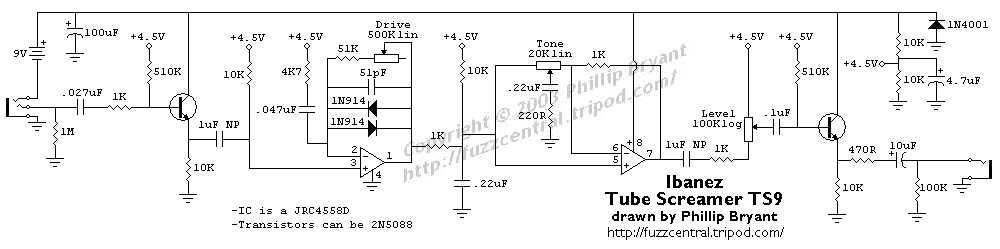
The Ibanez Tube Screamer is one of the most legendary and sought-after overdrive pedals in the world of guitar effects. Known for its warm, creamy tone and smooth clipping, the Tube Screamer has been an essential tool for countless guitarists across genres and styles.
At the heart of the Tube Screamer’s magic lies its electrical circuitry. The Ibanez Tube Screamer schematic provides a blueprint for understanding and replicating the pedal’s unique sound. By examining the schematic, guitar enthusiasts and DIY pedal builders can gain valuable insights into the design and operation of this iconic effect.
While there have been numerous variations of the Tube Screamer over the years, the classic TS808 model remains the most beloved. Its simplicity, transparent tone, and ability to push tube amps into natural overdrive have made it a staple on countless pedalboards.
In this article, we will explore the components and circuitry outlined in the Ibanez Tube Screamer schematic, shedding light on the design choices that contribute to its distinctive sound. Whether you’re a guitar player looking to understand the inner workings of your favorite pedal or a curious DIY enthusiast, this article will serve as a valuable resource to dive into the world of the Ibanez Tube Screamer.
Ibanez Tube Screamer Schematic: Everything You Need to Know
The Ibanez Tube Screamer is one of the most iconic and beloved guitar pedals in the world. It has been used by countless guitarists, from blues legends like Stevie Ray Vaughan to modern rockers like John Mayer. Its unique sound and versatile tone controls make it a go-to choice for many players. To fully understand the Tube Screamer, it is important to take a look at its schematic and how it functions.
The schematic of the Ibanez Tube Screamer is relatively simple compared to other complex guitar pedals. It consists of three main sections: the input buffer, the clipping stage, and the output buffer. The input buffer is responsible for matching the impedance between the guitar and the rest of the pedal circuit, ensuring optimal signal transfer. The clipping stage, controlled by the Overdrive knob, is where the magic happens. It uses diodes to shape the waveform and create the characteristic Tube Screamer distortion. Finally, the output buffer ensures that the pedal’s output can drive long cables and maintain consistent tone.
One of the key features of the Tube Screamer schematic is the use of asymmetrical clipping. This means that the positive and negative halves of the guitar signal are clipped differently, resulting in a smoother and more natural overdrive tone. The diodes used in the clipping stage can be modified to achieve different clipping characteristics, allowing players to customize the sound of their Tube Screamer.
The tone controls on the Tube Screamer, namely the Tone and Level knobs, play an important role in shaping its sound. The Tone knob acts as a high-frequency cut, allowing players to dial in the perfect amount of treble. The Level knob controls the overall volume of the pedal, allowing players to match it with their amp’s level or use it as a boost for solos.
In conclusion, understanding the Ibanez Tube Screamer schematic is essential for anyone looking to delve into its world of iconic overdrive tones. From its simple yet effective circuit design to its unique features like asymmetrical clipping and versatile tone controls, the Tube Screamer offers guitarists a wide range of possibilities. Whether you’re chasing that classic Stevie Ray Vaughan tone or looking to create your own signature sound, the Tube Screamer is a pedal that should be in every guitarist’s arsenal.
