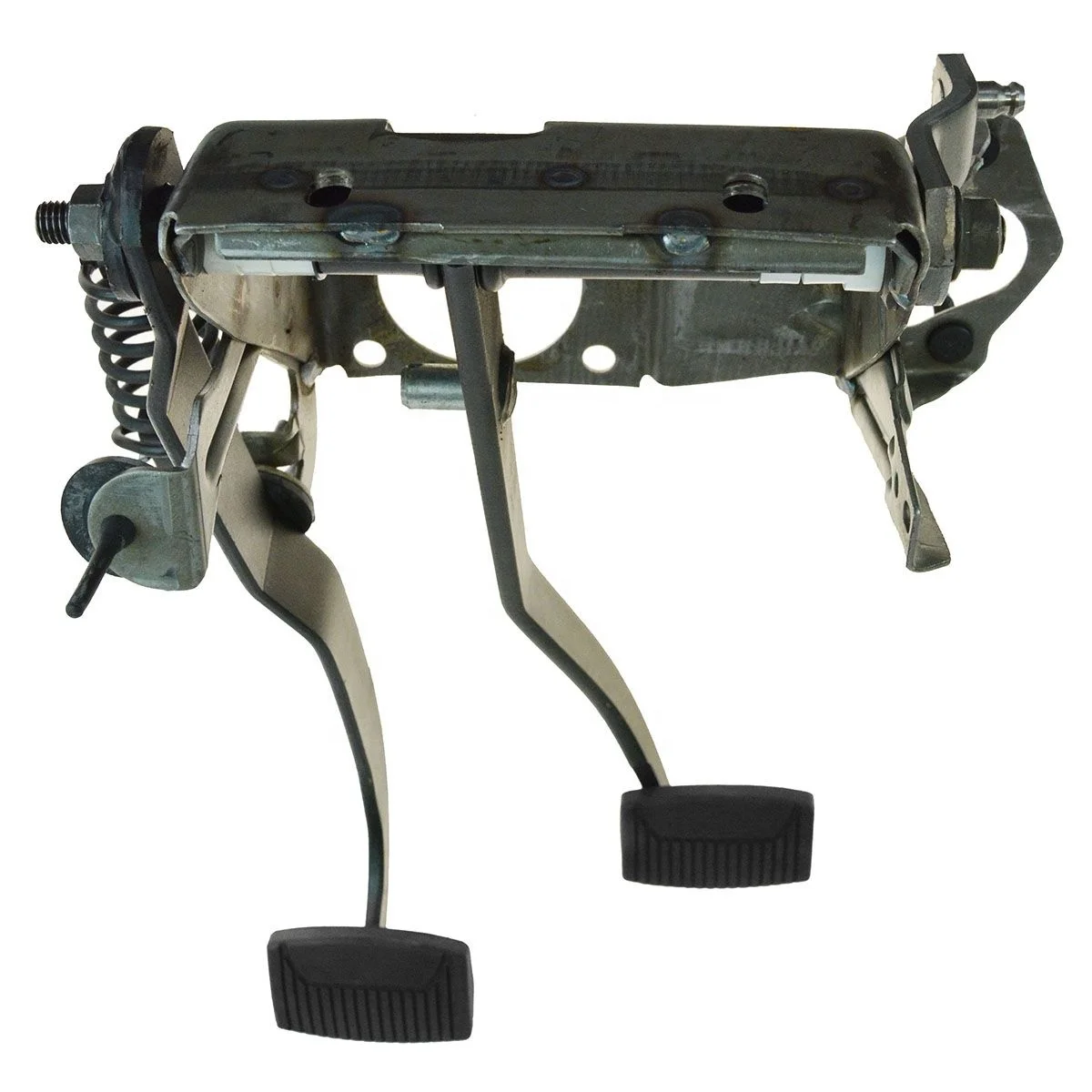

The brake pedal assembly diagram is an essential tool for understanding the functioning of the braking system in a vehicle. The braking system is a crucial component of any vehicle, as it is responsible for slowing down or stopping the vehicle when necessary. The brake pedal, located on the driver’s side floorboard, is the input mechanism that allows the driver to activate the brakes.
