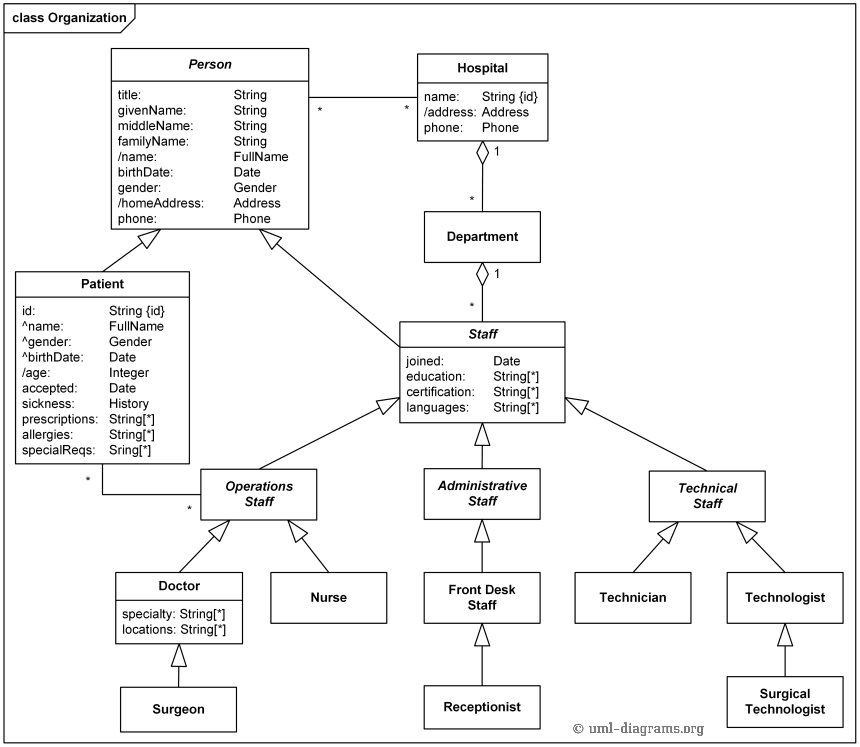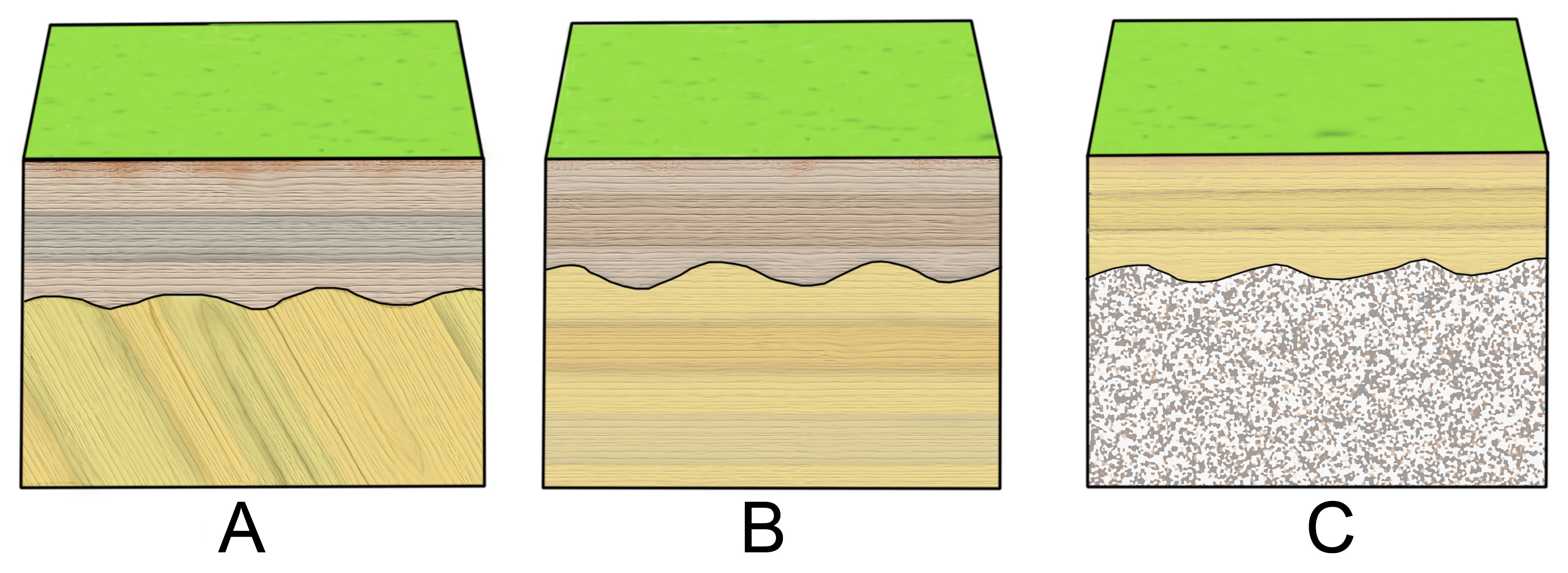
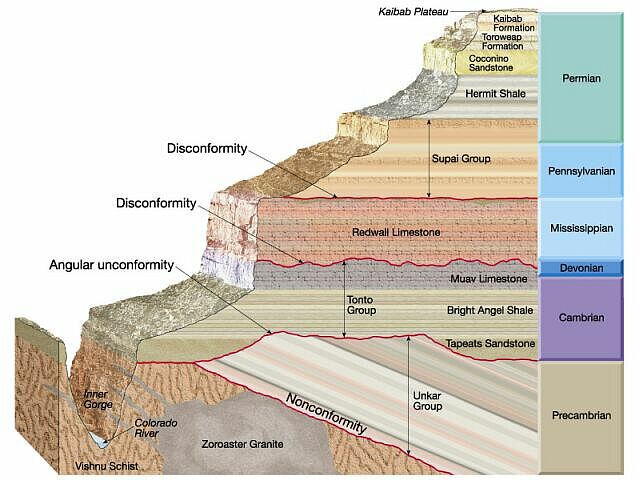
