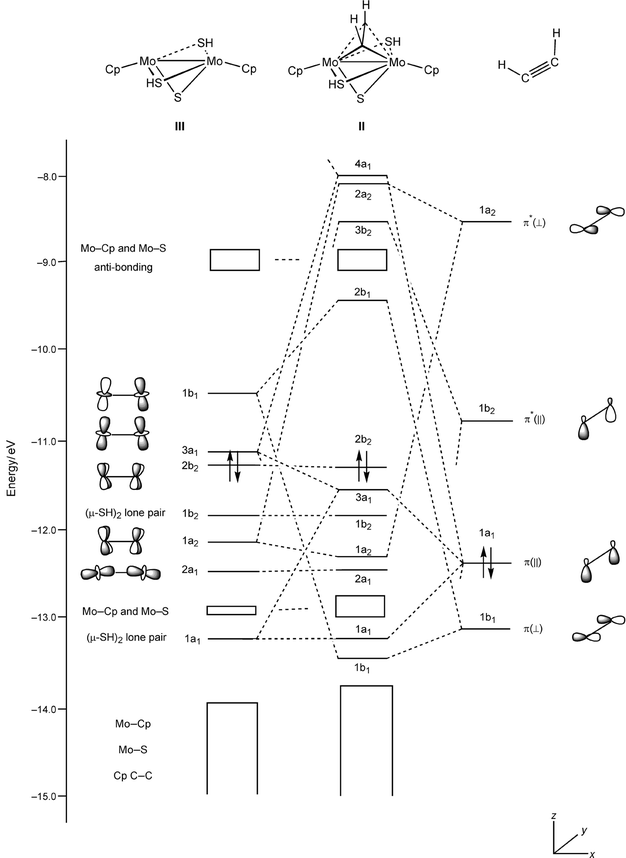
a complex MO diagram: B2H6 MO diagrams combine two fragments. Symmetry fragments . these are MOs from C2H4 which belongs to the D2h point group. Ethene C2H4 molecular orbitals.
Using MOLCAS I calculated the MO’s of ethene to see the sp2 hybridisation and to observe the pi and pi*. Loop Diagram.
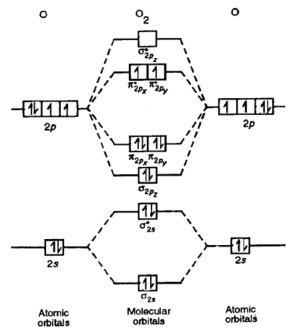
3dxy . Construct the molecular orbital diagram for dichlorine.
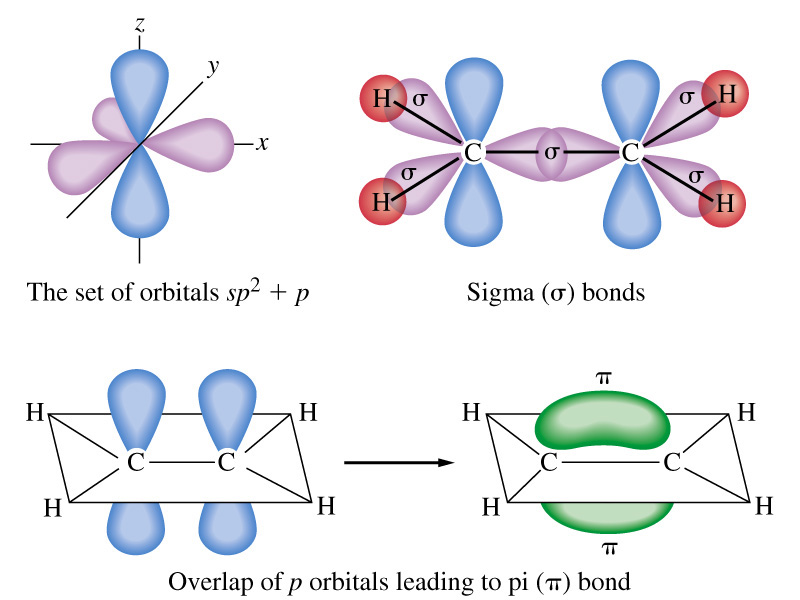
C2H4. Ethene from above the trigonal plane. The carbon atoms and orbitals are.

Many molecular orbital diagrams are not made up from atomic orbitals, but from fragment molecule (C2H4) is like the dxz AO and hence has b2g symmetry. Ethylene is the simplest molecule that has a double bond.
As we saw from the valence bond model, we should find the presence of a σ-bond framework, and a .where E is the energy of the molecular orbital. is the coefficient in the molecular orbital of the atomic wavefunction from the i-th atom. is the overlap integral between atoms i and j: (Note that the diagonal elements are equal to unity: since the atomic orbitals are normalised) and finally.
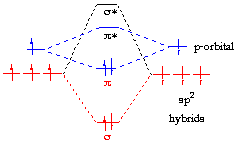
π Molecular Orbitals of Ethene. In chapter 1 we saw that the molecular orbitals of H 2 are created by the combination of 1s orbitals.; The in-phase combination gave the bonding orbital.
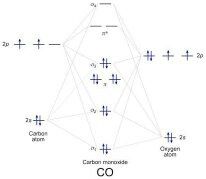
The out-of-phase combination the anti-bonding orbital. ORBITALS and MOLECULAR Construct the molecular orbital diagram for dichlorine.