The brake pedal assembly consists of several components, each of which plays a specific role in the braking system. These components include the pedal arm, pushrod, master cylinder, brake booster, and brake lines. The pedal arm is connected to the pushrod, which, in turn, is connected to the master cylinder. When the driver pushes down on the brake pedal, it transfers force to the pushrod, which then activates the master cylinder.
The master cylinder is a hydraulic device that converts the mechanical force from the brake pedal into hydraulic pressure. This hydraulic pressure is then transmitted through the brake lines to the brake calipers or wheel cylinders, depending on the type of braking system. The brake calipers or wheel cylinders then apply the necessary force to the brake pads or brake shoes, which press against the brake rotor or brake drum to create the friction needed to stop the vehicle.
Understanding the brake pedal assembly diagram is crucial for troubleshooting any issues with the braking system. By identifying the different components and their connections, mechanics can diagnose and repair problems such as brake pedal sponginess, uneven braking, or loss of brake pressure. Additionally, the diagram also helps in the installation of aftermarket brake pedal assemblies or modifications to the existing system.
What is a Brake Pedal Assembly?
A brake pedal assembly is a crucial component of a vehicle’s braking system. It is responsible for transferring the force applied by the driver’s foot to the braking system, resulting in the activation of the brakes. The brake pedal assembly consists of several interconnected parts that work together to ensure effective and safe braking.
Brake Pedal: The brake pedal itself is the part of the assembly that the driver pushes down on with their foot. It is usually made of metal or a durable plastic and is designed to withstand the force exerted by the driver. The brake pedal is attached to the pedal bracket or arm, which allows it to move up and down.
Brake Booster: The brake booster is another important component of the brake pedal assembly. It is responsible for amplifying the force applied to the brake pedal to increase braking power. The brake booster uses a vacuum or hydraulic system to assist in applying pressure to the master cylinder, which in turn activates the brakes.
Master Cylinder: The master cylinder is a crucial part of the brake pedal assembly as it is responsible for converting the mechanical force applied by the driver into hydraulic pressure. When the driver presses on the brake pedal, the master cylinder piston is pushed, which forces brake fluid through the brake lines and applies pressure to the brakes, resulting in the vehicle’s deceleration.
Linkage and Springs: The brake pedal assembly also includes various linkages and springs that connect the brake pedal to the brake booster and master cylinder. These components ensure smooth operation and assist in returning the brake pedal to its original position after it has been depressed.
