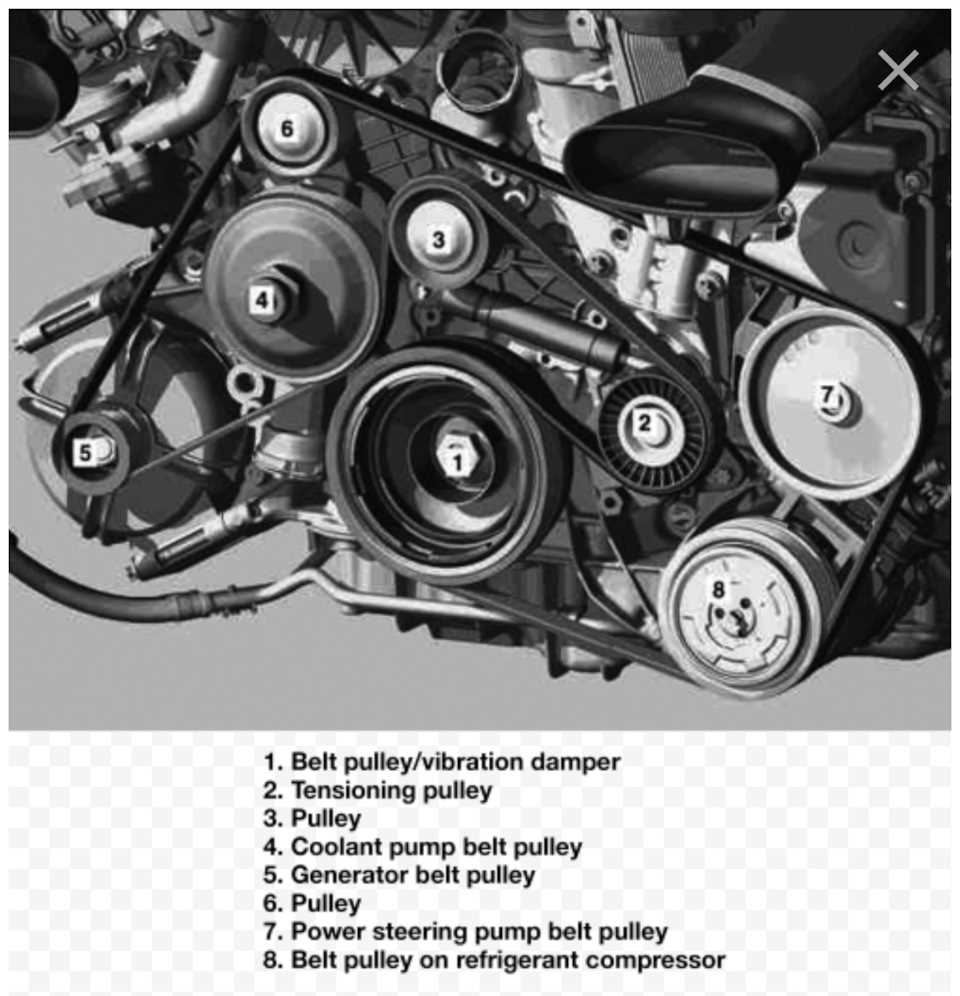
If you’re a proud owner of a 2008 Mercedes E350, then understanding the layout and functionality of its belt diagram is crucial for proper maintenance and troubleshooting. The belt diagram, also known as the serpentine belt diagram, illustrates the path that the belt follows around various engine components, ensuring that everything works together smoothly.
The belt in the 2008 Mercedes E350 is responsible for driving important engine accessories such as the alternator, power steering pump, and air conditioning compressor. Without a properly functioning belt, these components wouldn’t be able to operate effectively, leading to potential issues with your vehicle’s performance.
By referring to the belt diagram, you can easily identify the correct route and tension for the belt, ensuring that it is installed correctly. This helps prevent belt slippage, excessive wear, and potential damage to other engine components. Additionally, a properly installed belt can help improve fuel efficiency and reduce the risk of breakdowns or malfunctions.
