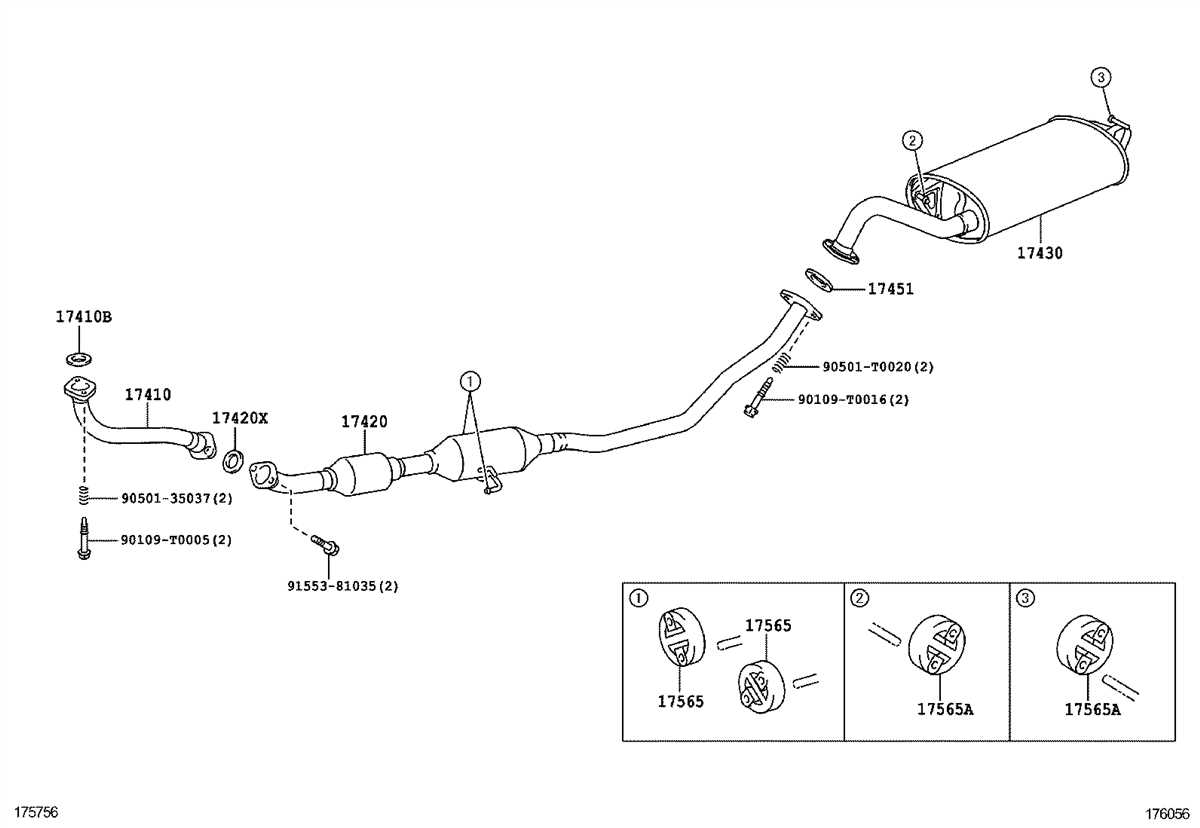
If you are a proud owner of a 2008 Dodge Dakota, you may be interested in understanding how the exhaust system in your vehicle works. The exhaust system plays a crucial role in the overall performance of your vehicle by ensuring proper engine airflow and reducing harmful emissions.
The exhaust system in the 2008 Dodge Dakota consists of several components, including the exhaust manifold, catalytic converter, muffler, and tailpipe. Each of these components has a specific function in the overall operation of the exhaust system.
The exhaust manifold is located at the front of the engine and collects the exhaust gases from the engine cylinders. It is connected to the cylinder head and directs the collected gases to the catalytic converter.
