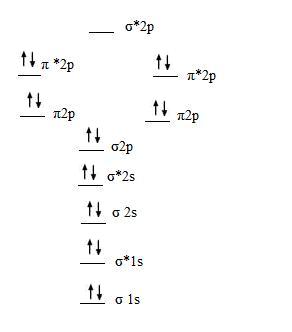
Molecular Orbital (MO) Theory helps us to explain and understand certain Part B – Molecular Orbital Energy Diagrams & Bond Order . + and Be2.
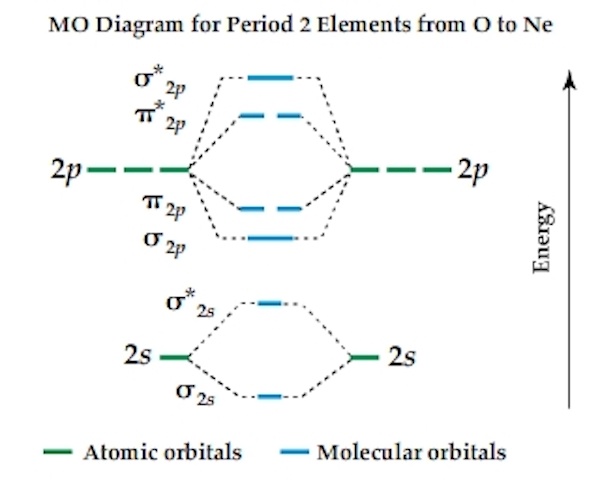
Even rather simple molecular orbital (MO) theory can be used to predict which we start reading from the bottom of the diagram because this is how MO diagrams are constructed, Diberyllium, Be2, has a bond order of zero and is unknown. Even rather simple molecular orbital (MO) theory can be used to predict which we start reading from the bottom of the diagram because this is how MO diagrams are constructed, Diberyllium, Be2, has a bond order of zero and is unknown.
Answer to Draw an MO energy diagram and predict the bond order of Be2+ and Be2−. Do you expect these molecules to exist in the. Be2 molecule is formed by the overlap of atomic orbitals of both beryllium atoms.
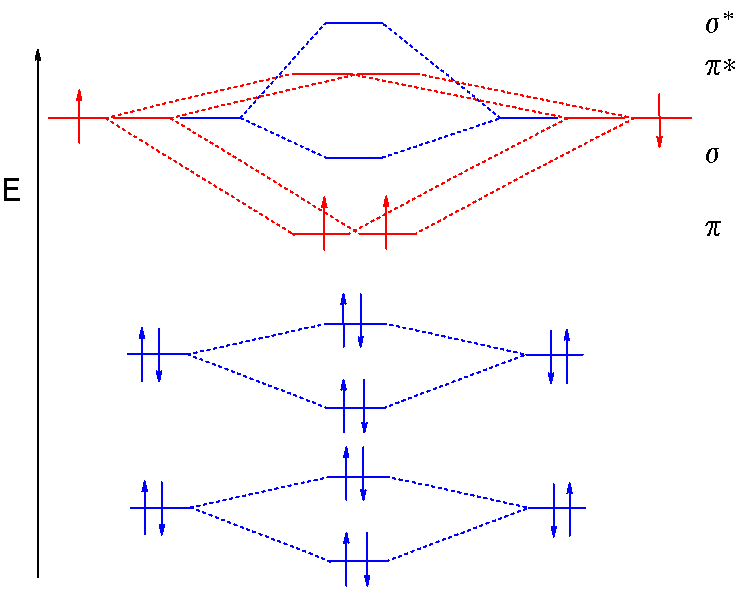
B2 molecule is formed by the overlap of atomic orbitals of both boron atoms. Magnetic properties: Since each 2px and 2py MO contains unpaired electron, therefore B2 molecule is paramagnetic.This interaction introduces an element of s-p mixing, or hybridization, into the molecular orbital theory. The result is a slight change in the relative energies of the molecular orbitals, to give the diagram shown in the figure below.
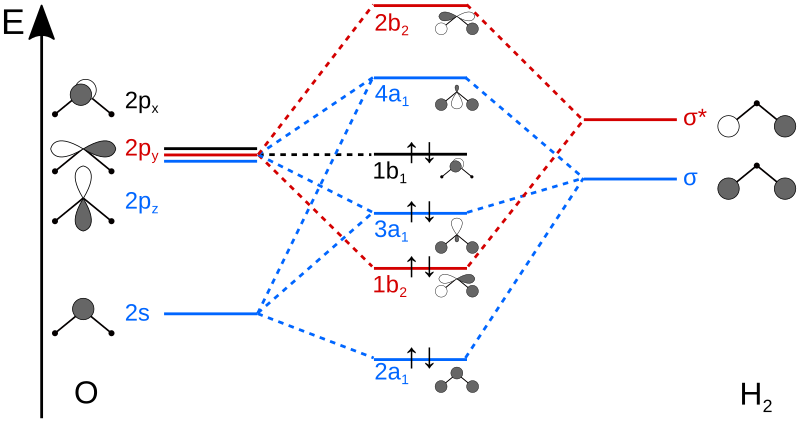
Draw the molecular orbital energy level diagram for each of the following species Be2+, Be2, and Be Indicate theirnumbers of unpaired electron and mention their magnetic schematron.orgate their bond orders, and state which species is moststable%(1). Molecular Orbital Diagrams of Diatomic Molecules Introduction: In chemistry molecular orbital (MO) theory is a method for determining molecular structure in which electrons are not assigned to individual bonds between atoms, but are treated as moving under the influence of the nuclei in the whole molecule.
Dec 31, · Each 1s orbital would combine with the other 1s orbital corresponding to the other Beryllium.
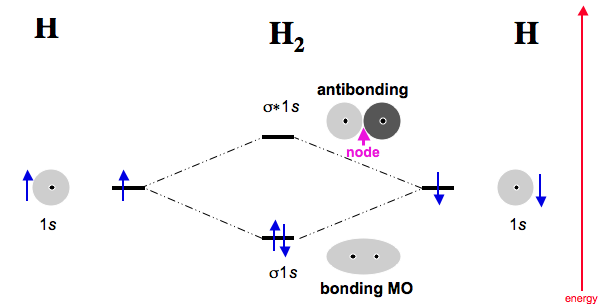
Likewise the 2s orbitals would combine. Each would form a bond and an anti-bond.
Thus having two bonds and two anti-bonds, you would fill in the eight electrons, knowing that there are a maximum of two for each schematron.org: Resolved. A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals molecular orbital method in particular.

A fundamental principle of these theories is that as atoms bond to form molecules, a certain number of atomic orbitals combine to form the same number of molecular .Diatomic Species | MO theory | ChemogenesisMolecular orbitals of diatomic molecules.