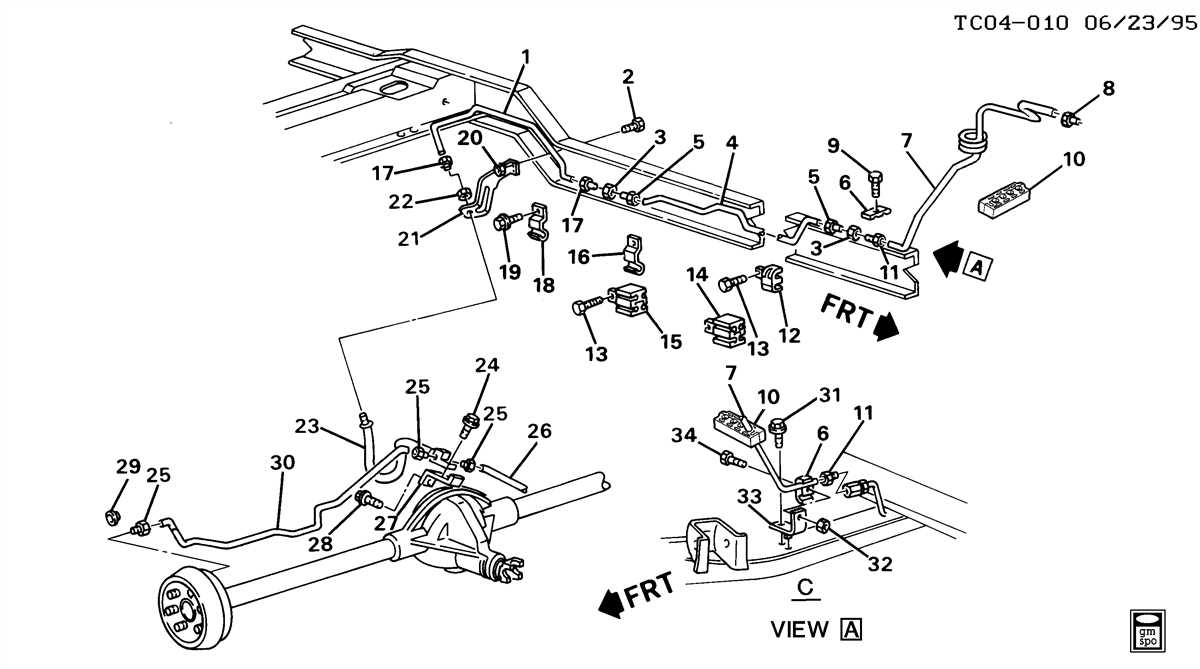
The ABS brake system in a 2003 Chevy Tahoe is designed to help prevent wheel lock-up during braking, improving the vehicle’s overall stability and control. However, over time, the brake lines in the system may develop issues that can affect its performance. Here are some common symptoms and diagnostic steps to identify ABS brake line problems:
1. Brake pedal pulsation: If you notice a pulsation or vibration in the brake pedal when applying the brakes, it could indicate an issue with the ABS system. This can be caused by a faulty ABS module or a damaged brake line.
2. ABS warning light: When there is a problem with the ABS system, the ABS warning light on the instrument panel will illuminate. This is a clear indication that something is wrong and needs to be addressed. Using a diagnostic tool, you can retrieve the specific ABS error codes to help pinpoint the issue.
3. Loss of braking power: If you experience a sudden loss of braking power, it could be due to a brake line leak or a malfunctioning ABS valve. It is important to inspect the brake lines for any signs of leaks, such as puddles of brake fluid under the vehicle.
4. Uneven brake pressure: If you notice that one or more wheels are not engaging properly during braking, it could be a sign of a blocked or restricted brake line. This can result in uneven braking performance and reduced overall stopping power.
5. ABS module failure: In some cases, the ABS module itself may be at fault. If all other components of the ABS system have been checked and appear to be in working order, the module may need to be replaced. It is recommended to consult with a professional mechanic for proper diagnosis and repairs.
Overall, diagnosing ABS brake line issues requires a careful examination of the various components in the system. It is important to address any problems promptly to ensure the safety and performance of your vehicle.