The catalytic converter is an essential part of the exhaust system as it helps in reducing harmful emissions. It contains a catalyst that converts harmful gases, such as carbon monoxide and nitrogen oxide, into less harmful substances, such as carbon dioxide and nitrogen.
The muffler is responsible for reducing noise produced by the engine by using a series of chambers or baffles to absorb sound waves. It also helps in maintaining the backpressure in the exhaust system, which is necessary for the engine’s performance.
The tailpipe is the final part of the exhaust system, and it directs the exhaust gases out from the vehicle. It is usually located at the rear of the vehicle and may have different shapes and designs depending on the model and trim level of the Dodge Dakota.
Understanding the various components of the exhaust system can help you in diagnosing any issues or problems you may encounter with your 2008 Dodge Dakota’s exhaust system. Regular maintenance and timely repairs can ensure the proper functioning of your vehicle’s exhaust system, resulting in better performance and reduced emissions.
What is an Exhaust System?
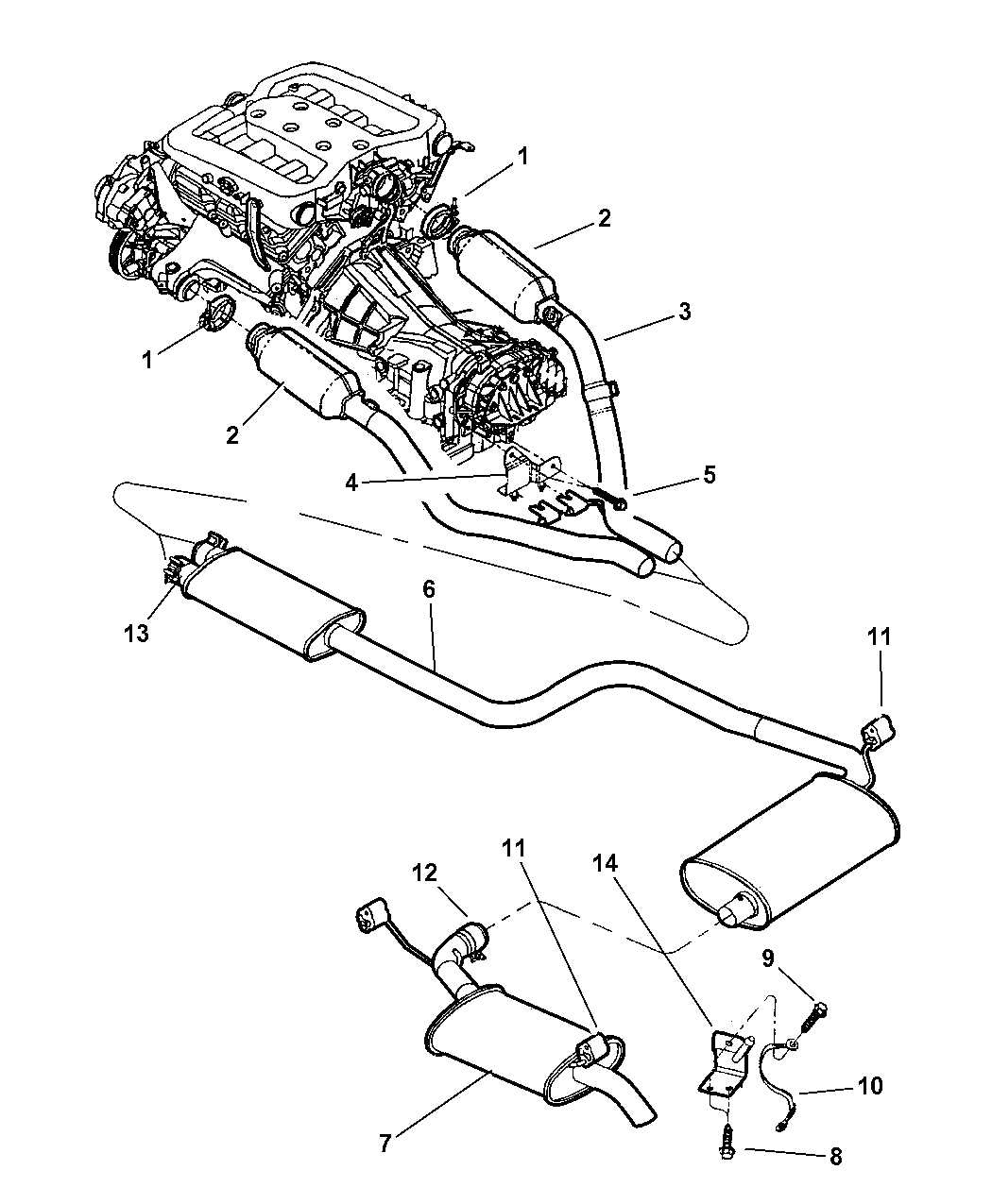
An exhaust system is a crucial component of a vehicle that is responsible for removing exhaust gases from the engine and expelling them out of the vehicle. It plays a vital role in maintaining the engine’s performance, reducing emissions, and providing a quieter driving experience.