Understanding the Ibanez Tube Screamer: A Brief Overview
The Ibanez Tube Screamer is a legendary overdrive pedal that has been a staple in countless guitarists’ pedalboards for decades. Known for its smooth, creamy tone and mid-range boost, the Tube Screamer has become synonymous with the classic blues and rock sound.
The circuit design of the Ibanez Tube Screamer is based on a symmetrical clipping diode configuration, which provides a distinctive and characteristic sound. The pedal features three main controls: drive, tone, and level. The drive control adjusts the amount of gain or overdrive, while the tone control shapes the overall tonal characteristics. The level control adjusts the output volume of the pedal.
The Tube Screamer’s symmetrical clipping diode configuration allows for a dynamic, responsive tone that is highly touch-sensitive. When the gain is set low, the pedal adds a subtle, transparent boost to the signal, while at higher gain settings, it produces a rich, saturated overdrive. The mid-range boost adds warmth and presence to the tone, making it ideal for soloing and cutting through the mix.
Key Features of the Ibanez Tube Screamer
- Symmetrical Clipping Diode Configuration: The Tube Screamer’s unique diode configuration creates its distinct overdrive sound.
- Drive, Tone, and Level Controls: The three main controls allow for precise adjustments and shaping of the tone.
- Dynamic and Touch-Sensitive Tone: The Tube Screamer responds to the player’s touch and playing style, providing a highly dynamic tone.
- Mid-Range Boost: The built-in mid-range boost adds warmth and presence to the tone, making it ideal for lead playing.
Whether you’re a blues, rock, or even metal guitarist, the Ibanez Tube Screamer can enhance your tone and provide that extra punch and character to your sound. Its iconic design and sound have made it a go-to pedal for many guitarists, and it continues to be a beloved classic in the world of overdrive pedals.
Breaking Down the Ibanez Tube Screamer Schematic
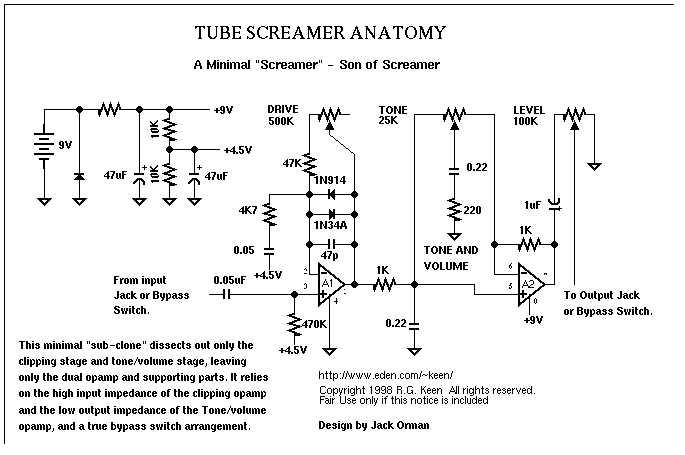
The Ibanez Tube Screamer is a legendary overdrive pedal that has been used by countless guitarists to achieve rich and creamy distortion tones. To better understand how this iconic pedal works, let’s break down its schematic and explore its key components.
1. Input Section
The input section of the Ibanez Tube Screamer consists of an input jack, a current-limiting resistor, and a coupling capacitor. The input jack is where the guitar signal enters the pedal. The current-limiting resistor helps protect the circuit from excessive current, while the coupling capacitor blocks any DC voltage from the guitar, allowing only the audio signal to pass through.
2. Op-Amp (Operational Amplifier)
The heart of the Ibanez Tube Screamer is the op-amp, which is responsible for amplifying and shaping the guitar signal. The op-amp is configured as an inverting amplifier, where the negative feedback path helps control the gain and frequency response of the pedal.
3. Tone Control
The Ibanez Tube Screamer features a tone control circuit that allows the user to adjust the frequency response of the effect. It consists of a tone potentiometer and a treble-cut capacitor. By rotating the tone knob, the user can either emphasize or attenuate the high frequencies, resulting in a darker or brighter tone.