Common Problems with the ABS Brake Line System
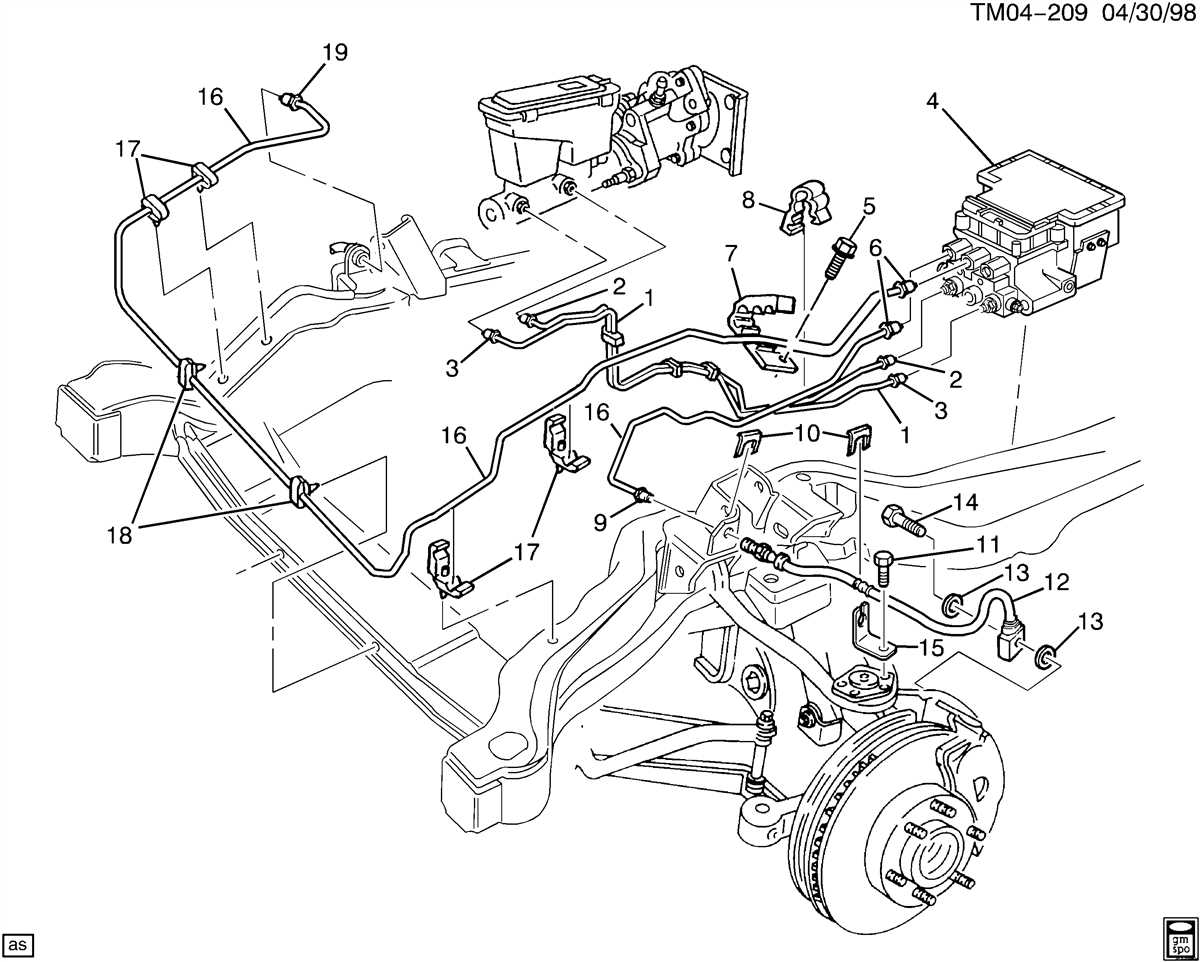
The ABS brake line system in vehicles, such as the 2003 Chevy Tahoe, is designed to enhance the braking performance and safety by preventing the wheels from locking up during sudden stops or on slippery surfaces. However, like any system, it can experience issues that may affect its functionality and require attention.