Components
The exhaust system consists of several components, each serving a specific purpose:
- Exhaust Manifold: This component collects the exhaust gases from the engine cylinders and directs them into the exhaust system.
- Catalytic Converter: The catalytic converter is responsible for reducing harmful emissions by converting them into less harmful substances.
- Muffler: The muffler is designed to reduce the noise generated by the engine’s exhaust gases. It contains baffles and chambers that help in the noise reduction process.
- Resonator: Some exhaust systems also include a resonator, which further reduces noise and creates a more pleasant sound.
- Tailpipe: The tailpipe serves as the final outlet for the exhaust gases, directing them away from the vehicle.
Functions
The main functions of an exhaust system are:
- Exhaust Gas Disposal: The primary purpose of the exhaust system is to safely remove the exhaust gases produced during the combustion process.
- Reducing Emissions: The catalytic converter plays a crucial role in reducing harmful emissions such as carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides, and hydrocarbons.
- Improving Engine Performance: An efficient exhaust system can help improve the engine’s performance by allowing it to expel exhaust gases more effectively, reducing backpressure, and increasing horsepower.
- Noise Reduction: The muffler and resonator are designed to reduce the noise generated by the engine’s exhaust gases, providing a quieter driving experience.
Maintenance
To ensure the proper functioning of an exhaust system, regular maintenance is essential. This includes inspecting for leaks, replacing damaged components, and cleaning or replacing the catalytic converter when necessary. It is also important to keep the exhaust system clean and free from debris to prevent clogs and restrictions.
Overall, an exhaust system is a critical component of a vehicle that not only serves the purpose of removing exhaust gases but also contributes to emissions control, noise reduction, and improved engine performance.
