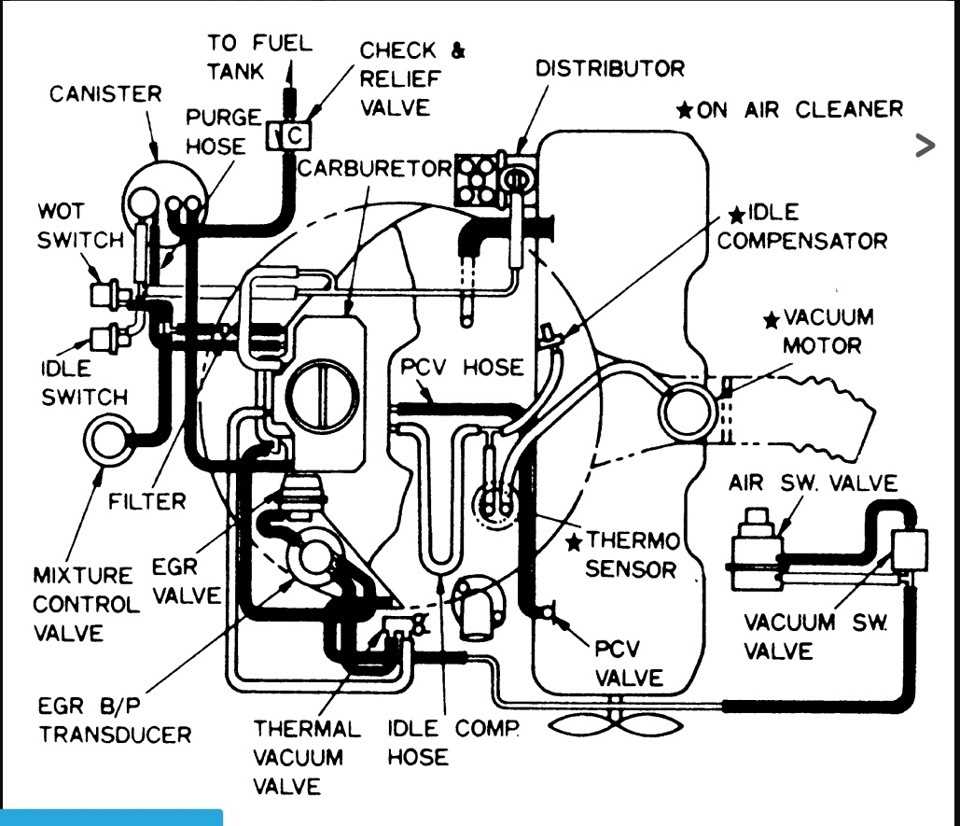
The vacuum diagram for a Chevy 350 engine is an important tool that helps ensure the engine operates efficiently and smoothly. The vacuum system plays a crucial role in controlling various components of the engine, such as the fuel delivery system, the emissions system, and the ignition system. Understanding the vacuum diagram and how it functions can be helpful for troubleshooting vacuum-related issues and maintaining the engine’s performance.
The Chevy 350 engine is a popular choice among car enthusiasts and has been used in a wide range of vehicles over the years. The vacuum diagram for this engine can vary depending on factors such as the year and model of the vehicle, as well as any aftermarket modifications that may have been made. It is important to consult the appropriate vacuum diagram for your specific engine to ensure accurate troubleshooting and maintenance.
The vacuum diagram typically consists of a series of lines and symbols that represent various components and connections in the vacuum system. These diagrams are usually found in the vehicle’s service manual or can be obtained from online sources. The diagram provides a visual representation of how the vacuum system is laid out and how the different components are interconnected.
Understanding the vacuum diagram can help in identifying and locating vacuum leaks, as well as understanding how different components in the engine rely on vacuum pressure for their operation. It is important to ensure that all the vacuum lines are properly connected and free from leaks, as any leaks can result in poor engine performance and increased emissions.
Vacuum Diagram for Chevy 350
The vacuum diagram for a Chevy 350 engine outlines the various vacuum lines and components that are connected to the engine and help with its operation. The vacuum system in an engine plays an important role in controlling different aspects of engine performance, including fuel delivery and emissions control.