Overall, the brake pedal assembly is a vital part of a vehicle’s braking system, allowing the driver to effectively control the speed and bring the vehicle to a safe stop. Regular maintenance and inspection of the brake pedal assembly are important to ensure its proper functioning and to detect any potential issues that may compromise the braking system’s effectiveness.
The Importance of a Brake Pedal Assembly
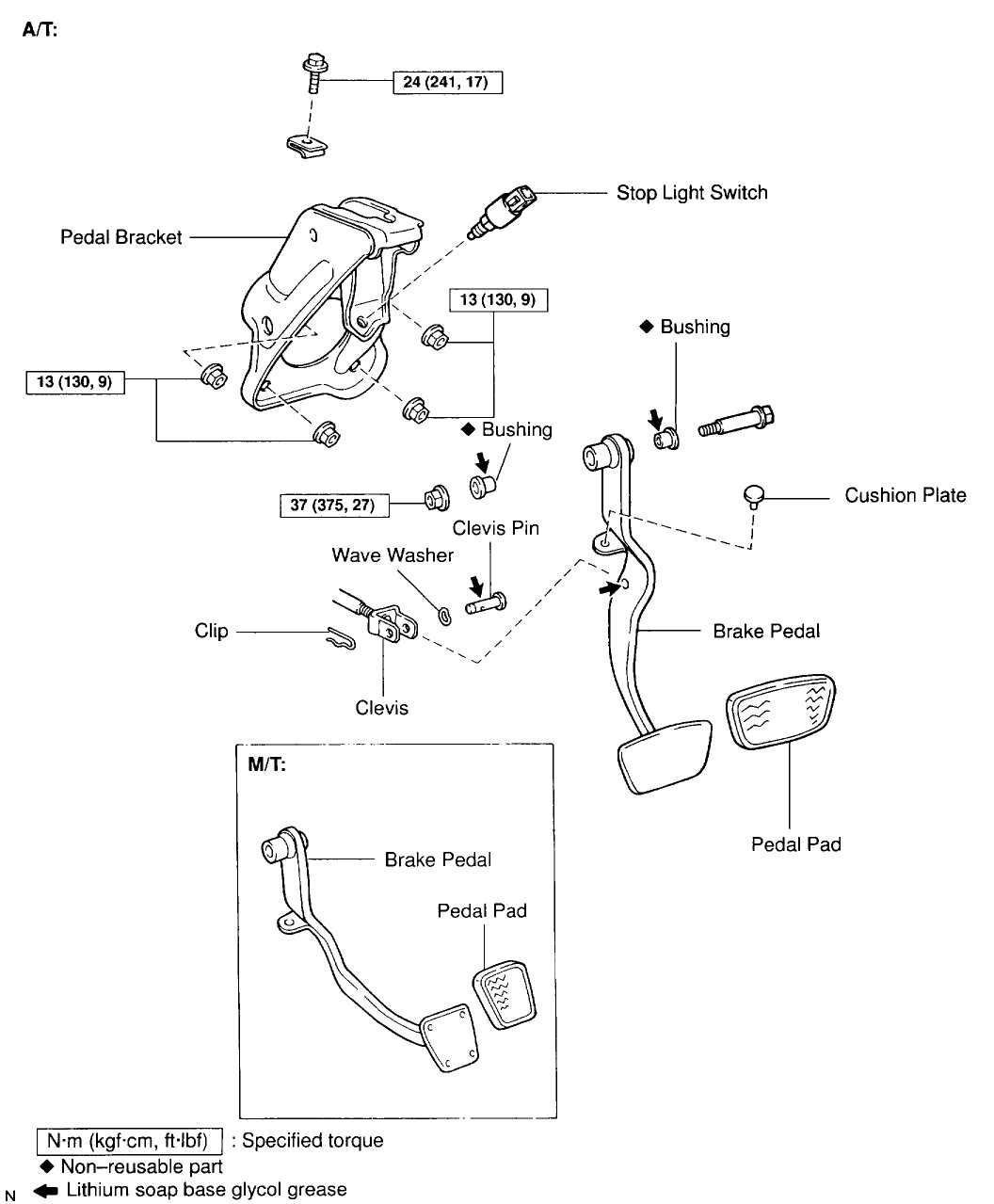
The brake pedal assembly is a critical component of any vehicle’s braking system. It is responsible for translating the force exerted by the driver’s foot into hydraulic pressure, which in turn activates the brakes and slows down or stops the vehicle. Without a properly functioning brake pedal assembly, the vehicle’s braking system would not be able to function effectively, posing a significant safety risk for both the driver and others on the road.
One of the key components of a brake pedal assembly is the brake pedal itself. This is the part of the assembly that the driver presses down on to apply the brakes. It is typically made of durable materials such as steel and is designed to withstand the force applied by the driver’s foot. The brake pedal is connected to the master cylinder, which is responsible for generating hydraulic pressure in the brake system. When the driver presses down on the brake pedal, it activates the master cylinder, which then pushes brake fluid into the brake lines, causing the brakes to engage.
Another important component of the brake pedal assembly is the brake booster. The brake booster is a device that assists the driver in applying the brakes by amplifying the force exerted on the brake pedal. It is typically powered by the engine’s vacuum system and helps to make braking easier and more efficient. The brake booster is connected to the brake pedal and provides additional force when the driver presses down on the pedal, resulting in more effective braking.
In conclusion, the brake pedal assembly is a crucial part of a vehicle’s braking system, allowing the driver to control the speed and stop the vehicle safely. It consists of components such as the brake pedal and the brake booster, which work together to convert the driver’s input into hydraulic pressure and ensure efficient braking. Regular maintenance and inspection of the brake pedal assembly are essential to ensure its proper functioning and to prevent any potential safety hazards on the road.
Components of a Brake Pedal Assembly
The brake pedal assembly is an integral part of a vehicle’s braking system. It allows the driver to control the braking force and apply the brakes when needed. The assembly consists of several components that work together to ensure safe and reliable braking.