Components of the Exhaust System
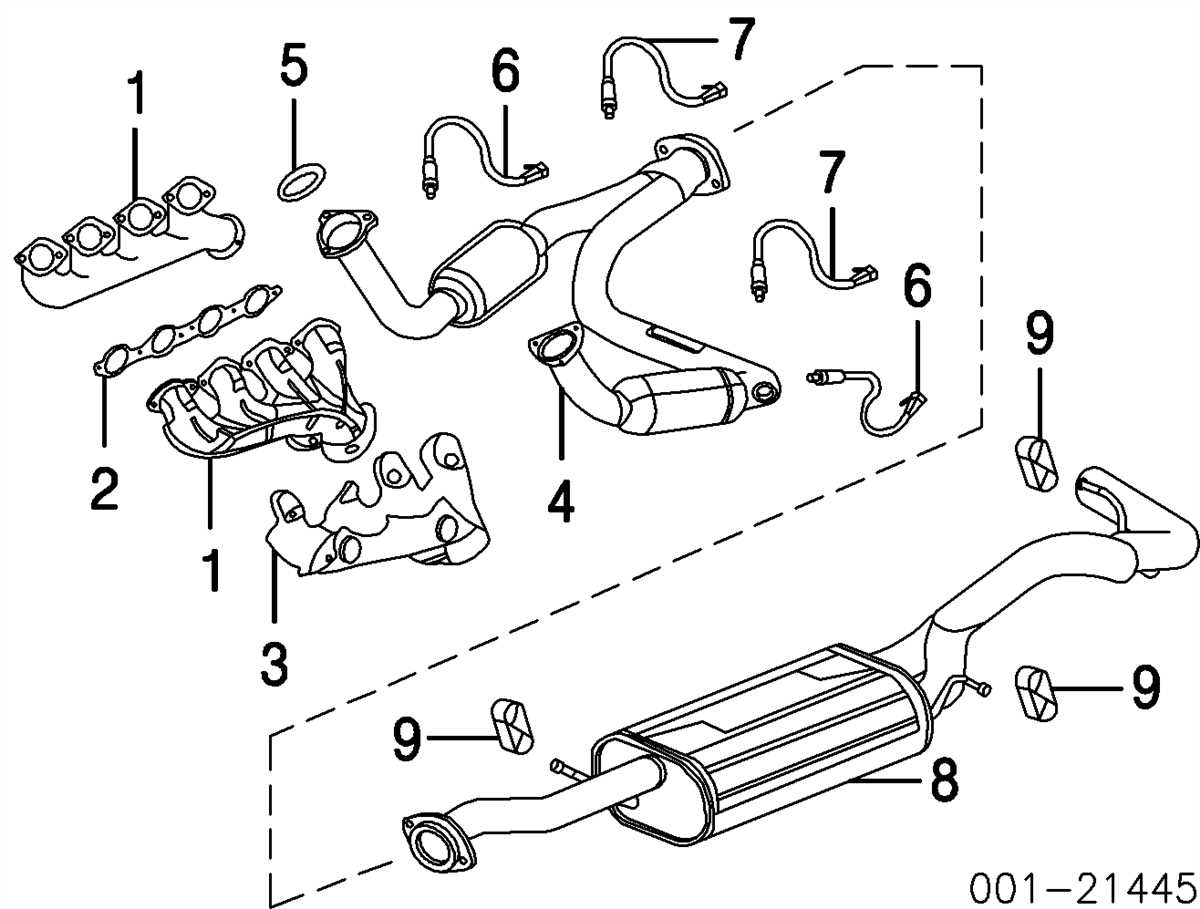
The exhaust system in a 2008 Dodge Dakota consists of several components that work together to safely and efficiently remove exhaust gases from the engine. These components include the exhaust manifold, catalytic converter, muffler, and tailpipe.
Exhaust Manifold: The exhaust manifold is located on the side of the engine and collects the exhaust gases from the individual cylinders. It is usually made of cast iron or stainless steel and is designed to withstand high temperatures and prevent leaks.
Catalytic Converter: The catalytic converter is an essential component of the exhaust system as it helps reduce harmful emissions. It contains a catalyst that converts toxic gases, such as carbon monoxide and nitrogen oxides, into less harmful substances, such as carbon dioxide and nitrogen. The catalytic converter also helps reduce engine noise.
Muffler: The muffler is responsible for reducing the noise produced by the exhaust gases. It contains a series of chambers and baffles that help dampen the sound waves and create a quieter exhaust note. The muffler also plays a role in backpressure, which can affect engine performance.
Tailpipe: The tailpipe is the final component of the exhaust system and is responsible for directing the exhaust gases away from the vehicle. It is usually made of stainless steel or aluminized steel and is designed to withstand corrosion and high temperatures. The tailpipe may also have a chrome or polished finish for aesthetic purposes.
Overall, these components work together to ensure that the exhaust gases are safely and efficiently removed from the engine, while also reducing harmful emissions and engine noise. Regular maintenance and inspection of the exhaust system is important to ensure its proper functioning and to prevent any issues that can affect engine performance and emissions.