4. Drive Control
The drive control determines the amount of distortion and overdrive in the pedal. It is a potentiometer that adjusts the negative feedback in the op-amp circuit, which ultimately affects the gain and clipping characteristics of the Tube Screamer. Higher drive settings result in more distortion and sustain.
5. Level Control
The level control determines the output volume of the pedal. It is a potentiometer that adjusts the amplification of the op-amp circuit, allowing the user to match the output level with the bypassed signal or boost it for soloing purposes.
6. Bypass Switching
The Ibanez Tube Screamer utilizes a true bypass switching system, which routes the guitar signal directly to the output when the pedal is not engaged. This ensures that the pedal does not color or degrade the tone when it is bypassed.
By understanding the schematic of the Ibanez Tube Screamer, guitarists can gain insights into how the pedal works and make modifications or tweaks to suit their personal preferences. This iconic overdrive pedal continues to be a staple in many guitar rigs, thanks to its versatile and timeless tone.
Exploring the Key Components of the Ibanez Tube Screamer
The Ibanez Tube Screamer is one of the most iconic overdrive pedals in the world of electric guitar. Its distinctive sound and versatility have made it a favorite among musicians of all genres. To understand what makes the Tube Screamer so special, let’s take a closer look at its key components.
1. Op-Amp Chip
The heart of the Tube Screamer is its op-amp chip, which is responsible for amplifying and shaping the guitar signal. The original Tube Screamers used the JRC4558 chip, while newer versions have employed different op-amps. The choice of op-amp can have a significant impact on the pedal’s overall tone and character.
2. Tone Control
The Tube Screamer features a simple yet effective tone control that allows players to shape the frequencies of their guitar signal. It boosts the midrange while cutting some of the highs and lows, resulting in a warmer and more focused tone. This particular EQ curve is one of the defining characteristics of the Tube Screamer sound.
3. Drive Control
The drive control on the Tube Screamer determines the amount of gain and overdrive applied to the signal. By adjusting this control, players can achieve anything from a subtle boost to a thick and saturated distortion. The drive control, combined with the tone control, offers a wide range of sonic possibilities.
4. Level Control
The level control, also known as the output control, sets the overall volume level of the Tube Screamer. It allows players to match the pedal’s output with the rest of their signal chain or to push the amp for more drive and saturation. Properly adjusting the level control is crucial for achieving the desired balance and dynamics.
5. True Bypass Switching
The Ibanez Tube Screamer typically features true bypass switching, which means that when the pedal is disengaged, it does not interfere with the guitar signal. This ensures that the signal remains pure and unaffected when the pedal is not in use.
By understanding the key components of the Ibanez Tube Screamer, guitarists can better harness its unique sound and incorporate it into their playing. Whether used as a clean boost, a midrange boost, or a versatile overdrive, the Tube Screamer continues to be a staple on countless pedalboards worldwide.
Tips and Tricks for Modifying the Ibanez Tube Screamer
The Ibanez Tube Screamer is a legendary overdrive pedal that has been a staple in many guitarists’ pedalboards for decades. While the stock Tube Screamer sounds great on its own, there are several modifications you can make to enhance its performance and tailor it to your specific playing style.
Replacing the Op-Amp: One of the most common modifications for the Tube Screamer is replacing the stock op-amp with a different one to achieve different tonal characteristics. The most popular op-amp replacements are the JRC4558, which provides a smoother and more vintage sound, and the Texas Instruments RC4558P, which offers a slightly more modern and cleaner tone.
Changing the Input and Output Capacitors: Another popular modification is changing the input and output capacitors of the Tube Screamer. This can affect the overall tone and frequency response of the pedal. Swapping the stock capacitors with high-quality audio-grade capacitors can result in a clearer and more defined sound, especially in the high-end frequencies.
Experimenting with Different Diodes: The diodes in the Tube Screamer play a crucial role in shaping the pedal’s clipping and distortion characteristics. By experimenting with different diodes, such as germanium, silicon, or even LED diodes, you can achieve different levels of saturation and compression. This can add more versatility and tonal options to your Tube Screamer.