One of the main components in the vacuum system is the vacuum pump, which uses engine power to create a vacuum that pulls air and fuel into the engine. The vacuum lines connect the vacuum pump to various parts of the engine, such as the intake manifold, carburetor, and emission control devices.
The vacuum diagram for a Chevy 350 engine typically depicts the routing and connections of these vacuum lines, along with any additional components, such as check valves or vacuum reservoirs. It is important to follow the correct routing of these lines and ensure that they are properly connected to maintain optimum engine performance.
There are several resources available to obtain a vacuum diagram for a Chevy 350 engine. One option is to consult the vehicle’s service manual or contact the manufacturer for an official diagram. Another option is to search for aftermarket manuals or online forums dedicated to Chevy 350 engines, where enthusiasts and experts may have shared vacuum diagrams and troubleshooting tips.
When working with the vacuum system of a Chevy 350 engine, it is important to ensure that all connections are secure and free of any leaks. Leaks in the vacuum system can cause poor engine performance, increased emissions, and potentially damage to engine components. Regular inspection and maintenance of the vacuum system is recommended to ensure optimal engine operation.
In conclusion,
A vacuum diagram for a Chevy 350 engine is an important resource for understanding and troubleshooting the vacuum system. It outlines the routing and connections of the vacuum lines and components, helping to ensure proper engine performance and emissions control. Regular inspection and maintenance of the vacuum system are essential for optimal engine operation.
What is a Vacuum Diagram?
A vacuum diagram is a schematic representation of the vacuum system in a vehicle. It shows the various components that make up the system and the connections between them. The diagram helps mechanics and DIY enthusiasts understand how the vacuum system works and how different components interact with each other.
