the σ bonds. I’ve drawn the overlaps below in the MO diagrams.
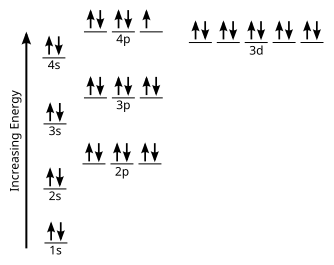
Each bromine would donate one 4pz electron to form a σ -bonding orbital. Orbital-Filling Diagram for Bromine.

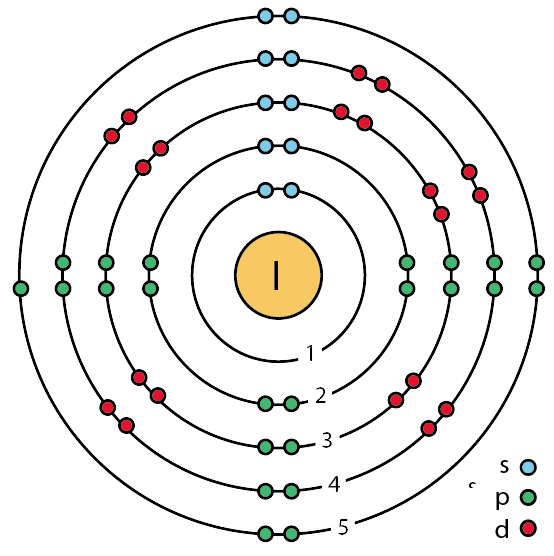
Bromine has 35 electrons, so it will have 35 arrows placed in its orbital-filling diagram as in figure The order bottom to top . Oxidation States, ±1,+5.

Electrons Per Shell, 2 8 18 7. Electron Configuration, [ Ar] 4s2 3d10 4p5.
1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d10 4p5. Orbital Diagram.
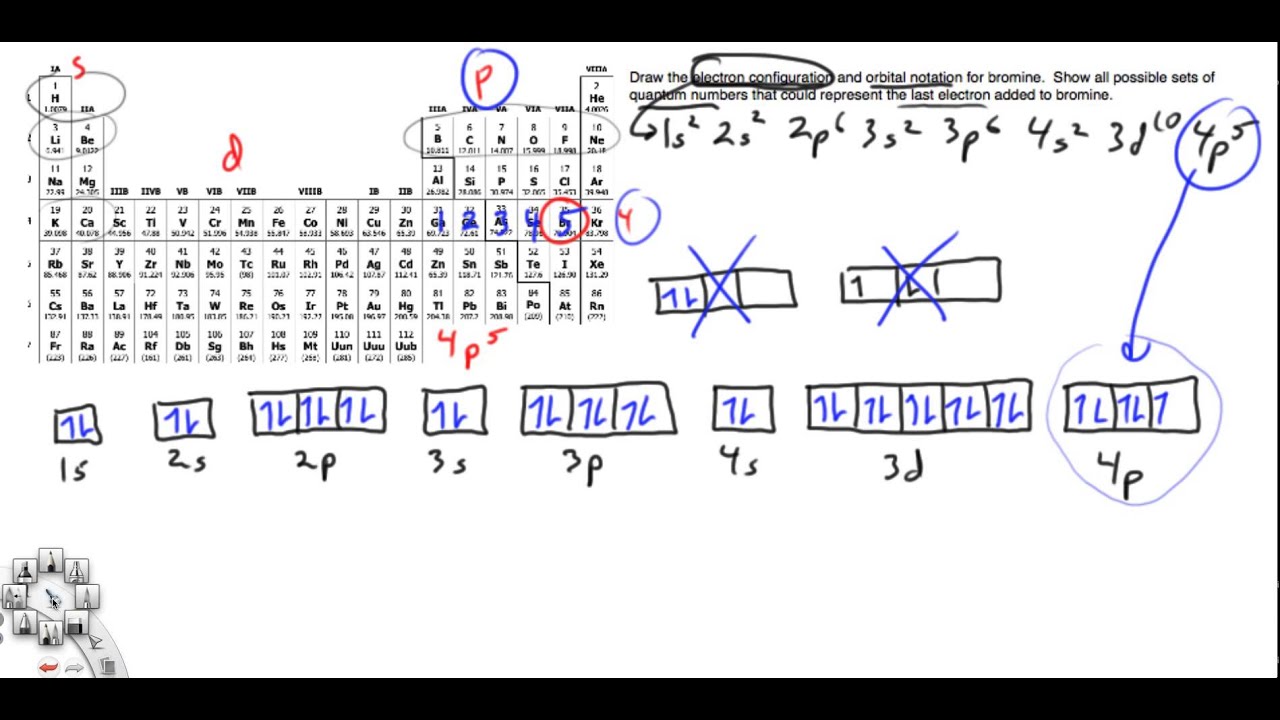
1s. ↿⇂. Explanation: All you need to do is work your way across the periodic table filling the orbitals as you go.