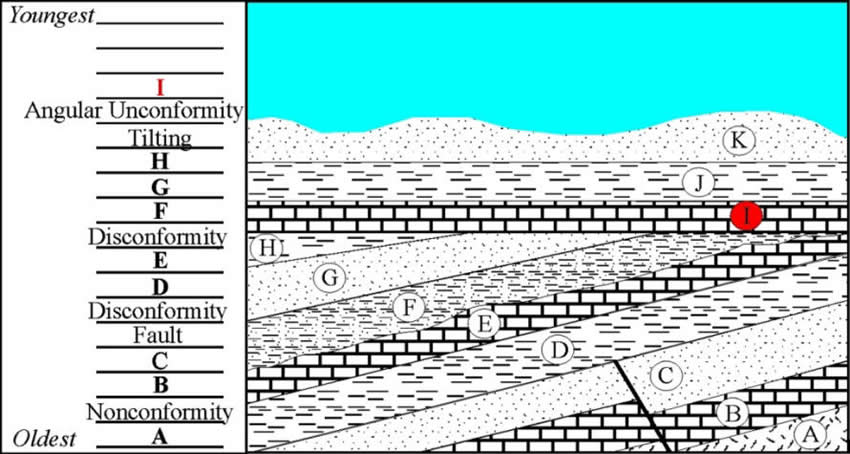
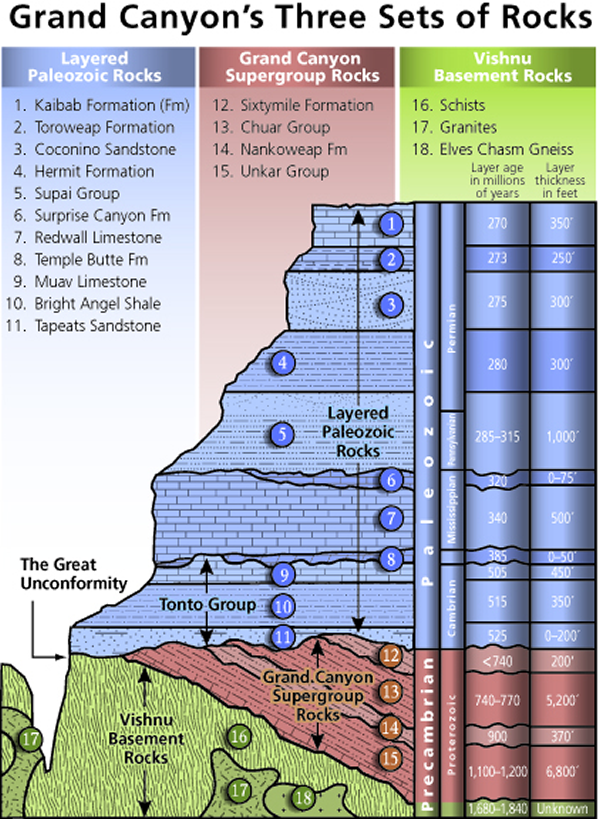
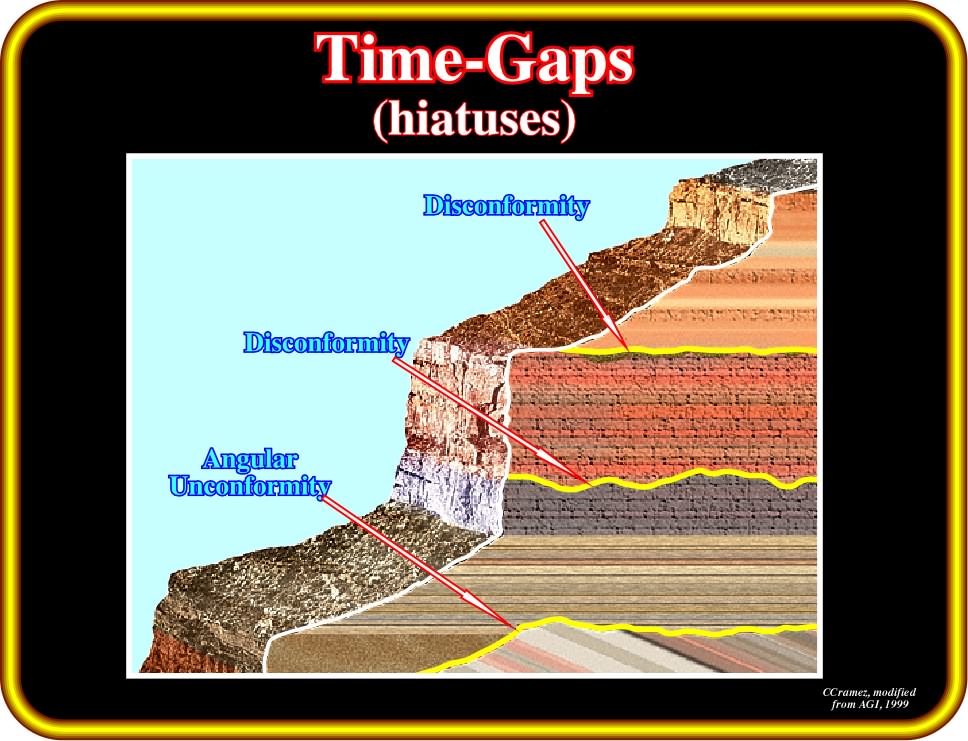
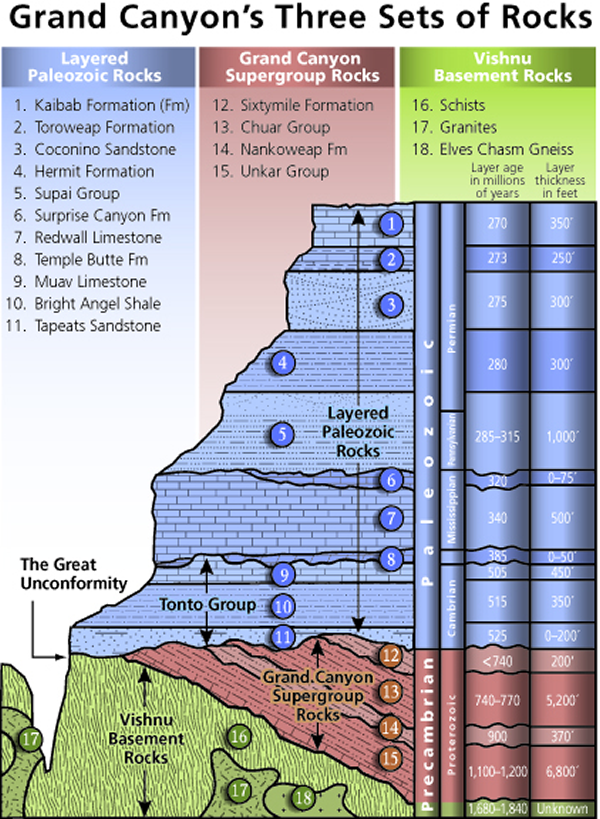
Diagrams and photos of different unconformity types. UNCONFORMITIES, CROSS SECTIONS AND GEOLOGICAL MAP DESCRIPTIONS.