The vacuum system plays an important role in the proper functioning of a vehicle’s engine. It helps regulate the air-fuel mixture and controls various engine functions, such as the operation of the brake booster, emissions system, and HVAC controls. Without a properly functioning vacuum system, the engine may experience performance issues, increased emissions, and other problems.
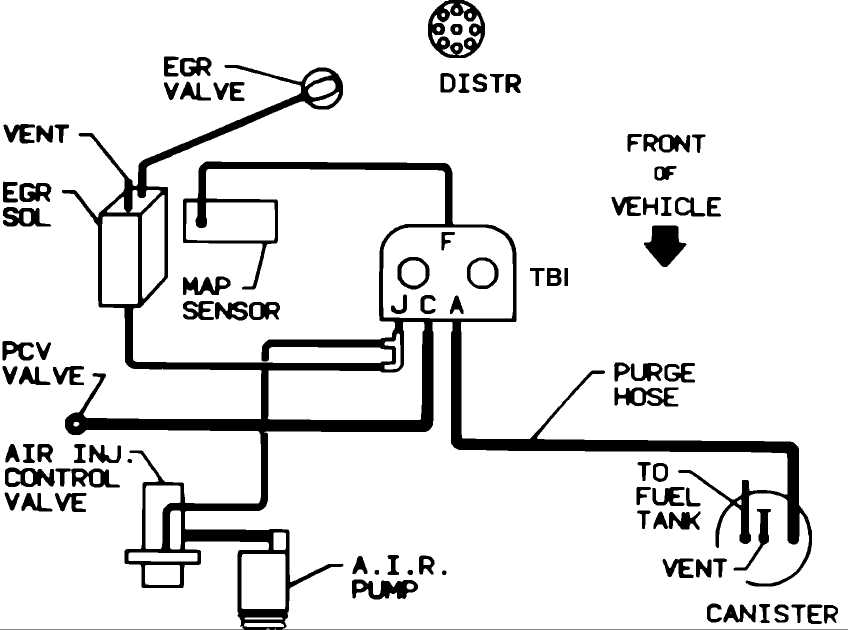
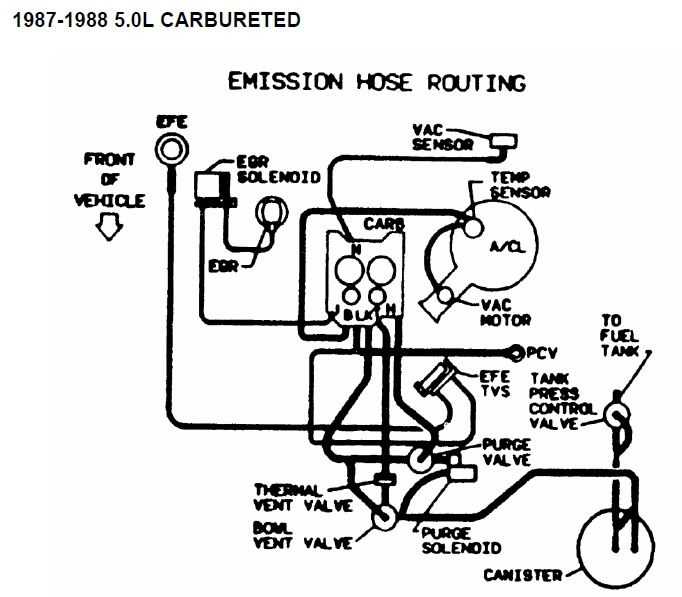
A typical vacuum diagram for a Chevy 350 engine would include components such as the intake manifold, carburetor, distributor, EGR valve, PCV valve, and various vacuum hoses. The diagram would show how these components are connected and how the vacuum is routed throughout the engine.
Understanding the vacuum diagram is essential for troubleshooting and diagnosing vacuum-related issues in a vehicle. It helps identify potential leaks, blockages, or malfunctioning components that could be affecting engine performance. By following the vacuum diagram, mechanics can locate and address the root cause of the problem, ensuring that the engine operates optimally.
In summary, a vacuum diagram is a visual representation of the vacuum system in a vehicle, showing the connections and components involved. It is an essential tool for understanding and troubleshooting vacuum-related issues in a Chevy 350 engine.
Importance of Vacuum Diagram for Chevy 350
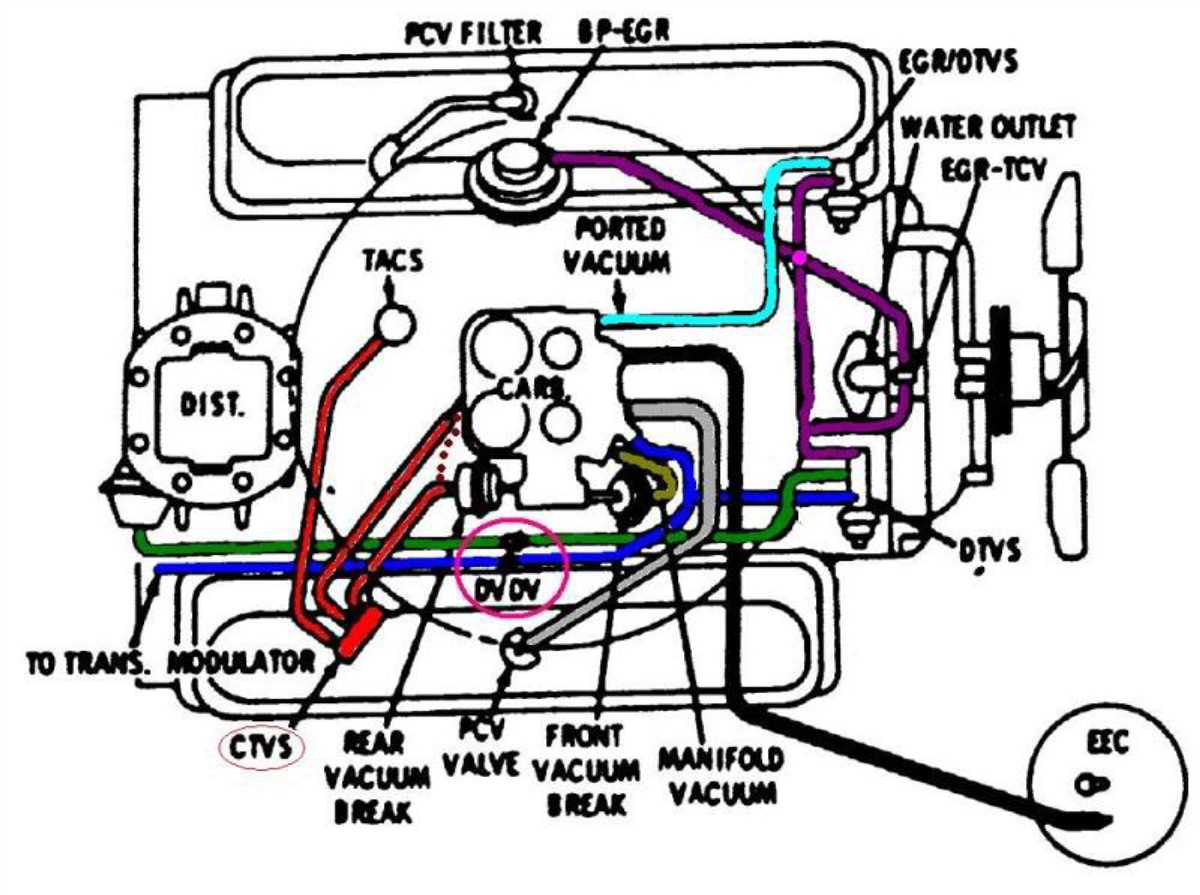
The vacuum diagram for a Chevy 350 engine plays a crucial role in ensuring that the engine operates efficiently and smoothly. The vacuum system in an engine helps control various functions, such as fuel delivery, ignition timing, and emission control.
A vacuum diagram is a visual representation of the various vacuum lines and components in the engine. It shows how the vacuum lines connect to different parts of the engine, such as the carburetor, intake manifold, and emission control devices. This diagram helps mechanics and car owners understand the routing and connections of the vacuum lines, making it easier to diagnose and fix any issues that may arise.
Vacuum leaks: One of the main reasons why a vacuum diagram is important for a Chevy 350 engine is to identify and fix vacuum leaks. Vacuum leaks can cause a variety of problems, such as rough idle, poor fuel efficiency, and decreased engine performance. By referring to the vacuum diagram, mechanics can locate and repair any leaks in the vacuum lines, ensuring that the engine operates at its best.
