Introduction. The core eudicots are an extremely large, diverse assemblage of flowering plants, with an enormous range of variation in habit, morphology. Introduction.
The core eudicots are an extremely large, diverse assemblage of flowering plants, with an enormous range of variation in habit, morphology. *”Dicots” are now referred to as Eudicots, although the “dicot” features described below pertain to many non-monocot plants (e.g.
many magnoliids). 4 Describe the fundamental characteristics of a eudicot. 9 Compare and contrast the flowers of eudicots and monocots.
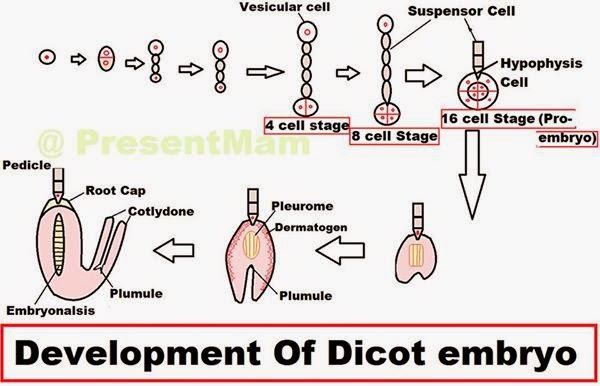
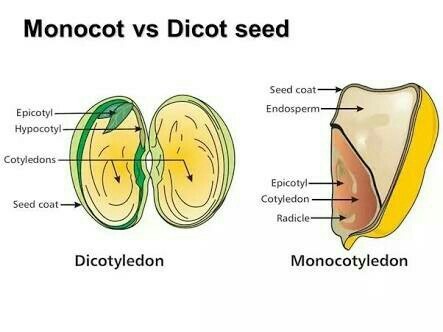
10 Label the diagram to the right. 1. The dicotyledons, also known as dicots are one of the two groups into which all the flowering The largest clade of the dicotyledons are known as the eudicots.

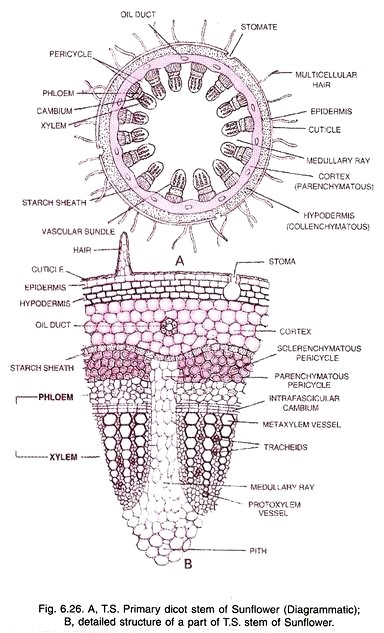
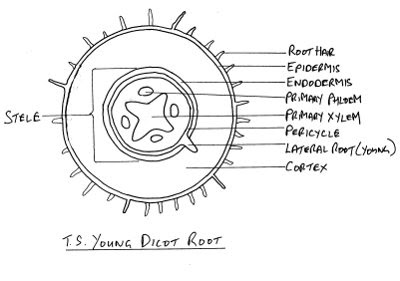
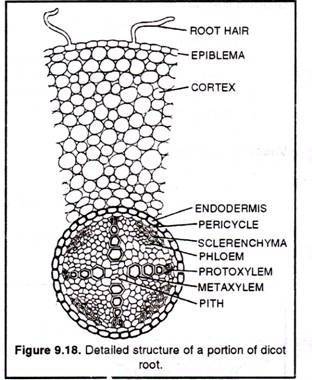
They are distinguished from all other flowering plants by the structure of their.Anatomy of Dicot root (gram) The structure of dicot root varies greatly from that of the monocots. By understanding the structure of dicot root and monocot root, we can make comparisons between them and distinguish them by studying them under a microscope.
Roots, Stems and Leaves Diagrams. External Root Structure.
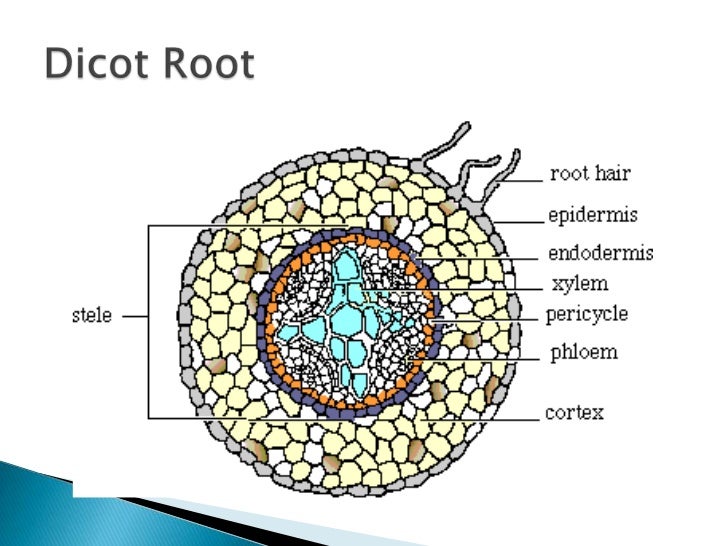
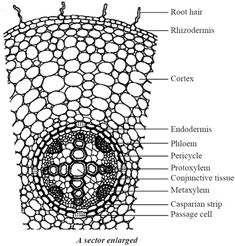
Monocot Root. Dicot Root.
External Structure of a Woody Stem. Monocot Stem.
Woody Dicot Stem. Monocot Leaf.
Dicot Leaf. Leaf Cross Section.
Plant Tissues. Monocot roots, interestingly, have their vascular bundles arranged in a ring.
Dicot roots have their xylem in the center of the root and phloem outside the xylem. A carrot is an example of a dicot root. Diagram illustrating the tissue layers and their organization within monocot and dicot roots.
A labeled monocot stem is a diagram that features the cross section of a monocot plant stem. In this diagram, the parts of the monocot stem are labeled and usually consist of the vascular bundle, the parenchyma, the cortex, the epidermis, the xylem, and the phloem.
The following points highlight the top four types of monocot and dicot stems. The types are: 1.
Normal Monocot Stems 2. Monocot Stem with Secondary Thickenings 3.Plant Structure IIMonocot and Dicot Roots (With Diagram) | Plants