For efficient troubleshooting, it’s crucial to know the exact location and function of each component in the vehicle’s power distribution setup. Start by locating the primary junction area, typically situated under the hood and inside the cabin. Familiarize yourself with the specific arrangement of electrical connections to avoid errors when replacing or inspecting individual relays or circuits.
Each part in the assembly serves a distinct role, from managing power to the lights to controlling the engine’s ignition system. Pay close attention to the labeling, which helps identify the precise positions of the fuses, ensuring that you don’t mistakenly replace a non-faulty one or overload a particular circuit.
Key Tip: Always check the owner’s manual or a reliable repair guide to ensure accuracy when interpreting the layout. Misunderstanding the wiring setup can lead to short circuits or malfunctions. Additionally, it’s recommended to use the right amperage when replacing a blown fuse to prevent further electrical issues.
Lastly, for any electrical work, always ensure that the power is turned off before you begin inspecting or handling any components to avoid electric shock or unintentional damage.
Electrical System Layout and Components for 2008 Pickup Truck
Start by identifying the main electrical distribution panels located within the cabin and engine area. These control circuits powering vital systems like lights, air conditioning, and engine functions. It’s crucial to be familiar with the placement and labeling of each terminal to quickly address any malfunction or fuse replacement.
Below is an overview of key components and their locations:
- Interior Panel: Located on the driver’s side, typically near the footwell or beneath the dashboard. This unit governs interior accessories, dashboard instruments, and safety features like airbags.
- Engine Compartment Unit: Positioned near the battery, this assembly manages power distribution to the engine, alternator, and external lighting systems.
If a system isn’t functioning as expected, check these elements in the following order:
- Examine the main control units in both areas.
- Ensure the terminals are secure and free of corrosion.
- Consult the panel label for identification of faulty circuits.
- Replace any malfunctioning components with exact replacements to avoid further electrical issues.
Common problems can often be resolved by replacing blown circuits in the appropriate panel. Always ensure that replacements match the required amperage rating to prevent electrical damage.
To enhance the vehicle’s electrical system’s reliability, consider regularly inspecting the components for wear or dirt buildup and cleaning terminals to maintain optimal performance.
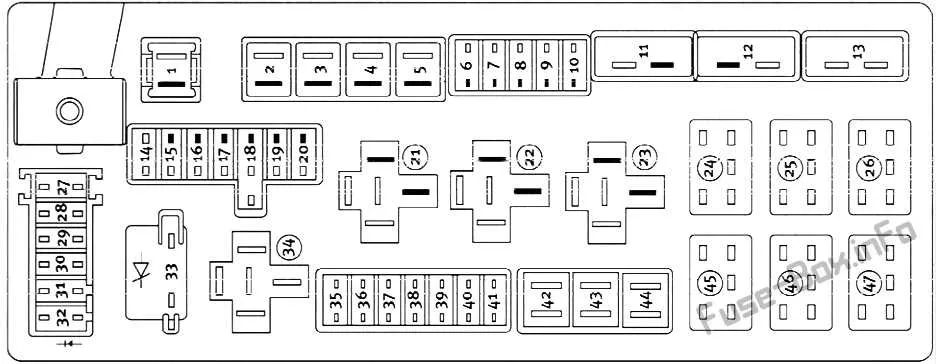
Locating the Electrical Panel in a 2008 Pickup
The primary electrical panel can be found inside the cabin, to the left of the steering wheel, near the driver’s side dashboard. To access it, open the driver-side door and look for a panel cover just beneath the instrument cluster. It may be necessary to remove a plastic cover by pulling it off gently.
Additionally, there is another panel located in the engine compartment. Open the hood and locate the panel on the driver’s side near the fender. It is usually secured with clips or bolts that must be undone before you can open it. This panel houses fuses for critical engine components and electrical systems.
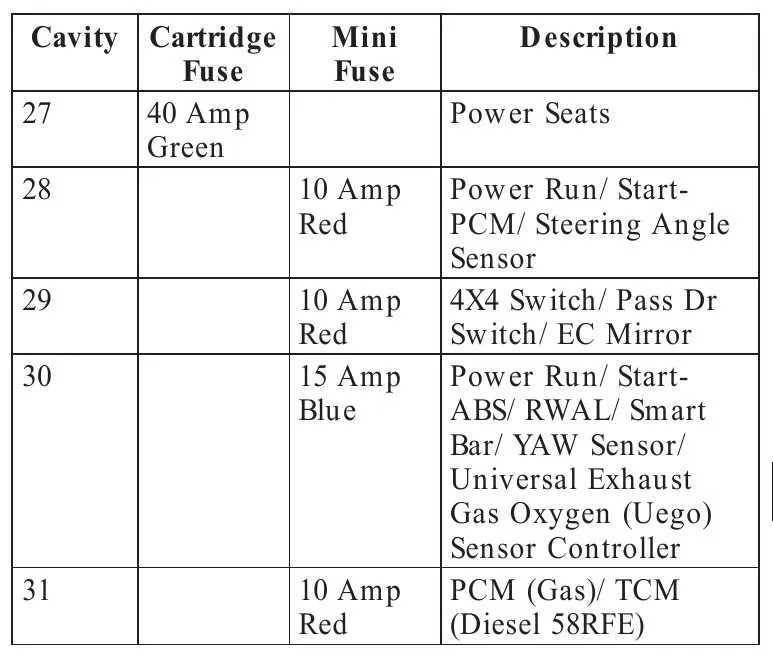
Understanding the Fuse Layout for Electrical Components
Identify the exact location of each electrical component in your vehicle before starting any maintenance. Refer to the component identification chart to match each part with the corresponding protection unit. For instance, ignition circuits, lights, and climate control systems typically have distinct units assigned for quick troubleshooting. It’s essential to double-check if the protection units are rated correctly for the system’s voltage to avoid potential overloads.
In many vehicles, the components are organized into separate sections: engine-related systems, interior systems, and accessories. Ensure that the primary system handling engine management has a dedicated circuit, as it’s crucial for the vehicle’s performance. Secondary circuits, like the ones powering air conditioning or wipers, often have a lower amperage requirement. Understanding this distinction helps avoid confusion during repairs.
Be aware that some protection devices might serve multiple components simultaneously, so tracing the wire connections is key to locating the correct unit. If there’s any malfunction, the most probable issue is often a blown unit; however, consider inspecting the connections for signs of corrosion or wear, which could contribute to malfunctioning as well.
When replacing protection units, always ensure that the replacement matches the manufacturer’s specifications. A wrong part could cause further electrical issues or even permanent damage to the vehicle’s components. Make sure to test each function after replacement to confirm that everything operates as intended.
Replacing Fuses and Troubleshooting Common Issues
If a circuit fails to work, inspect the related protection component first. Ensure the power is off before replacing any protective link. Check the metal strip inside the unit for a break, which signifies the need for a replacement. Choose a replacement that matches the exact amperage to avoid damaging the electrical system.
Common issues include malfunctioning lights, non-working accessories, or dead electrical components. These problems often stem from a blown link due to overloading or electrical spikes. If replacing the protective element doesn’t resolve the issue, check for signs of a short circuit or faulty wiring that might be contributing to the recurring problem.
Use a multimeter to check the continuity of the component. If the new protection does not work, it may indicate an underlying problem like an incorrectly wired circuit or a malfunctioning relay. For persistent issues, consult the vehicle’s electrical schematics for further diagnostics.