Adjusting the Clipping Options: Some Tube Screamer models, such as the TS808, offer different clipping options. These can be selected using the “Mode” switch on the pedal. Experimenting with different clipping options can alter the pedal’s response and dynamics, allowing you to find the perfect balance between sustain and transparency for your playing style.
Bypassing or Modifying the Tone Control: While the Tube Screamer’s tone control is part of its signature sound, some players prefer to bypass it altogether or modify its range. Bypassing the tone control can result in a more transparent and open sound, while modifying its range can allow for more extreme tone shaping options.
Summary: Modifying the Ibanez Tube Screamer can be an exciting and rewarding process that allows you to customize the pedal to your own preferences. Whether it’s swapping op-amps, changing capacitors, experimenting with diodes, adjusting clipping options, or modifying the tone control, there are plenty of options to explore. Remember to take your time, experiment, and always be careful when working with electronics.
Troubleshooting Common Issues with the Ibanez Tube Screamer
Despite being a popular and reliable overdrive pedal, the Ibanez Tube Screamer can still encounter some common issues. Here are some troubleshooting tips to help you diagnose and fix these problems:
No Sound
If you’re not getting any sound from your Tube Screamer, there are a few potential causes to consider:
- Check your cables and connections to ensure they are properly plugged in.
- Make sure the power supply is connected and providing the correct voltage.
- Check the battery if you’re using one, as it may be dead and in need of replacement.
- Verify that the pedal is engaged by checking the LED indicator.
Distorted or Noisy Sound
If your Tube Screamer is producing a distorted or noisy sound, try the following troubleshooting steps:
- Check the input and output levels of the pedal. Adjusting these levels can help eliminate unwanted distortion or noise.
- Clean the input and output jacks with an electronics cleaner to remove any dirt or debris that may be causing the issue.
- Inspect the internal components for any signs of damage or loose connections. If necessary, consult a professional for repair.
Inconsistent Tone or Effect
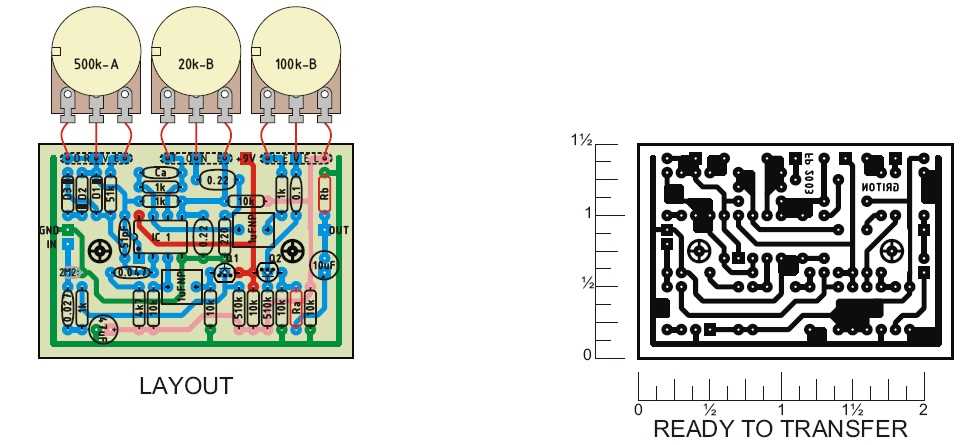
If you’re experiencing inconsistent tone or effect from your Tube Screamer, consider the following troubleshooting tips:
- Check the battery if you’re using one, as a low battery can affect the overall performance and tone of the pedal.
- Verify that the controls on the pedal are set to the desired settings. Make sure the knobs are not loose or experiencing any excessive slippage.
- If you’re using a power supply, ensure it is providing the correct voltage and has enough current capacity to power the pedal adequately.
- Try using different cables and guitars to rule out any issues with the instrument or other connections in your setup.
By following these troubleshooting tips, you should be able to diagnose and resolve common issues with the Ibanez Tube Screamer. Remember, if you’re unsure about any electrical repairs or modifications, it’s always best to consult a qualified technician for assistance.