Performance tuning: The vacuum diagram is also essential for performance tuning of the Chevy 350 engine. By understanding the vacuum system and its connections, car owners and mechanics can make adjustments to optimize the engine’s performance. This may involve adjusting the timing, fine-tuning the carburetor, or installing performance-enhancing components. Having a clear vacuum diagram makes it easier to make these adjustments accurately and effectively.
Emissions control: The Chevy 350 engine, like any modern engine, is equipped with emission control devices to reduce harmful pollutants. The vacuum diagram helps in understanding how these emission control devices, such as the EGR valve and PCV valve, are connected to the engine. Any issues with these devices or their connections can lead to increased emissions and may result in a failed emissions test. By referring to the vacuum diagram, mechanics can properly diagnose and repair any problems with the emission control system.
In conclusion, the vacuum diagram for a Chevy 350 engine is crucial for maintaining its optimal performance, diagnosing and fixing vacuum leaks, tuning for better performance, and ensuring proper emissions control. It serves as a valuable reference tool for mechanics and car owners, helping them understand the vacuum system and its connections, and ultimately, keeping the engine running smoothly.
Understanding the Components of the Vacuum System
The vacuum system is a crucial component of the engine, responsible for various functions such as regulating air intake, controlling emissions, and operating certain engine accessories. It consists of several components that work together to create and maintain the desired vacuum levels. Understanding these components and their roles is essential for troubleshooting and maintaining the vacuum system of a Chevy 350 engine.
Vacuum Lines: The vacuum lines are the pathways through which the vacuum is distributed throughout the engine. These lines are usually made of rubber or plastic and can deteriorate over time, leading to vacuum leaks. It is important to inspect the vacuum lines regularly and replace any damaged or worn-out lines to ensure the proper functioning of the vacuum system.