Topography Fig. 2. Block diagram of an angular unconformity UU’.
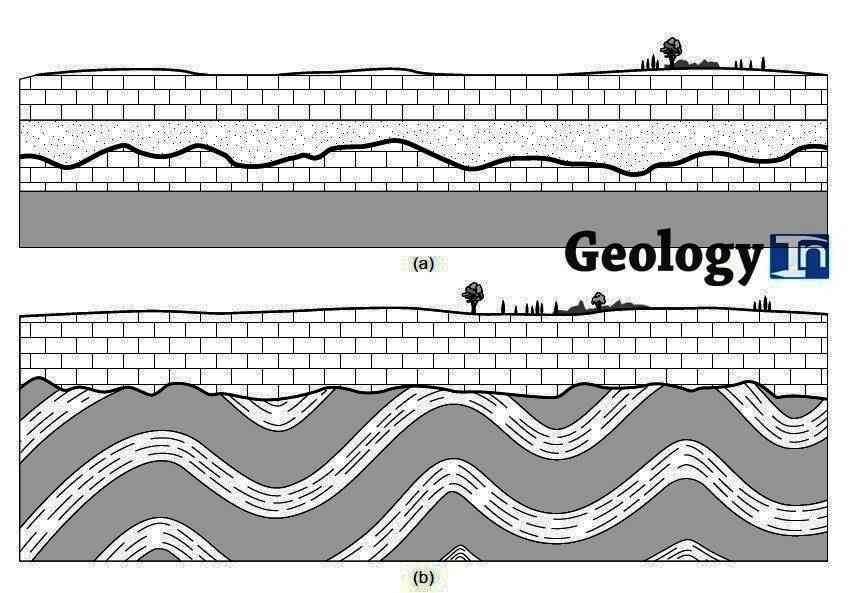
Fig. 3. Unconformities are gaps in the geologic record that may indicate episodes of In the diagram at left, the disconformity is indicated by an irregular black line.
How Do Unconformities Mark Missing Time? Web Links; Glossary Terms .
and the older, tilted strata beneath. angular unconformity diagram.
An unconformity is a buried erosional or non-depositional surface separating two rock masses or strata of different ages, indicating that sediment deposition was.Disconformity At a disconformity, beds of the rock sequence above and below the unconformity are parallel to one another, but there is a measurable age difference between the two sequences. The disconformity surface represents a period of nondeposition and/or erosion (Figure 1.
a). A) disconformity.
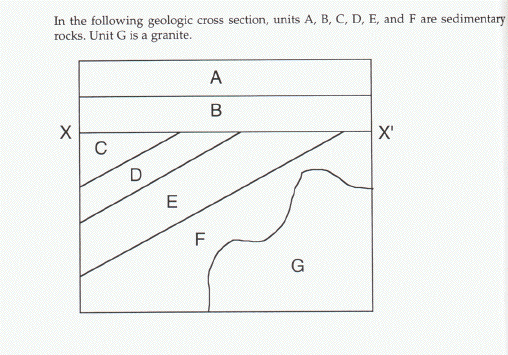
B) A) disconformity. B) nonconformity.
C) angular unconformity. D) a conformable depositional contact. In the block diagram below, the contact between rock unit 4 and the underlying rock unit 3 is an example of a(n) A) disconformity.
A type of unconformity in which layered sedimentary rocks lie a type of unconformity in which the sedimentary layers above a A cross-section diagram of a sequence of strata summarizing in. A disconformity is an unconformity between parallel layers of sedimentary rocks which represents a period of erosion or non-deposition. Disconformities are marked by features of subaerial erosion.
This type of erosion can leave channels and paleosols in the rock record. In the diagram at left, the disconformity is indicated by an irregular black line between the 3rd and 4th rock unit from the bottom. This picture shows a disconformity in Capitol Reef National Park, Utah.Unconformity – WikipediaUnconformity – Wikipedia