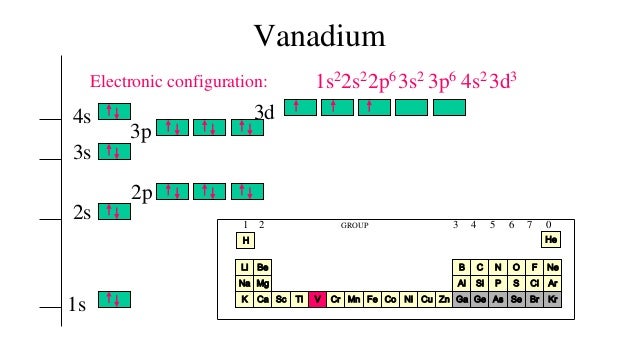
The full version of this is. Answer to Draw an orbital diagram for each element:(a) magnesium; (b) aluminum; (c) bromine.Answer to Write the electron configuration and give the orbital diagram of a bromine (Br) atom (Z = 35). A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) molecular orbital method in particular.
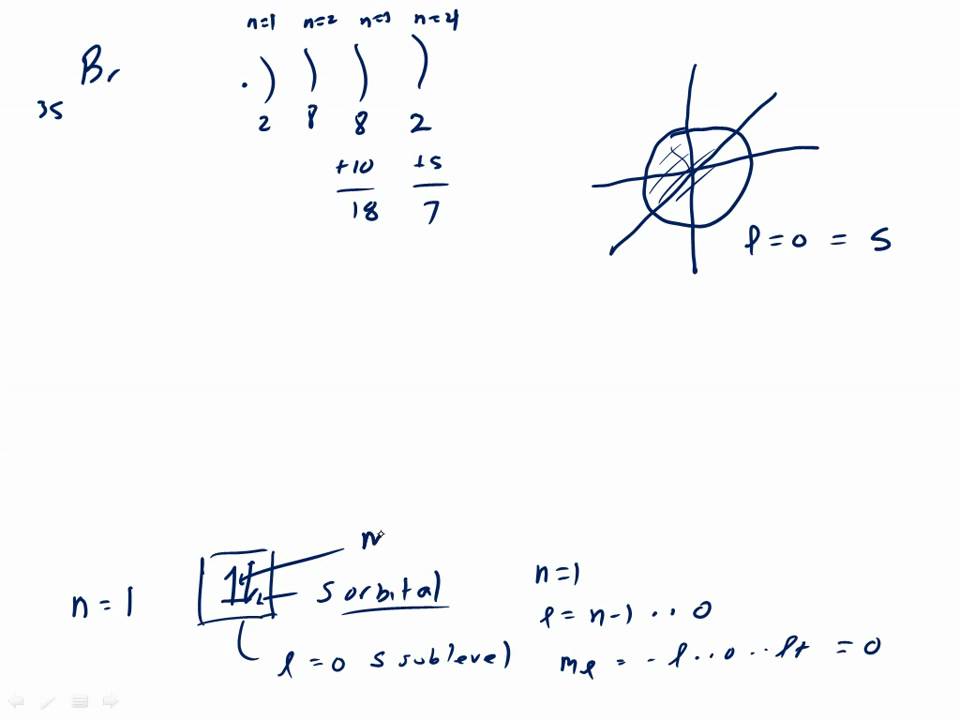
The orbital diagram for bromine shows four concentric circles around a dot representing a nucleus, with two dots on the first circle, eight on the second, 18 on the third and seven on the fourth. Each dot on a circle represents an electron.
Bromine (Br) has an atomic mass of Find out about its chemical and physical properties, states, energy, electrons, oxidation and more. 1.
Describe the two differences between a 2p x orbital and a 3p y orbital. The 2px orbital lies on the x-axis. The 3py orbital lies on the y-axis and is larger than the 2px orbital.
2. The lobes of a p orbital disappear at the nucleus.
What does this tell us about electrons in p orbitals?File:Electron configuration schematron.org – Wikimedia CommonsMolecular orbital diagram – Wikipedia