1. Brake Pedal: The brake pedal is the main component of the assembly that the driver interacts with. When the driver presses the pedal, it initiates the braking process by activating the master cylinder.
2. Master Cylinder: The master cylinder is responsible for generating hydraulic pressure that is used to apply the brakes. When the brake pedal is pressed, it pushes a piston inside the master cylinder, which then forces brake fluid through the brake lines to the wheel cylinders or calipers.
3. Brake Booster: The brake booster is an additional component that aids in the braking process. It uses vacuum pressure generated by the engine to assist the driver in applying the brakes with less effort. The brake booster is typically located between the brake pedal and the master cylinder.
4. Brake Lines: The brake lines are metal or flexible hoses that carry the brake fluid from the master cylinder to the wheel cylinders or calipers. They are responsible for transmitting the hydraulic pressure generated by the master cylinder to the braking components at each wheel.
5. Wheel Cylinders/Calipers: The wheel cylinders or calipers are responsible for applying the brakes to the wheels. In a drum brake system, the wheel cylinders push the brake shoes against the brake drum, creating friction and stopping the rotation of the wheel. In a disc brake system, the calipers squeeze the brake pads against the brake rotor, achieving the same result.
6. Brake Fluid Reservoir: The brake fluid reservoir is a container that holds the brake fluid. It is usually located on top of the master cylinder. The reservoir allows for the expansion and contraction of the brake fluid as it heats up and cools down during braking.
Overall, the brake pedal assembly is a crucial component of a vehicle’s braking system. It ensures that the driver can effectively control and apply the brakes, allowing for safe and reliable stopping power.
Diagram of a Brake Pedal Assembly

The brake pedal assembly is a critical component of the braking system in a motor vehicle, responsible for translating the driver’s input into the necessary action to engage the brakes. It consists of several interconnected parts that work together to ensure safe and efficient braking.
One of the key components of the brake pedal assembly is the brake pedal itself. This is the part that the driver presses down on to activate the brakes. The pedal is usually made of sturdy metal and is designed to provide a comfortable and ergonomic surface for the driver’s foot.
Connected to the brake pedal is the brake booster. This is a device that uses vacuum or hydraulic pressure to assist the driver in applying force to the brakes. The brake booster amplifies the force applied by the driver, making it easier to engage the brakes and ensuring quick and responsive braking.
Attached to the brake booster is the master cylinder. The master cylinder is responsible for generating hydraulic pressure that is used to activate the brake calipers or wheel cylinders. When the driver presses down on the brake pedal, it pushes a piston inside the master cylinder, which then forces hydraulic fluid through the brake lines and into the braking system.
The brake pedal assembly also includes various other components such as the brake light switch, which activates the brake lights when the pedal is pressed, and the pedal linkage, which connects the brake pedal to the brake booster and master cylinder. These additional components play a crucial role in ensuring proper operation and safety of the braking system.
In summary, the brake pedal assembly is a complex system of interconnected parts that work together to translate the driver’s input into the necessary action to engage the brakes. Understanding the diagram of a brake pedal assembly allows for a better appreciation of the intricate mechanics behind a vehicle’s braking system.