Vacuum Pump: The vacuum pump is responsible for creating the vacuum in the system. It draws in air from the intake manifold and exhausts it to the atmosphere. The pump consists of an impeller that rotates to create the suction needed for the vacuum. Over time, the impeller can wear out or become damaged, resulting in reduced vacuum pressure. Regular maintenance and inspection of the vacuum pump are essential to ensure its optimal performance.
Vacuum Reservoir: The vacuum reservoir is a storage tank that stores the vacuum created by the vacuum pump. It helps maintain a steady supply of vacuum to the engine, especially during high-demand situations. The reservoir is typically made of metal or plastic and is connected to the vacuum lines. If the vacuum reservoir is damaged or has a leak, it can result in fluctuating vacuum levels, leading to engine performance issues.
Vacuum Regulator Valve: The vacuum regulator valve, also known as a vacuum control valve or vacuum modulator, is responsible for regulating the vacuum pressure in specific parts of the engine. It controls the amount of vacuum supplied to various engine components, depending on their requirements. A faulty or malfunctioning vacuum regulator valve can lead to improper engine performance and increased emissions.
Vacuum Check Valve: The vacuum check valve is a one-way valve that allows the flow of vacuum in one direction and prevents it from flowing in the opposite direction. It ensures that the vacuum is properly directed and utilized by the engine components. A faulty or clogged check valve can disrupt the vacuum flow, leading to engine performance issues.
Overall, the vacuum system of a Chevy 350 engine is made up of various components that work together to create and maintain the desired vacuum levels. Understanding the role of each component and regularly inspecting and maintaining them is crucial for ensuring optimal engine performance and minimizing emissions.
Step-by-Step Guide to Reading a Vacuum Diagram for Chevy 350
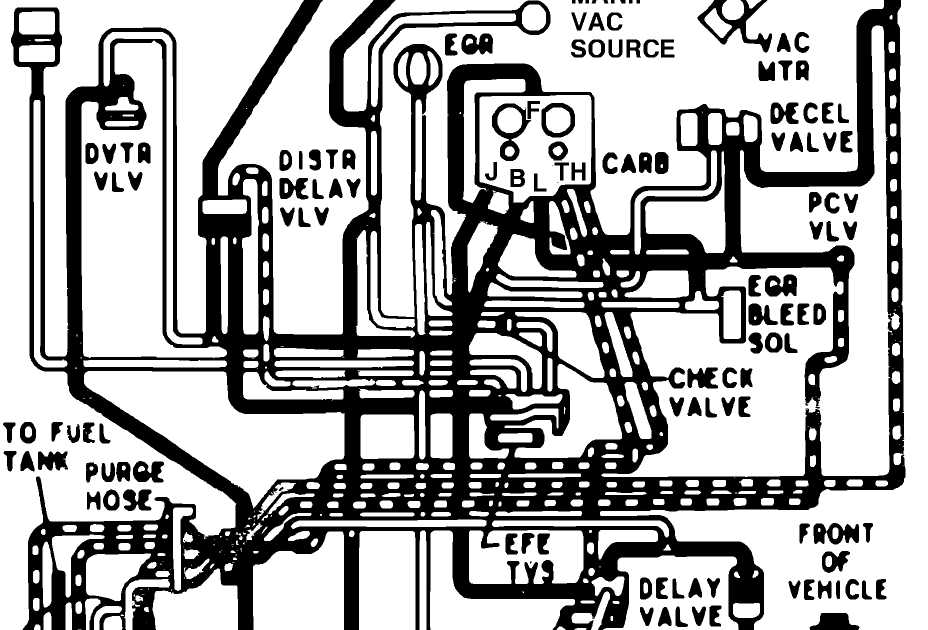
If you are a Chevy 350 owner and need to understand how the vacuum system works in your engine, reading a vacuum diagram can help you gain a better understanding. Here is a step-by-step guide to reading a vacuum diagram specifically designed for Chevy 350 engines.