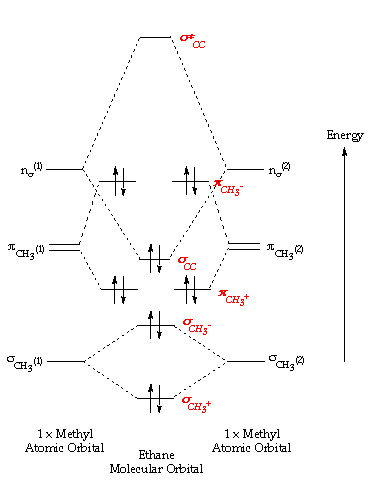
x y z z y 3 x y z z y 4 Showing the p orbitals. Showing the s and p orbitals. ORBITALS AND MOLECULAR REPRESENTATION CARBON ORBITALS Methane Ethane METHANE AND ETHANE C H H H H CH4 C C H H H H H H C2H6 1 2 Color conventions: Hydrogen atoms are shown in gray.
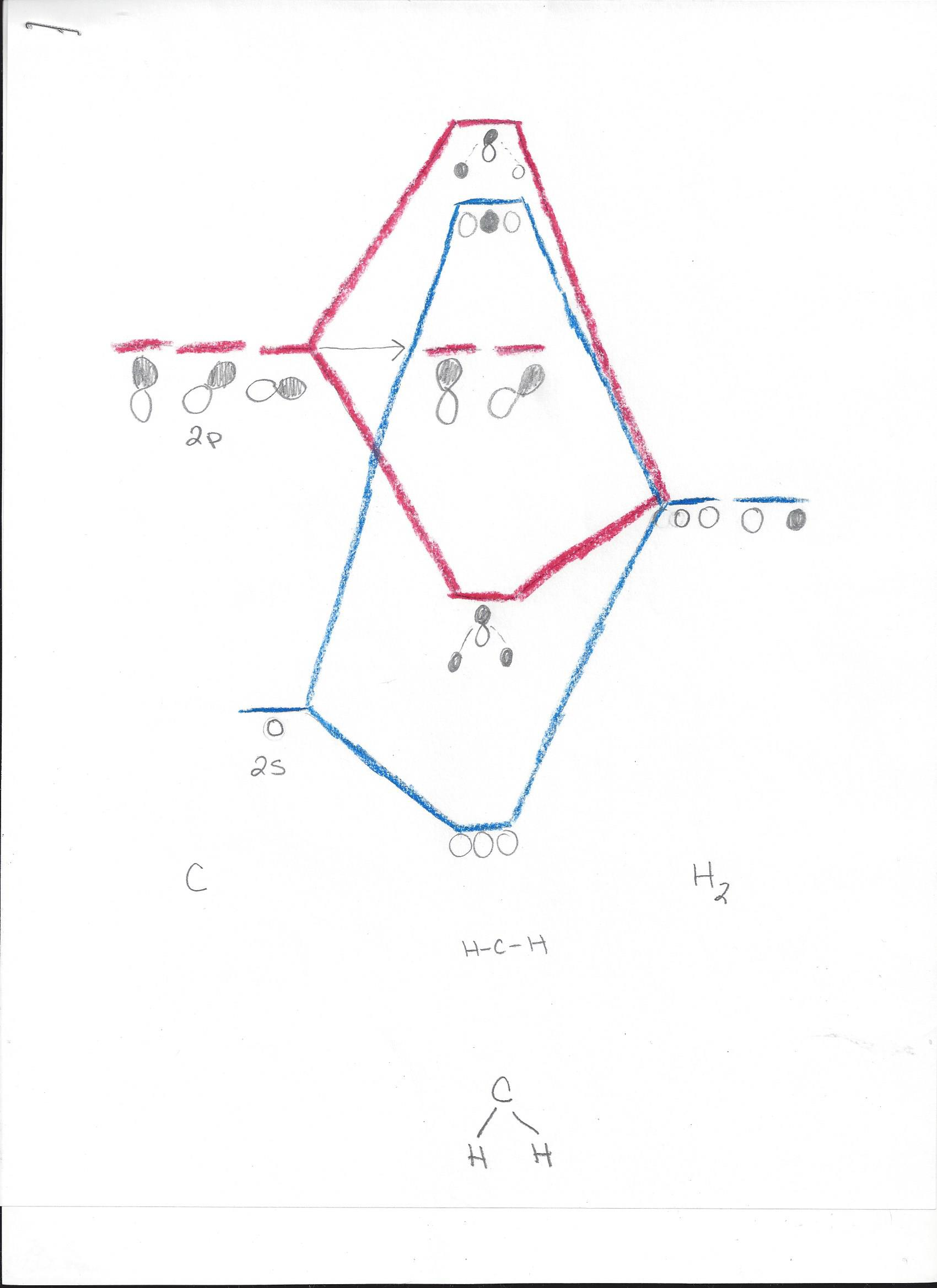
alternative bonding model, molecular orbital theory, which has solid empirical support. Molecular orbital theory (MOT) for methane forms bonding molecular orbitals involving linear combinations of the unhybridized carbon 2s and 2p valence orbitals with the hydrogen 1s orbitals as .
Bonding orbitals in Ethene (Ethylene) sp 2 Background: Use the buttons to display the sp 2 orbitals that make up the sigma framework and the remaining p orbitals which form the pi-bond.Contrasting MO and VB theory – Chemistry LibreTextsMolecular Orbitals: Ethene (Ethylene)