One common problem with the ABS brake line system is brake fluid leakage. This can occur due to worn-out brake lines or damaged fittings. When there is a leak in the system, it can result in a loss of brake fluid, causing reduced braking performance or even a complete brake failure. Regular inspection of the brake lines and fittings is essential to identify and fix any leaks promptly.
Another issue that can arise with the ABS brake line system is the accumulation of air bubbles. When air enters the brake lines, it can disrupt the hydraulic pressure and affect the ABS functionality. This can result in a spongy brake pedal or a longer stopping distance. Proper bleeding of the brake system is necessary to remove any trapped air and restore optimal braking performance.
Corrosion is yet another common problem that affects the ABS brake line system. Over time, brake lines can become corroded due to exposure to salt, moisture, and other environmental factors. Corroded brake lines can weaken and develop leaks, compromising the integrity of the system. Regular inspection and maintenance, including the application of rust prevention measures, can help prevent corrosion-related issues.
In conclusion, the ABS brake line system can encounter various problems, including brake fluid leakage, air bubble accumulation, and corrosion. Regular inspection, maintenance, and timely repairs or replacements can help ensure the optimal functionality and safety of the ABS brake line system in vehicles, such as the 2003 Chevy Tahoe.
Repairing and Replacing ABS Brake Line Components
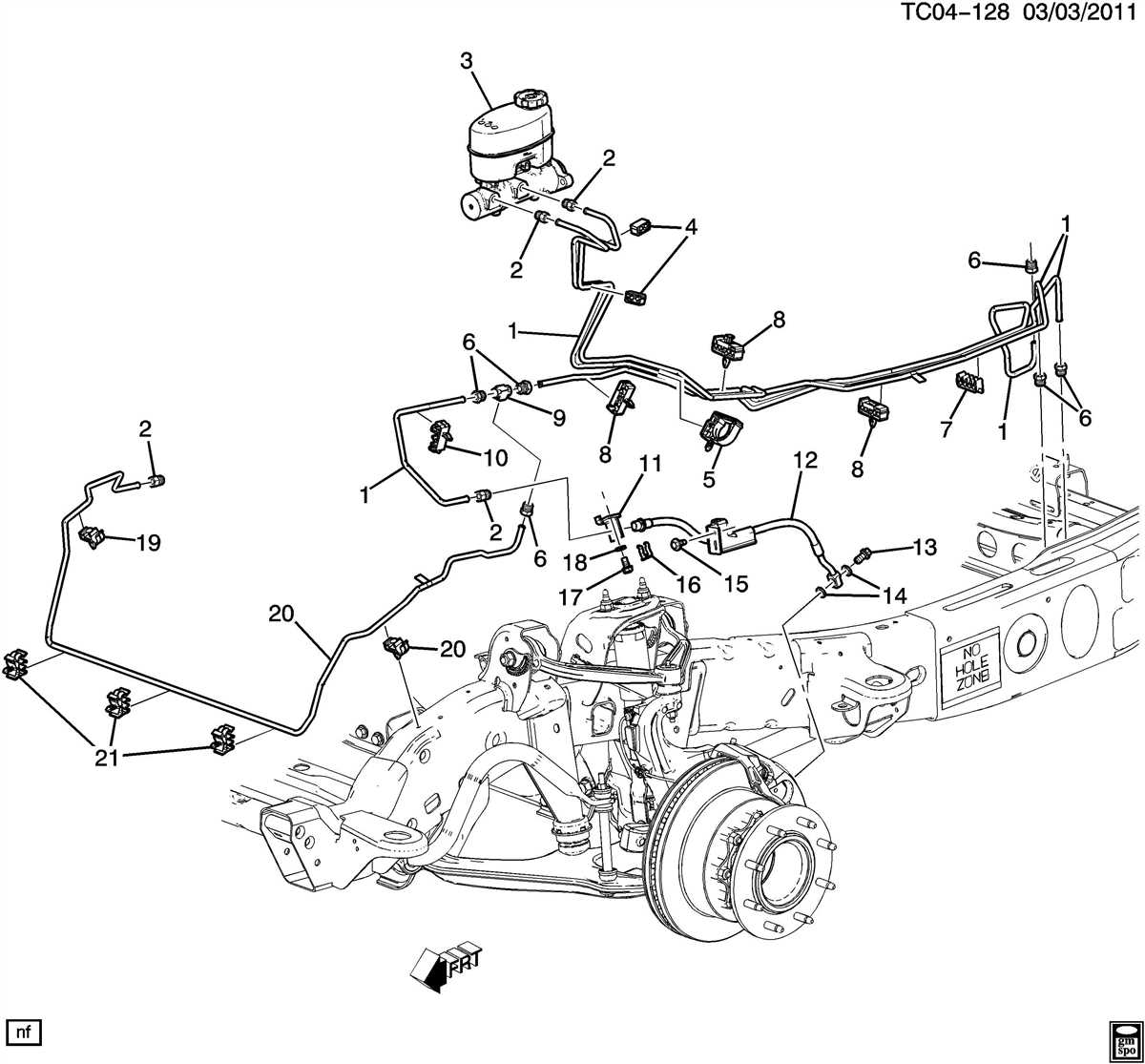
The ABS (anti-lock brake system) in a 2003 Chevy Tahoe relies on a complex network of brake lines and components to function properly. Over time, these components can wear out or become damaged, leading to decreased braking performance and potential safety issues. When facing an ABS brake line problem, it is important to understand the various components involved and how they can be repaired or replaced.