In this article, we will provide you with a comprehensive guide to the 2008 Mercedes E350 belt diagram. We will explain the functions of various engine components, discuss common issues related to the belt system, and offer tips for proper maintenance. Whether you’re a DIY enthusiast or a professional mechanic, this guide will equip you with the knowledge you need to keep your 2008 Mercedes E350 running smoothly.
Overview of the 2008 Mercedes E350
The 2008 Mercedes E350 is a luxury sedan that offers a combination of style, performance, and comfort. It is part of the Mercedes E-Class lineup, known for its refinement and elegance. The E350 is equipped with a powerful V6 engine that delivers smooth acceleration and impressive fuel efficiency.
One of the standout features of the 2008 Mercedes E350 is its sleek and timeless design. The exterior is characterized by clean lines, a bold front grille, and elegant headlights. Inside, the cabin is well-appointed with high-quality materials, comfortable seats, and advanced technology. The E350 offers a spacious and luxurious driving experience, making it ideal for long journeys or everyday commutes.
Under the hood, the 2008 Mercedes E350 is powered by a 3.5-liter V6 engine that produces 268 horsepower. It is mated to a seven-speed automatic transmission, providing smooth and responsive gear shifts. The E350 also offers good fuel economy, with an estimated 17 mpg in the city and 24 mpg on the highway.
In terms of safety, the 2008 Mercedes E350 comes equipped with a range of advanced features. These include antilock brakes, stability control, front and side airbags, and a tire pressure monitoring system. The E350 also features Mercedes’ Pre-Safe system, which prepares the car for a possible collision by tightening seat belts and adjusting the front seats.
Overall, the 2008 Mercedes E350 is a luxury sedan that delivers a combination of performance, comfort, and style. Whether you’re looking for a car for daily commuting or long road trips, the E350 offers a luxurious driving experience with its refined design and advanced features.
Mercedes E350 Belt Diagram
When it comes to maintaining and servicing a Mercedes E350, understanding the belt diagram is essential. The belt diagram shows the routing and configuration of the belts that drive various components of the car’s engine. This diagram is crucial for properly installing and tensioning the belts in order to avoid damage to the engine and ensure optimal performance.
The Mercedes E350 has multiple belts that power different components such as the alternator, power steering pump, air conditioning compressor, and water pump. Each belt has a specific path it follows, indicated by the belt diagram. It is important to consult the correct belt diagram for your specific year and model of Mercedes E350 to ensure accuracy.
Here is a general overview of the belt routing for a 2008 Mercedes E350:
- Belt 1: This belt drives the alternator and water pump.
- Belt 2: This belt drives the power steering pump, air conditioning compressor, and water pump.
- Belt 3: This belt drives the accessories, such as the air conditioning compressor and power steering pump.
Properly installing and tensioning the belts is crucial for the longevity and performance of the Mercedes E350. It is recommended to consult the vehicle’s manual or a professional mechanic for specific instructions and torque specifications for the belt tensioner and pulleys.
In conclusion, the Mercedes E350 belt diagram is a useful tool for understanding the routing and configuration of the belts that power various components of the engine. Following the correct belt diagram and properly installing and tensioning the belts is crucial for the optimal performance and longevity of the vehicle.
Understanding the Belt System in the 2008 Mercedes E350
The belt system in the 2008 Mercedes E350 is a vital component of the vehicle’s engine, responsible for transferring power and driving various auxiliary components. It consists of multiple belts, each serving a specific purpose in the operation of the vehicle. Understanding how the belt system works is essential for proper maintenance and troubleshooting. This article will provide an overview of the belt system in the 2008 Mercedes E350.
The 2008 Mercedes E350 belt system includes the serpentine belt, also known as the drive belt, and the accessory belts. The serpentine belt drives the engine’s main components, such as the alternator, power steering pump, and air conditioning compressor. The accessory belts, on the other hand, are responsible for operating additional components like the water pump, air pump, and fan. Each belt is specially designed to withstand the demands of its corresponding component and ensure efficient functionality.