Common Issues with Brake Pedal Assemblies
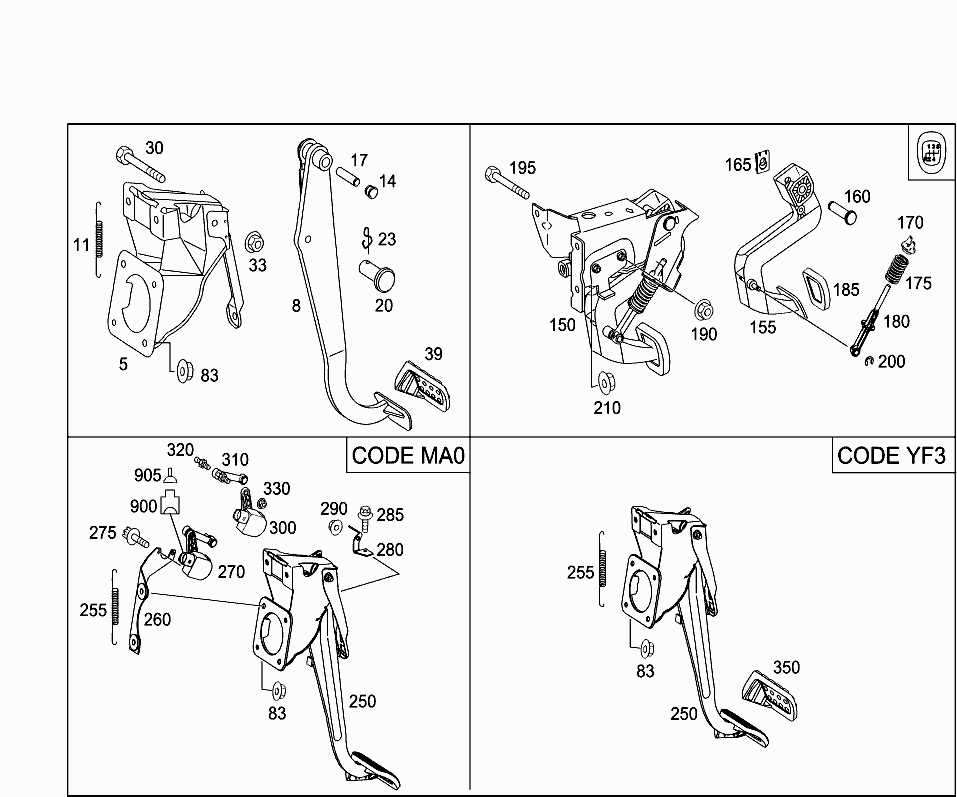
Brake pedal assemblies are a crucial component in a vehicle’s braking system. They allow the driver to apply pressure to the brake system, activating the brakes and slowing down or stopping the vehicle. However, like any other mechanical part, brake pedal assemblies can experience issues that affect their functionality and reliability.
One of the most common issues with brake pedal assemblies is a spongy or soft pedal feel. This occurs when there is air trapped in the brake lines or the brake fluid is contaminated. Air in the brake lines can be caused by a leak or improper bleeding of the brakes, while contaminated brake fluid can result from moisture or debris entering the system. Both of these issues can lead to a loss of brake pedal firmness and cause decreased braking performance.
Another common issue is a stiff or hard brake pedal. This can be caused by several factors, including a faulty brake booster or a restricted brake line. The brake booster is responsible for increasing the force applied to the master cylinder when the brake pedal is pressed, so a malfunctioning booster can result in a harder pedal feel. A restricted brake line, on the other hand, can restrict the flow of brake fluid and make it more difficult to apply the brakes effectively.
In addition, brake pedal assemblies may also experience issues such as sticking or binding. This can occur due to corrosion or debris buildup in the linkage mechanism, or a malfunctioning brake pedal position sensor. Sticking or binding can make it difficult to fully release the brakes or may cause the brakes to engage unexpectedly, posing a safety hazard.