Importance of a Properly Functioning Exhaust System

Having a properly functioning exhaust system is crucial for the overall performance and safety of your vehicle. The exhaust system plays a vital role in removing harmful gases and pollutants from the engine, as well as reducing noise levels. It is important to understand the various components of your exhaust system and how they work together to ensure the proper functioning of your vehicle.
One of the key components of the exhaust system is the catalytic converter, which is responsible for converting harmful gases into less harmful substances before they are released into the atmosphere. A malfunctioning catalytic converter can lead to increased emissions, which not only harm the environment but can also result in your vehicle failing emissions tests and inspections. Regular maintenance and timely replacement of the catalytic converter, if needed, is essential for keeping your exhaust system in optimal condition.
Another important component is the muffler, which is designed to reduce the noise produced by the exhaust gases. A malfunctioning or damaged muffler can result in excessive noise, which can be a nuisance to both yourself and others on the road. In addition, a malfunctioning muffler can also impact the overall performance of your vehicle, as it can affect the back pressure in the exhaust system and lead to reduced horsepower and fuel efficiency.
Proper maintenance of your exhaust system includes regular inspections to check for any leaks or damages, as well as ensuring that all components are securely fastened. It is also important to pay attention to any changes in noise levels or emissions, as these can be indicators of a potential issue with your exhaust system. By addressing any problems promptly and seeking professional assistance when needed, you can ensure that your exhaust system continues to function properly and effectively.
8 Dodge Dakota Exhaust System Overview
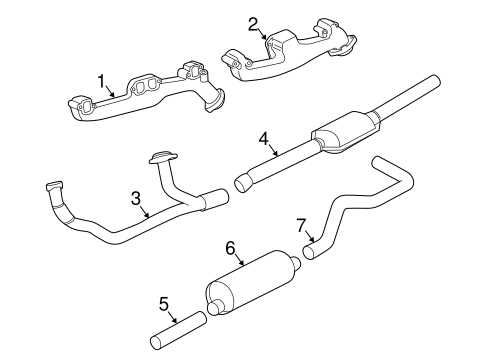
The exhaust system of a 2008 Dodge Dakota plays a crucial role in the overall performance and efficiency of the vehicle. It is responsible for directing and expelling the exhaust gases produced by the engine, while also reducing noise and emissions.
The exhaust system consists of several components that work together to achieve these goals. These include the exhaust manifold, catalytic converter, muffler, and tailpipe. Each component has a specific function and contributes to the overall functionality of the system.
- Exhaust Manifold: The exhaust manifold is located at the engine’s cylinder head and collects the exhaust gases from each cylinder. It is designed to withstand high temperatures and prevent leaks.
- Catalytic Converter: The catalytic converter is responsible for reducing harmful emissions by converting toxic gases into less harmful substances. It contains a catalyst, usually made of platinum, palladium, and rhodium, that facilitates this chemical reaction.
- Muffler: The muffler is an essential component of the exhaust system that reduces noise produced by the engine. It contains chambers and baffles that help to quiet the exhaust gases as they pass through.
- Tailpipe: The tailpipe is the final component of the exhaust system and is responsible for expelling the treated exhaust gases away from the vehicle. It typically extends out from the back of the vehicle and can have various designs.
Overall, the exhaust system of the 2008 Dodge Dakota plays a vital role in maintaining the vehicle’s performance, reducing emissions, and minimizing noise. Regular maintenance and inspection of the system is important to ensure its proper functioning and to address any issues that may arise.