The serpentine belt in the 2008 Mercedes E350 follows a specific routing pattern, guided by a belt diagram located on the engine cover or in the owner’s manual. It is important to refer to this diagram when replacing the belt or performing any maintenance on the engine. Incorrect belt routing can cause serious damage to the engine and other components. Additionally, regular inspection of the belts for signs of wear, cracks, or fraying is crucial to ensure their integrity and prevent sudden belt failure.
Proper tensioning of the belts is also essential for their optimal performance. The tension is typically adjusted automatically by the belt tensioner, a component that maintains the correct tension by keeping the belt tight. However, over time, the belt tensioner may lose its effectiveness, leading to belt slippage or noise. In such cases, the belt tensioner may need to be replaced to ensure proper functionality of the belt system.
- To summarize, the belt system in the 2008 Mercedes E350 is a crucial aspect of the vehicle’s engine functionality.
- It consists of various belts, including the serpentine belt and accessory belts, each serving a specific function.
- Proper maintenance, including regular inspection and correct tensioning, is necessary to ensure the longevity and efficient operation of the belt system.
- Following the belt diagram and referring to the owner’s manual are essential steps when working with the belt system in the 2008 Mercedes E350.
Identifying the Belts in the Engine

When it comes to understanding the layout of a car engine, identifying the belts is an important step. The belts in an engine play a crucial role in powering various components and ensuring their smooth operation. In the case of a 2008 Mercedes E350, there are several belts that need to be identified and properly maintained.
Main drive belt: The main drive belt in the engine of a 2008 Mercedes E350 is responsible for driving the alternator, power steering pump, and air conditioning compressor. It is typically a serpentine belt that wraps around various pulleys, transferring power from the crankshaft to these components. This belt is crucial for maintaining the electrical and cooling systems of the vehicle.
Accessory belt: Another important belt in the engine is the accessory belt. This belt powers additional components such as the water pump, air injection pump, and air compressor. It is typically a V-belt that connects the crankshaft pulley to the pulleys of these components. The accessory belt is essential for the proper functioning of the engine’s cooling and air conditioning systems.
Timing belt: The timing belt in a 2008 Mercedes E350 is responsible for synchronizing the movement of the engine’s camshafts and crankshaft. It ensures that the valves open and close at the right time, allowing for efficient combustion. The timing belt is crucial for the overall performance and longevity of the engine.
Other belts that may be present in the engine of a 2008 Mercedes E350 include the fan belt, which powers the engine cooling fan, and the power steering belt, which powers the power steering pump. It is important to regularly inspect and replace these belts to prevent any potential issues and ensure the smooth operation of the engine.
Understanding and identifying these belts in the engine of a 2008 Mercedes E350 is essential for proper maintenance and troubleshooting. Regular inspections and replacements of worn or damaged belts can help prevent costly repairs and ensure the optimal performance of the vehicle.