One common issue with ABS brake lines is corrosion or rust. This can occur due to exposure to moisture and salt on the road, especially in areas with harsh winter conditions. Rust can cause the brake lines to weaken and eventually develop leaks. In such cases, it is necessary to replace the affected brake lines with new ones. The damaged section of the line is typically cut out, and a new line is then installed using compression fittings or flare fittings.
In addition to brake line replacement, other components of the ABS system may also need to be repaired or replaced. This can include the ABS module, which is responsible for controlling the operation of the system, as well as the ABS sensors located at each wheel. If the ABS module is malfunctioning, it may need to be reprogrammed or replaced entirely. Similarly, if an ABS sensor is faulty or damaged, it should be replaced to ensure accurate brake performance.
When repairing or replacing ABS brake line components, it is important to use high-quality parts that are specifically designed for your Chevy Tahoe. OEM (original equipment manufacturer) parts are recommended, as they are designed to meet the specifications set by the manufacturer. This helps to ensure proper fit and function, as well as long-lasting reliability.
In conclusion, repairing and replacing ABS brake line components in a 2003 Chevy Tahoe requires an understanding of the various parts involved and their specific functions. Whether it is replacing corroded brake lines, repairing the ABS module, or replacing faulty sensors, it is crucial to use high-quality parts to ensure the proper functioning of the ABS system and maintain optimal braking performance and safety.
Regular Maintenance for the ABS Brake Line System
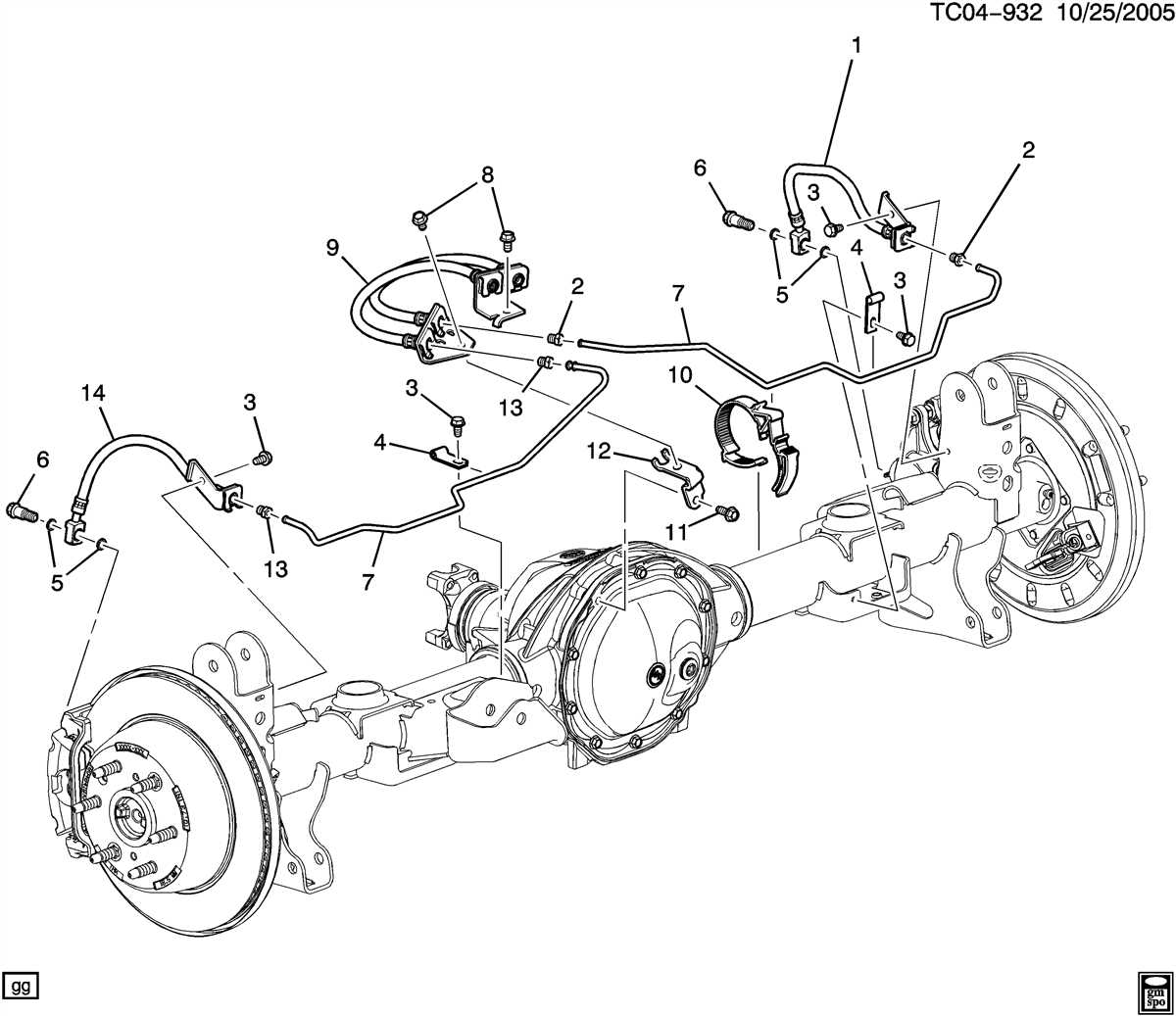