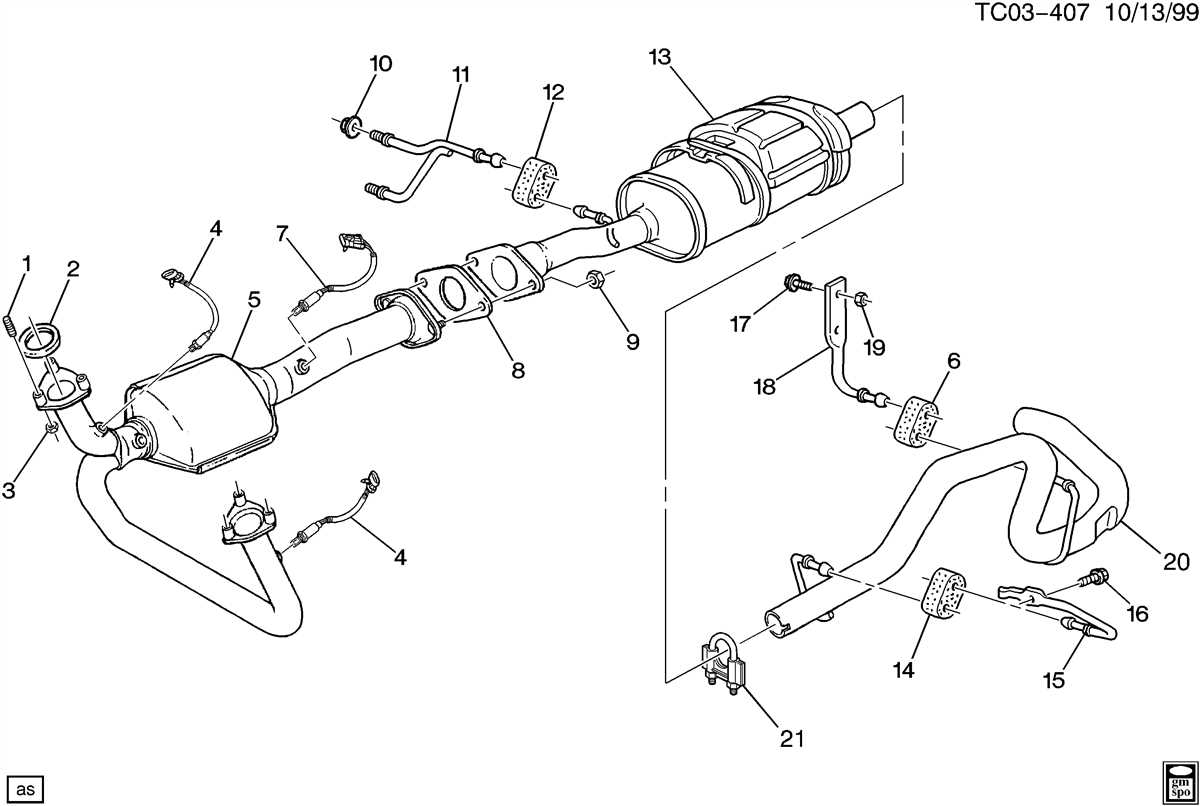
Diagram of the 2008 Dodge Dakota Exhaust System
The 2008 Dodge Dakota is equipped with an exhaust system that plays a crucial role in the vehicle’s performance and emissions control. The exhaust system is responsible for carrying the exhaust gases from the engine to the tailpipe, where they are released into the atmosphere. This system is made up of several components, including the exhaust manifold, catalytic converter, muffler, and tailpipe.
The first component of the exhaust system is the exhaust manifold, which is attached to the engine’s cylinder head. The exhaust manifold collects the exhaust gases from the individual cylinders and channels them into a single pipe. This helps improve exhaust flow and reduce backpressure, allowing the engine to operate more efficiently.
Next in line is the catalytic converter, which is responsible for reducing harmful emissions. The catalytic converter contains a catalyst that interacts with the exhaust gases to convert harmful pollutants into less harmful substances. This helps to reduce the vehicle’s impact on the environment and ensures compliance with emission regulations.
After the catalytic converter, the exhaust gases flow into the muffler. The muffler acts as a sound suppressor, reducing the noise produced by the engine. Inside the muffler, the exhaust gases pass through a series of chambers and perforated tubes, which help to reduce noise by reflecting and absorbing sound waves.