Step-by-Step Guide to Replace the Belts
Replacing the belts on your 2008 Mercedes E350 is a relatively straightforward process that can be done with some basic tools and a little bit of patience. Follow this step-by-step guide to ensure a successful belt replacement:
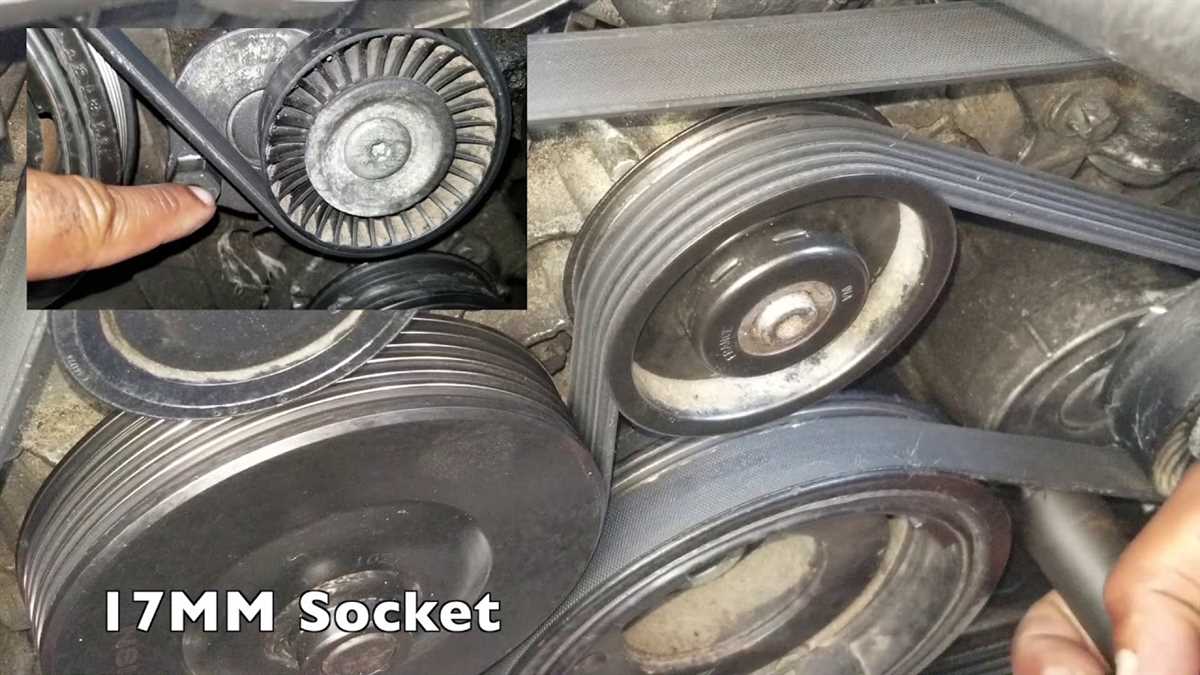
1. Gather the Necessary Tools and Materials
Before getting started, make sure you have all the tools and materials you will need. This includes a new belt, a belt tensioner tool, a socket set, a breaker bar, and a torque wrench. It’s also a good idea to have some gloves and safety glasses for protection.
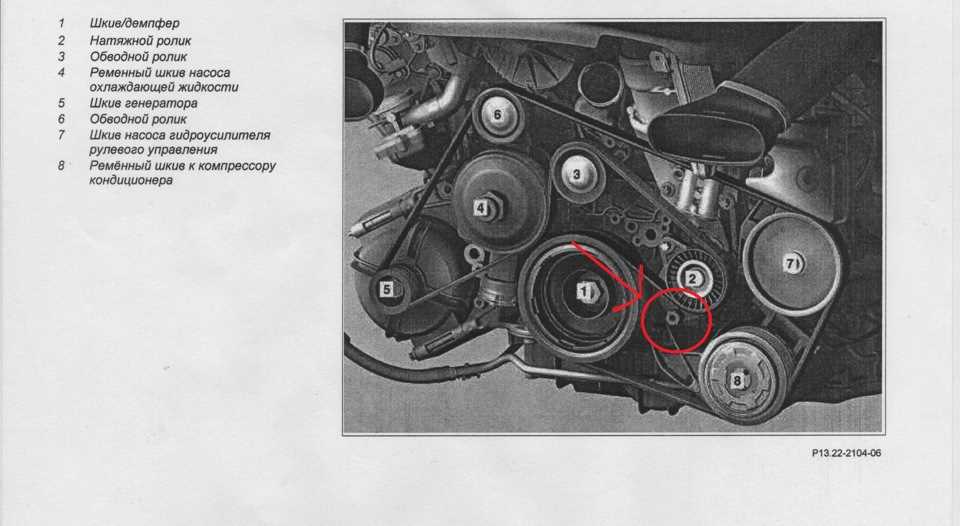
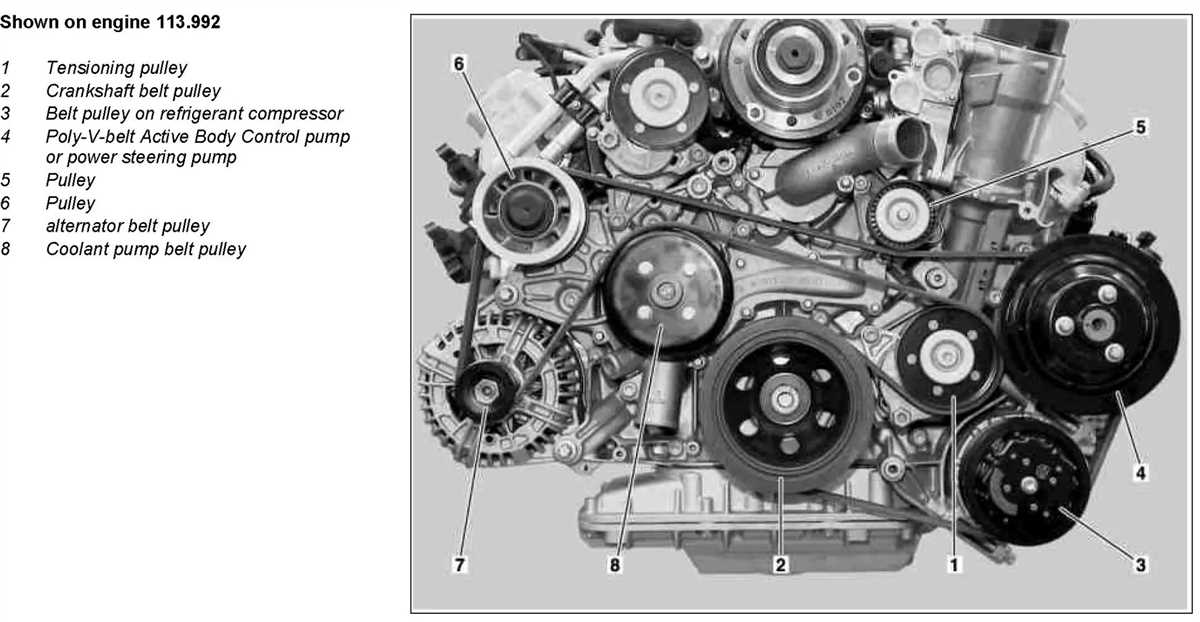
2. Locate the Belt Routing Diagram
Refer to the belt routing diagram located on the engine or in the owner’s manual. This diagram will show you how the belts are routed around the various pulleys in the engine compartment. Take a moment to familiarize yourself with the diagram before proceeding.
3. Loosen the Belt Tensioner
Using the belt tensioner tool, locate the belt tensioner and insert the tool into the appropriate slot. Apply pressure to release the tension on the belt and slide it off the pulleys. Be careful not to let go of the tool too quickly, as the tensioner can snap back and cause injury.
4. Remove the Old Belt
Once the tension is released, carefully remove the old belt from the pulleys. Take note of how the belt is routed around each pulley to ensure proper installation of the new belt later on. Inspect the old belt for any signs of damage or wear and replace it if necessary.
