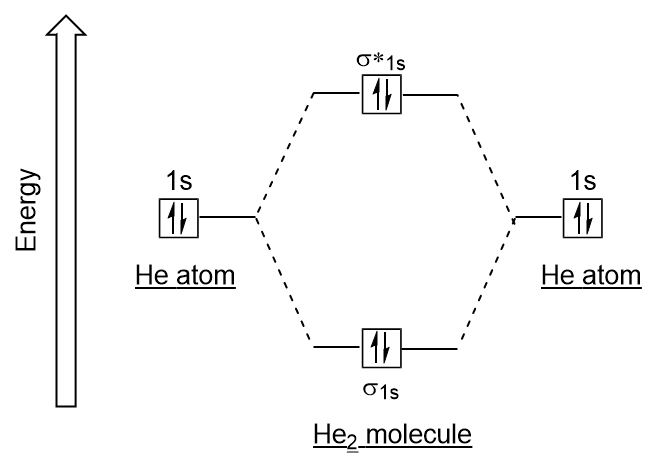
Molecular orbital theory of He2. confusingly showing for the energy diagram for He2 that the change in energy up to the anti-bonding orbital.
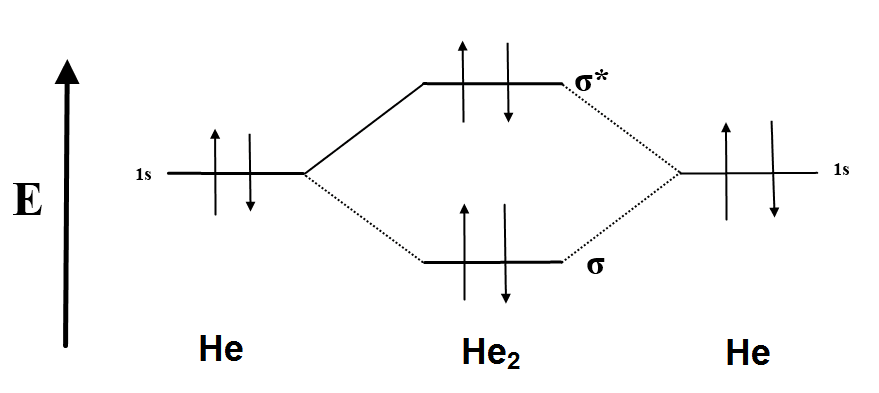
He2 is not possible. He MO Diagram.
Eg: He + H; same mixing as above. Three electrons, two in sigma, one in sigma*.
One more electron in. Atomic orbitals available for making Molecular Orbitals are 1s from each Helium.
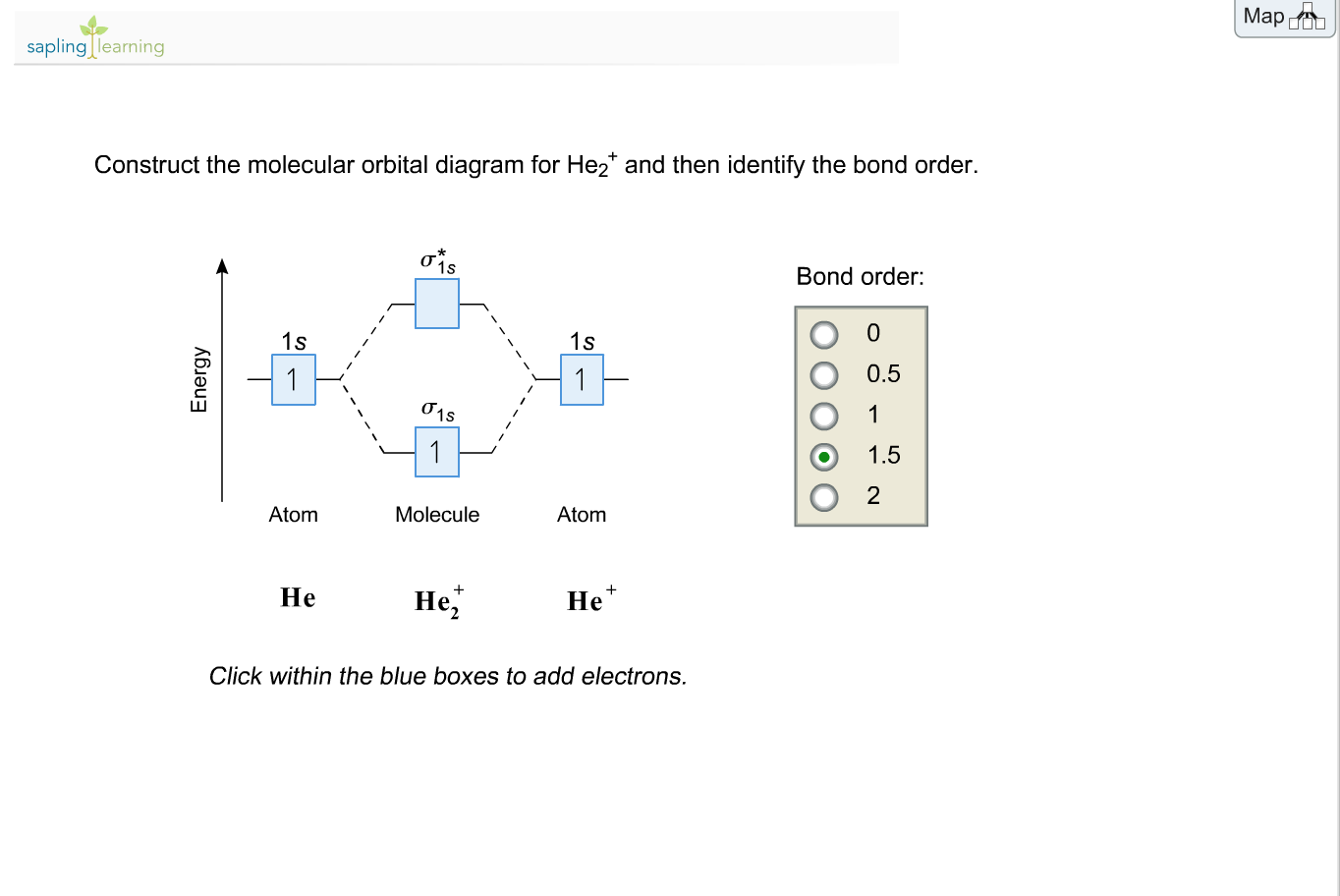
And total Since the bond order is zero so that He2 molecule does not exist. Chemical bonding – Molecular orbitals of H2 and He2: The procedure can be The molecular orbital energy-level diagram, which is a diagram that shows the.
The first ten molecular orbitals may be arranged in order of energy as follow: σ(1s ) ∗(1s) Molecular orbital of He2 molecule. Electronic.After a preliminary check with He2 and He2+, self‐consistent field calculations have been carried out for the nitrogen and carbon monoxide molecules and some of their positive ions for the range of internuclear distances from about times equilibrium down to bohr. The reason oh He2 Molecule to not exist can be explained on the basis of 1)MOLECULAR ORBITAL THEORY.