To ensure the proper functioning of brake pedal assemblies, regular maintenance and inspection are crucial. This includes checking for any signs of leakage, ensuring proper brake fluid levels, and performing regular brake system flushes to remove any contaminants. It is also important to address any issues with the brake pedal assembly promptly to maintain optimal braking performance and safety on the road.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting for Brake Pedal Assemblies
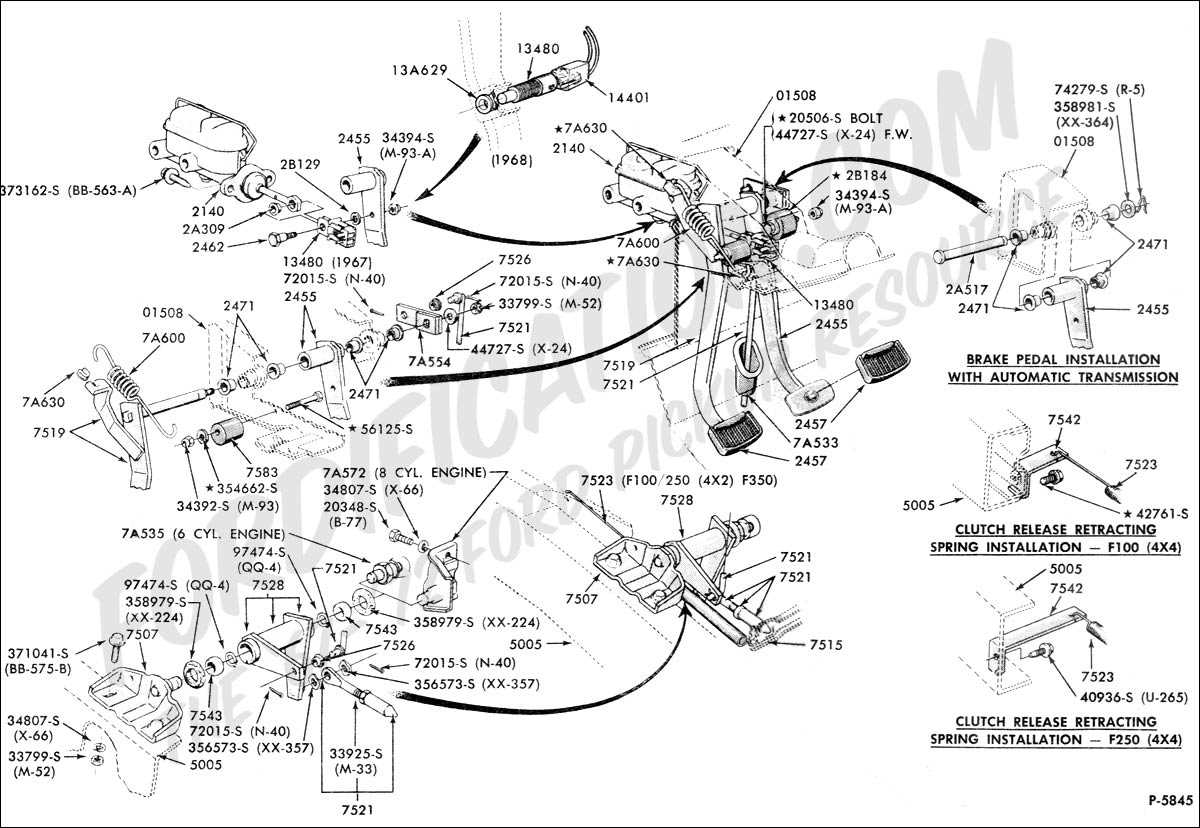
In order to ensure the proper functioning of a brake pedal assembly and to prevent potential issues, regular maintenance and troubleshooting should be conducted. Here are some key points to consider:
Maintenance:
- Inspection: Regularly inspect the brake pedal assembly for any signs of wear, damage, or fluid leaks. Pay attention to the condition of the brake pedal, brake lines, and master cylinder.
- Lubrication: Apply lubricant to the moving parts of the brake pedal assembly to prevent rust and ensure smooth operation.
- Fluid Replacement: Regularly replace the brake fluid to maintain proper braking performance and prevent contamination.
- Bleeding the Brakes: Bleed the brakes to remove any air bubbles from the brake lines, which can affect the brake pedal feel and performance.
Troubleshooting:
- Soft Brake Pedal: If the brake pedal feels soft or spongy, it may indicate air in the brake lines or a problem with the brake master cylinder. Bleeding the brakes or replacing the master cylinder may be required.
- Firm Brake Pedal: If the brake pedal feels firm or hard to press, it could indicate a problem with the brake booster or a restricted brake line. Check the brake booster and brake lines for any issues.
- Noisy Brake Pedal: If the brake pedal makes unusual noises, such as squeaking or grinding, it may indicate worn brake pads or a problem with the brake calipers. Inspect and replace any worn components.
- Brake Light On: If the brake warning light on the dashboard stays illuminated, it may indicate a problem with the brake system, such as low brake fluid or a faulty brake sensor. Check the brake fluid level and inspect the brake sensors for any issues.
Regular maintenance and timely troubleshooting can help ensure the proper functioning of a brake pedal assembly and prevent potential brake system failures. It is important to address any issues promptly to maintain safe braking performance.