5. Install the New Belt
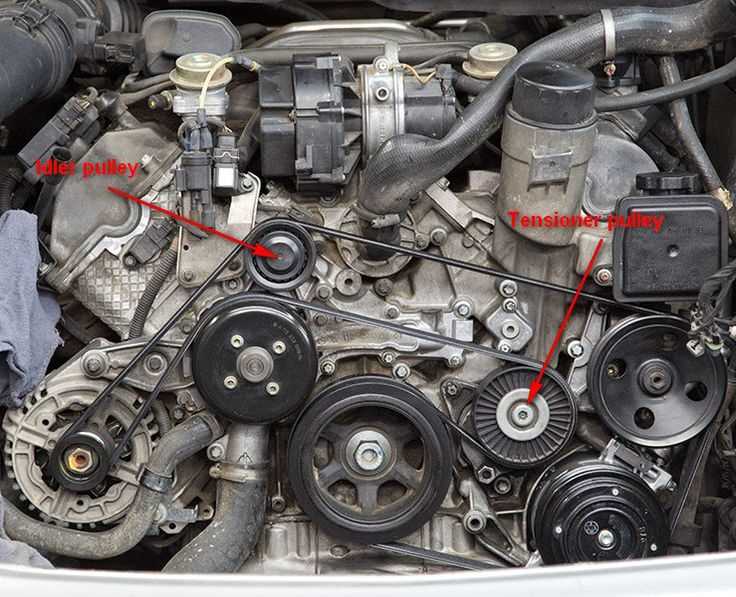
Using the belt routing diagram as a guide, route the new belt around the pulleys in the same pattern as the old belt. Begin by sliding the new belt onto the most accessible pulley and gradually work your way around the engine compartment, ensuring that the belt is properly seated on each pulley.
6. Tighten the Belt Tensioner
Once the new belt is in place, use the belt tensioner tool again to apply pressure and tighten the belt. Check the tension of the belt by pressing down on it with your thumb – it should have about a half inch of deflection.
7. Double-Check Everything
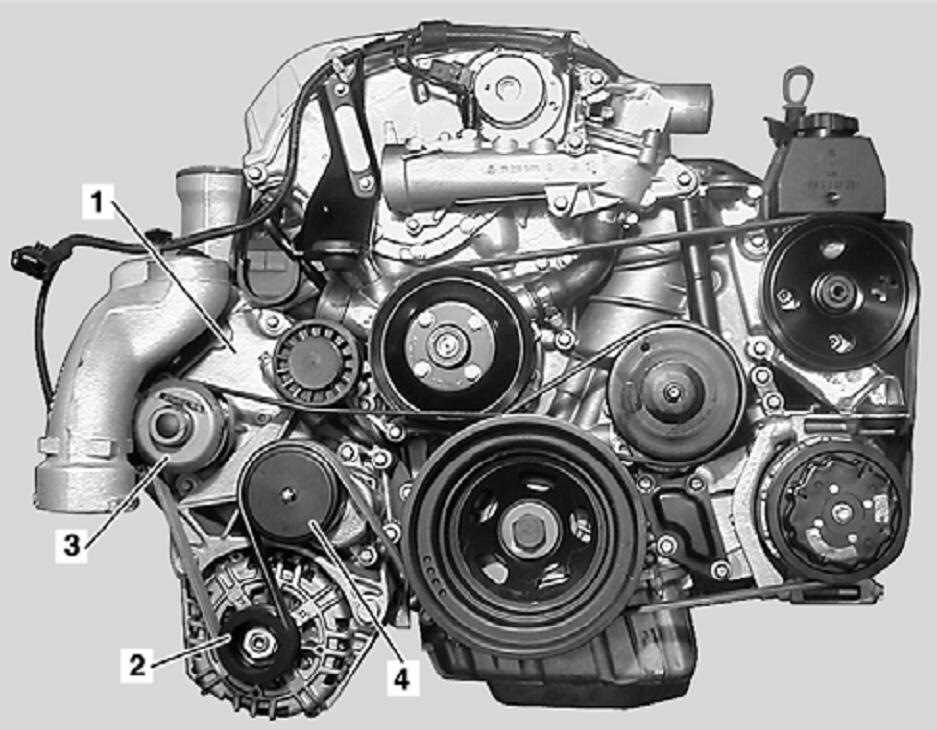
Before finishing up, double-check that the new belt is properly seated on all of the pulleys and that it is routed correctly according to the diagram. Make any necessary adjustments if needed.
8. Test the Belts
Start the engine and let it run for a few minutes to ensure that the new belts are functioning properly. Monitor for any unusual noises or vibrations, which could indicate an issue with the belt installation.
Congratulations! You have successfully replaced the belts on your 2008 Mercedes E350. Regularly inspect and replace belts as needed to keep your vehicle running smoothly and prevent any potential issues down the road.