He has configuration of 1s2, if we draw its MOT DIAGRAM, 2 e’s enter the Bonding molecular Orbital and 2 e’s enter the AntiBonding molecular Orbital, thus net effect of the anti bonding and bonding is cancelled. The orbital correlation diagram in predicts the same thing–two electrons fill a single bonding molecular orbital.
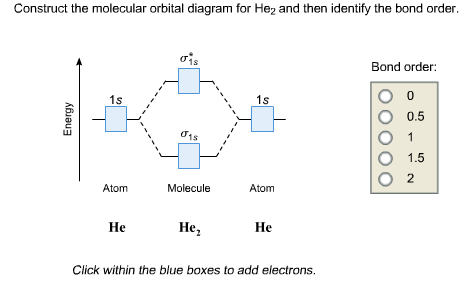
To further demonstrate the consistency of the Lewis structures with M.O. theory, we will formalize a definition of bond order–the number of bonds between atoms in a molecule. A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) molecular orbital method in particular.
The energy-level diagram for He2 is shown above, the two electrons in each of the 1s atomic orbital give total of 4 electrons in this molecule. Two are placed in the bonding orbital, the other two in antibonding orbital. The bond order = 1/2 x (Number of Bonding Electrons – Number of Antibonding Electrons) = .Molecular orbital theory of He2Molecular Orbital Theory