Regular maintenance is essential for keeping your ABS brake line system in good working order. By following these maintenance tips, you can help prevent issues with your brake lines and ensure optimal performance of your vehicle’s braking system.
1. Regular Inspection: Inspect the ABS brake lines for any signs of wear, leaks, or damage. Look for any bulges, cracks, or corrosion on the brake lines. If you notice any issues, have them repaired or replaced immediately.
2. Brake Fluid Flush: Regularly flush and replace the brake fluid in the ABS brake system. Brake fluid can become contaminated over time, affecting the performance of the braking system. Consult your vehicle’s manual for the recommended interval for brake fluid replacement.
3. Bleeding the Brakes: Bleed the brakes to remove any air bubbles that may have entered the brake lines. Air bubbles can cause spongy or ineffective braking. Bleeding the brakes should be done annually or whenever you replace brake components.
4. Caliper Maintenance: Inspect and clean the brake calipers regularly. Ensure that the calipers are properly lubricated, and the pistons are functioning correctly. Clean off any dirt or debris that may have accumulated on the calipers.
5. Brake Pad and Rotor Inspection: Regularly inspect the brake pads and rotors for wear. Replace any worn-out brake pads or damaged rotors to maintain optimal braking performance. Consult your vehicle’s manual for the recommended interval for brake pad and rotor replacement.
6. Professional Inspection: Schedule regular inspections with a qualified mechanic to ensure the overall health of your ABS brake line system. An experienced technician can detect any underlying issues and provide the necessary repairs or replacements.
By following these maintenance tips, you can extend the lifespan of your ABS brake line system and ensure safe and efficient braking. Remember, regular maintenance is crucial for the overall performance and safety of your vehicle.