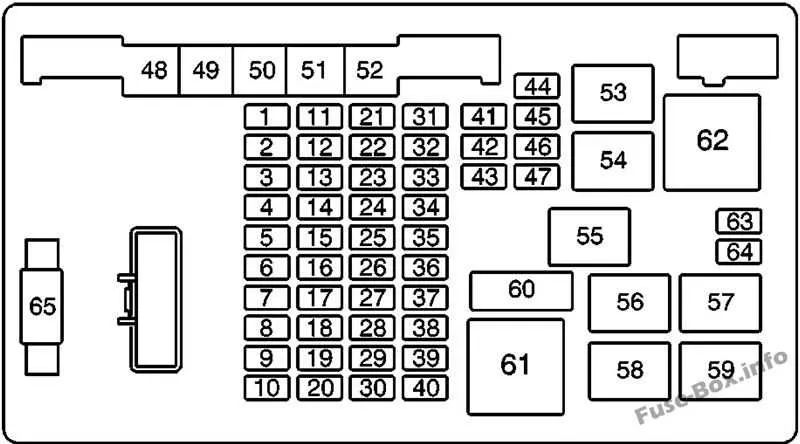
If you’re experiencing electrical issues or need to perform maintenance on your vehicle’s wiring, it’s crucial to know where the critical components are located. Refer to the schematic of the electrical panel for accurate placement of relays, fuses, and other vital parts. This will ensure you can quickly address power failures or troubleshoot faulty circuits without unnecessary confusion.
Start by locating the central power distribution unit, which houses most of the primary connections for the vehicle’s electrical systems. Depending on the model, this may be positioned under the hood or within the interior cabin. Understanding the layout of each component and its function will help prevent mistakes when replacing or testing circuits.
Pay attention to the configuration of relay slots and fuse positions, as these are often misinterpreted due to the complex arrangement. Clear markings for each electrical function are essential to ensure proper functionality. Using the correct spare part for the corresponding spot is key to maintaining the integrity of the system.
Finally, always confirm the amperage ratings and the placement of each protective element within the setup. Incorrect installation can lead to circuit damage or malfunction. For reliable troubleshooting, refer to the official vehicle maintenance guide for further details and step-by-step instructions on electrical system repairs.
Electrical Component Layout
If you are troubleshooting electrical issues, locating the proper panel is crucial. For this model, you will find the primary power distribution cluster beneath the dashboard and another near the engine compartment. Make sure you identify both locations for quick access.
The interior unit typically handles low-voltage components such as interior lights, HVAC, and the radio. Ensure the terminals are clean and free from corrosion when inspecting. This cluster includes the main relay for the ignition and various fuses responsible for essential vehicle functions.
The external unit serves to control higher power systems, including the engine’s electrical sensors, headlights, and charging system. The design often splits the high-current applications into individual sections to minimize overload risk. Pay attention to the connectors and verify that no loose terminals are causing power failures.
Important Tips: Always use a multimeter to check continuity in case of suspected faulty connections. Refer to the legend located on the back of the panel cover to identify each section. When replacing any part, ensure that the amperage rating matches the original specifications to avoid damage to the wiring or components.
Pro Tip: Disconnect the battery before conducting any inspections or replacements to prevent any electrical shock or accidental short-circuiting. Always replace a blown element with an identical one to maintain the system’s safety and efficiency.
Understanding the Layout of the 2003 Dodge Ram Fuse Box
The electrical system of this vehicle relies on a central unit for managing power distribution across critical components. Located under the hood and inside the cabin, these units feature specific slots for relays, fuses, and circuit protection elements. Each one is labeled to make troubleshooting and maintenance easier. Knowing the exact positioning and function of each element allows for quick identification of blown components or circuits that may be malfunctioning.
The main unit under the hood is dedicated to high-power systems like the ignition, engine control, and air conditioning. Components inside the cabin focus on features like lighting, audio systems, and accessories. Make sure to refer to the label on the cover or nearby schematic for precise positioning when replacing any part, as some connections are closely grouped.
Each relay and fuse corresponds to specific electrical features, and overloading one can damage other systems connected to it. Always replace them with the correct amperage to prevent further electrical issues. Keep a toolkit on hand for easy access to the compartment when inspecting or replacing components. When replacing, confirm that all fuses are firmly seated and properly aligned with their slots to avoid future issues.
If an issue persists after replacing a blown component, it’s critical to inspect wiring for any short circuits or damage in the circuits leading to the unit. A professional diagnostic tool can assist in determining if there’s an issue beyond just a faulty part, such as a deeper electrical malfunction.
How to Identify and Replace a Blown Fuse in Your Pickup
To restore functionality to your vehicle’s electrical components, follow these steps to identify and replace a faulty circuit protector.
- Locate the Electrical Panel – Find the main control unit inside the cabin or under the hood. Refer to the owner’s manual for precise locations.
- Inspect the Protectors – Examine each protector carefully. A broken filament or discoloration indicates one is blown. You can also use a multimeter to check for continuity.
- Identify the Correct Rating – Ensure you replace the damaged item with one of the same rating. Overloading circuits can cause further damage.
- Remove the Faulty Part – Use plastic tweezers or fuse pullers to safely extract the damaged component. Avoid using metal objects to prevent accidental short circuits.
- Insert the New Component – Carefully place the replacement into the corresponding slot. Ensure it fits snugly and securely.
- Test the System – Turn on the vehicle and check if the affected electrical system is functioning properly.
Regularly inspect these components to avoid future issues. Always keep spares on hand for emergencies.
Key Fuses to Check for Common Electrical Issues
If you experience electrical failures, check the following circuits to diagnose and fix problems efficiently:
- Fuel Pump Relay – Located in the engine compartment, this relay controls the fuel delivery system. A blown relay can cause stalling or failure to start.
- Headlight Circuit – Check the headlights’ related circuit if you notice dim or non-functioning lights. This often affects the front lamps and interior lights.
- Ignition System – If the engine won’t crank, inspect the ignition switch and starter motor circuits, as they are key to initiating the start-up sequence.
- ABS (Anti-lock Brake System) – Problems with braking performance may stem from an issue with the ABS relay. A malfunction here can prevent proper braking control.
- Power Window Control – Non-operational windows often point to a blown fuse in the power window circuit. Inspect this if your windows are stuck or won’t respond to the switch.
- Charging System – A malfunction in the alternator or battery charging system is often caused by an issue with the corresponding electrical circuit.
Inspect the associated fuses regularly and replace them if any electrical issue persists. Proper diagnostics will prevent larger, costly repairs.