- Locate the vacuum diagram: The vacuum diagram for your Chevy 350 engine can usually be found under the hood, on the emission control label, or in the owner’s manual. Look for a diagram that shows the different vacuum hoses and their connections.
- Identify the components: The vacuum diagram will feature different components represented by symbols or labels. Familiarize yourself with these symbols to understand what each component represents. Typical components include the carburetor, distributor, EGR valve, PCV valve, and various sensors.
- Follow the lines: The vacuum diagram will have lines connecting the components. These lines represent the vacuum hoses or pathways that carry the vacuum pressure from one component to another. Follow the lines to see how the vacuum is routed around the engine.
- Understand the line types: The vacuum diagram will use different line types to differentiate between different vacuum pressures. Solid lines typically represent full vacuum pressure, while dotted or dashed lines indicate partial or weak vacuum pressure.
- Check for color codes: Some vacuum diagrams may use color coding to make it easier to differentiate between different vacuum lines. Refer to the color legend provided on the diagram to understand the meaning of each color.
- Note the connections: Pay close attention to the connections between the components. The vacuum diagram will show how the vacuum hoses are connected to each component and where they are attached. Make sure the connections match the diagram to ensure proper vacuum flow.
- Consult the legend: If there is a legend or key provided on the vacuum diagram, refer to it to understand any additional symbols or labels that may not be immediately clear.
By following these steps and understanding the vacuum diagram for your Chevy 350 engine, you can gain a better understanding of how the vacuum system works and troubleshoot any issues that may arise. It is always a good idea to consult the manufacturer’s documentation or seek professional help if you are unsure about any aspect of your engine’s vacuum system.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting Tips for the Vacuum System
Having a properly functioning vacuum system is crucial for the performance of your Chevy 350 engine. However, like any other system, issues may arise over time. Here are some common problems that you may encounter with your vacuum system and some troubleshooting tips to help you resolve them.
Vacuum Leaks
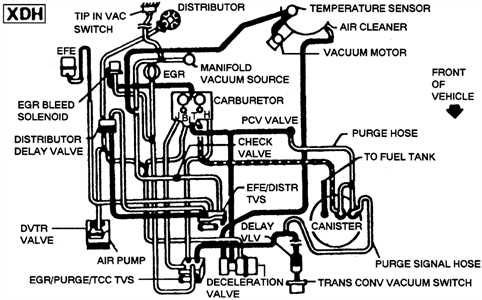
One of the most common issues with vacuum systems is leaks. These leaks can disrupt the vacuum pressure and cause poor engine performance. To identify a vacuum leak, you can use a vacuum gauge or listen for hissing sounds under the hood. Once you locate the leak, you can repair it by replacing the faulty hose or sealing the connection.
Weak Vacuum Pressure
If you notice a decrease in vacuum pressure, it can lead to issues such as poor brake performance or difficulty in shifting gears. This problem can be caused by a few factors, including a worn-out vacuum pump, a clogged filter, or a malfunctioning check valve. To troubleshoot this problem, you can inspect and clean the filter, check and replace the vacuum pump if necessary, or test the check valve for proper functioning.
Erratic Idling
An erratic idle can be a sign of a vacuum system problem. Irregular fluctuations in the engine’s RPM can occur due to a vacuum leak or a malfunctioning idle control valve. Inspect the vacuum lines for leaks and check the idle control valve for proper operation. Cleaning or replacing the idle control valve may help resolve this issue.
Inconsistent HVAC Performance
If you experience inconsistent heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) performance, it could be related to a vacuum system malfunction. A faulty vacuum actuator or blend door can cause improper airflow or temperature control. Inspect these components and replace them if necessary to restore proper HVAC functioning.
Remember, proper maintenance and regular inspection of your vacuum system can prevent potential issues and ensure optimal engine performance. If you are unsure or unable to troubleshoot the problem yourself, it is recommended to consult a professional mechanic.
Understanding and addressing common issues with the vacuum system of your Chevy 350 engine will help ensure its longevity and smooth operation.