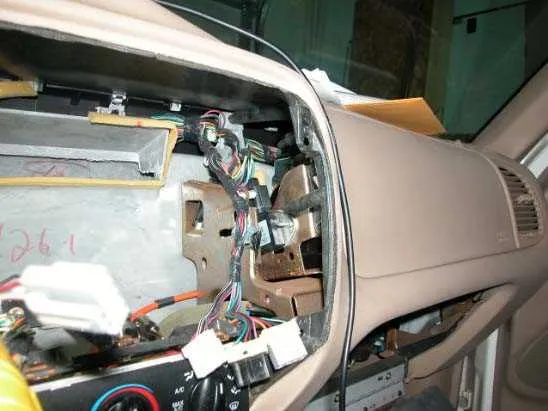

If you’re having trouble locating or understanding the electrical system components, it’s essential to know the exact positioning of the relays and circuits. A clear understanding of the power distribution system can help pinpoint issues like blown fuses or malfunctioning wiring. Begin by checking the main assembly under the dashboard for vital connections.
Next, identify the secondary panel often located under the hood. It controls several critical systems, such as the lighting and air conditioning. Ensure to consult the detailed pinout to verify the placement of each relay and fuse according to the model year of your vehicle.
For troubleshooting, start with the primary circuits, and verify each component against the provided wiring scheme. Double-check each connection for potential loose terminals or worn-out parts. A clear understanding of the layout will save you time when diagnosing or replacing electrical components.
Remember, the fuse panel configuration can vary slightly based on factory options, so always confirm the layout with your specific vehicle’s manual to avoid mistakes. Precision is key to preventing unnecessary repairs or replacements when dealing with electrical faults.
Electrical Component Layout for 2004 Model
For troubleshooting or replacing specific electrical parts, it’s essential to know the proper configuration of the internal power distribution. This vehicle features multiple locations for critical components, including under-hood and interior spaces.
Ensure the engine compartment features a large unit where key systems like the ignition and fuel are controlled. This unit is typically located near the battery, offering access to the most critical relays and fuses. Inside, you will find smaller sections responsible for various accessories, like air conditioning and the audio system.
For the cabin section, it’s located below the dashboard on the driver’s side, near the kick panel. This unit handles lower-voltage circuits such as lighting and climate control, with each slot carefully mapped for user convenience.
Always check the labeling to confirm the correct configuration for each component. Cross-referencing with the manual can prevent accidental damage when removing or replacing any elements, especially if you are dealing with power-hungry systems like the headlights or alternator.
Identifying Electrical Component Locations
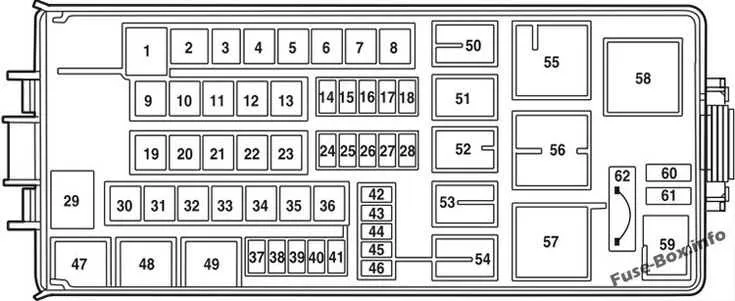
To find the right circuit protection, follow these steps:
- Start with the interior panel, typically located near the driver’s side dashboard or below the steering column.
- Check the engine compartment area near the battery or on the driver’s side near the fender.
- Look for a secondary panel inside the cabin near the rear seating area or under the glove compartment.
Each of these panels houses various relays and electrical connectors for different vehicle systems. Use the cover label to match each component with the appropriate number.
- Interior panels generally control features such as lighting, the radio, and cabin climate systems.
- Engine area panels primarily handle engine-related electrical systems like ignition, fuel pump, and cooling fans.
Refer to the numbered grid on the inside of the panel cover for precise identification of each unit. If unclear, use a multimeter to test for continuity to ensure accuracy.