Finally, the exhaust gases exit the vehicle through the tailpipe. The tailpipe is usually located at the rear of the vehicle and is designed to direct the exhaust gases away from the vehicle’s body. Some vehicles may have dual tailpipes, which provide a sportier appearance and can further enhance exhaust flow and performance.
In summary, the 2008 Dodge Dakota exhaust system is a complex system that includes the exhaust manifold, catalytic converter, muffler, and tailpipe. Each component plays a crucial role in improving engine performance, reducing emissions, and minimizing noise. Proper maintenance and regular inspection of the exhaust system is essential to ensure optimal performance and compliance with emission regulations.
Common Issues with the 2008 Dodge Dakota Exhaust System
The 2008 Dodge Dakota is a reliable and capable truck, but like any vehicle, it can develop issues over time. One area that can experience problems is the exhaust system. Here are some common issues that owners may encounter:
- Exhaust Leaks: One of the most common problems with the 2008 Dodge Dakota’s exhaust system is leaks. These can occur at various points along the exhaust system, including the manifold gasket, flange connections, and welds. Leaks can result in loud exhaust noises, reduced engine performance, and increased emissions. It’s important to have any leaks repaired promptly to prevent further damage.
- Rust and Corrosion: Over time, the exhaust system of the 2008 Dodge Dakota can develop rust and corrosion. This is especially true in areas where road salt is used during the winter months. Rust and corrosion can weaken the exhaust components, leading to leaks and potential failure. Inspecting the exhaust system regularly and addressing any signs of rust or corrosion is essential for maintaining its longevity.
- Broken Hangers: The hangers that support the exhaust system can break or become loose over time. This can result in the exhaust system hanging lower than it should or coming into contact with other components, causing rattling noises and potential damage. Replacing broken hangers is a relatively simple fix that can prevent further issues.
- Catalytic Converter Failure: The catalytic converter is an important component of the exhaust system that helps reduce harmful emissions. In some cases, the catalytic converter in the 2008 Dodge Dakota may fail prematurely. Signs of catalytic converter failure can include decreased engine performance, increased fuel consumption, and a rotten egg smell from the exhaust. A professional inspection is necessary to diagnose and replace a faulty catalytic converter.
- Exhaust System Misalignment: In some instances, the exhaust system on the 2008 Dodge Dakota may become misaligned. This can be due to a variety of factors, including loose or broken mounts, accidents, or improper installation. A misaligned exhaust system can cause rattling noises, excessive vibration, and potential damage to other components. Addressing any misalignment issues promptly is crucial to prevent further complications.
In conclusion, while the 2008 Dodge Dakota is a reliable truck, its exhaust system can develop common issues over time. These can include exhaust leaks, rust and corrosion, broken hangers, catalytic converter failure, and exhaust system misalignment. Regular maintenance and prompt repairs are key to ensuring the longevity and performance of the exhaust system in the 2008 Dodge Dakota.
Q&A:
What are some common issues with the 2008 Dodge Dakota exhaust system?
Some common issues with the 2008 Dodge Dakota exhaust system include rust and corrosion, leaks, and a loud or unusual noise coming from the exhaust system.
How can I determine if there is a leak in my 2008 Dodge Dakota exhaust system?
You can determine if there is a leak in your 2008 Dodge Dakota exhaust system by checking for any visible signs of leaking or holes in the pipes, hearing a hissing sound coming from the exhaust, or smelling exhaust fumes inside the vehicle.
What are the potential causes of a loud or unusual noise from the 2008 Dodge Dakota exhaust system?
The potential causes of a loud or unusual noise from the 2008 Dodge Dakota exhaust system include a damaged or loose muffler, a cracked or leaking exhaust manifold, or a faulty catalytic converter.
How can I prevent rust and corrosion in the 2008 Dodge Dakota exhaust system?
You can prevent rust and corrosion in the 2008 Dodge Dakota exhaust system by regularly inspecting and maintaining the system, avoiding driving in harsh conditions, such as salty or wet roads, and using rust-resistant coatings or paints on the exhaust system components.