Common Electrical Issues and Solutions
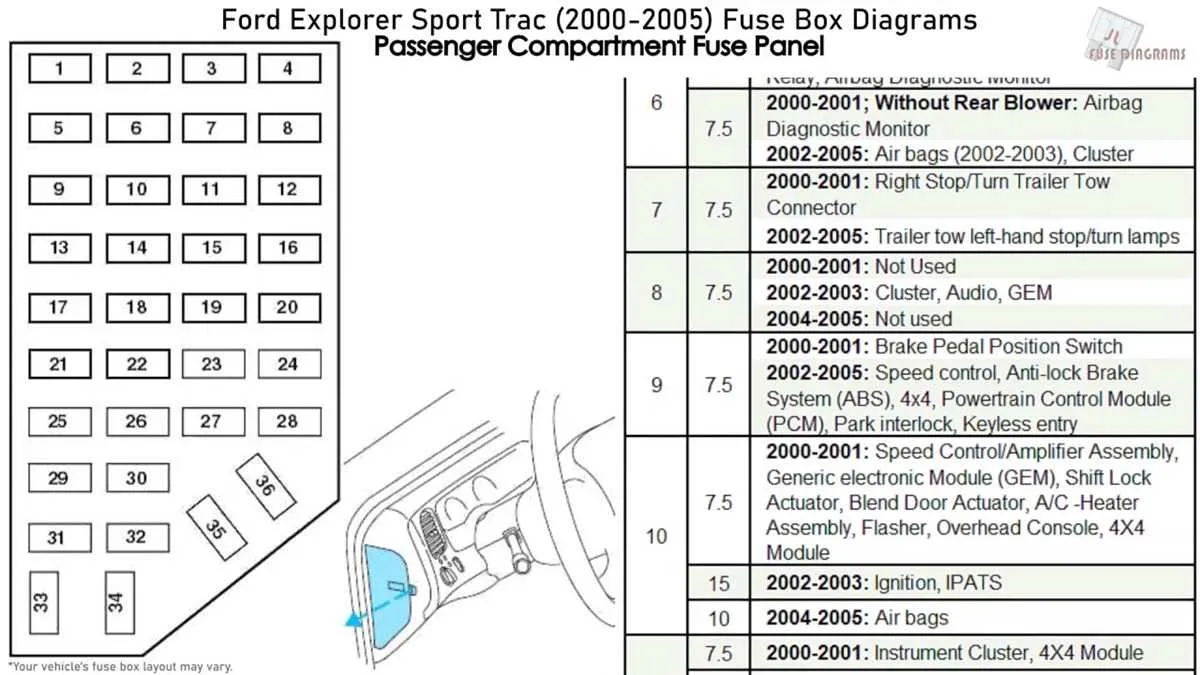
If the vehicle’s electrical system stops working or some features stop responding, it’s crucial to check the related circuit protectors. One frequent issue involves blown circuit protectors which can disrupt power supply to various components like lights, radio, or wipers. If this happens, inspect the power distribution unit or relay panels for faulty connections.
Another typical problem arises from improper connections or damaged terminals. A weak or intermittent connection can lead to the electrical components sporadically turning on and off. Clean all contacts and ensure they are firmly attached to prevent unreliable operation.
Overloading of specific circuits is also a common cause of malfunction. Excessive current flow can cause the protective mechanisms to shut down automatically. Always verify that electrical accessories do not exceed the recommended power limits. Replacing or upgrading the protective components in this case can solve the problem.
Lastly, corrosion can form on the connectors over time, particularly in areas exposed to moisture or extreme temperatures. Regular inspection and cleaning can prevent these issues. Use a wire brush or appropriate cleaning tools to clear off any corrosion that might impair the circuit performance.
Understanding the Electrical System of the Vehicle through the Fuse Layout
To effectively troubleshoot electrical issues, it’s essential to familiarize yourself with the vehicle’s wiring layout and power distribution points. These components are organized in specific clusters that can be found in designated panels, which house multiple relays and connectors for various circuits. Refer to the power distribution panel for critical components like lights, ignition, and power windows, which are typically fused in specific sections.
The key to diagnosing faults is recognizing which circuit controls specific functions and checking if the related relay or connector is functioning. For instance, if your headlamps fail, look for the headlight circuit and check if the related component in the panel is intact or needs replacement. Make sure to verify the amperage ratings to avoid overloading any circuit during repairs.
It’s also crucial to inspect the connections for any signs of wear, corrosion, or loose wiring, as these are common culprits in electrical malfunctions. Over time, some components may lose connection due to environmental factors, which could lead to unpredictable behavior in electrical systems.
Always ensure the replacement parts match the specified amperage, as mismatched components could risk damage to the electrical system or even pose a fire hazard. Regularly consulting the vehicle’s manual for updates on circuit specifications and placement is recommended for long-term maintenance.