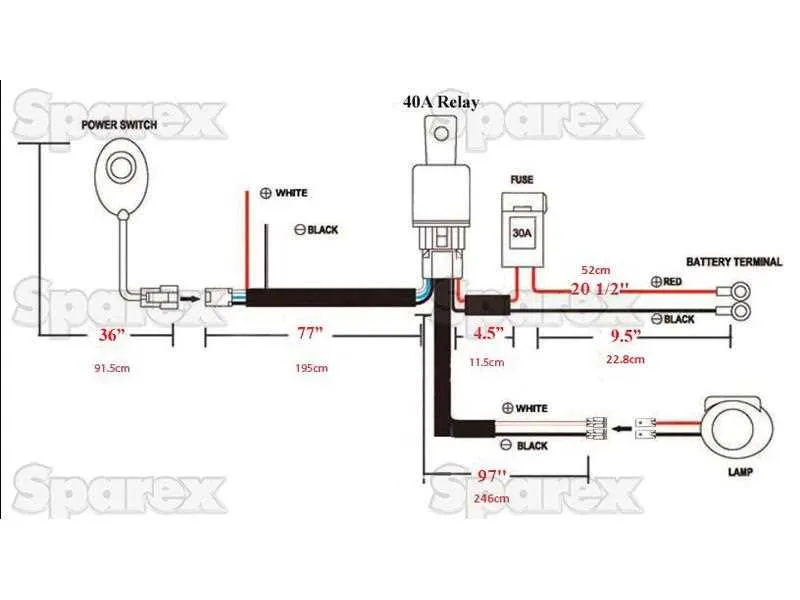
For efficient installation, begin by organizing the components in a clear, step-by-step sequence. Ensure that the main power source matches the required voltage and current ratings for the setup. Using a compatible transformer or adapter will prevent unnecessary strain and ensure a long lifespan for your installation.
Next, connect the segments in series or parallel, depending on your configuration. When wiring several segments, take care to maintain consistent polarity to avoid malfunction. Each connection should be secure, and where applicable, solder joints should be clean and insulated to prevent any short circuits.
Ensure that any controller or dimmer is rated to handle the full load. This will allow you to adjust brightness and color temperature without overloading the system. Proper heat dissipation must also be factored in, especially when working with high-output configurations. Utilize heat sinks or thermal pads if necessary to maintain operational stability.
Finally, double-check all connections before powering on. Use a multimeter to verify the voltage and continuity. Any irregularities in voltage could indicate poor connections or potential hazards. Performing these checks will help prevent issues and ensure a smooth and reliable performance.
Wiring Guide for Off-Road Illuminators
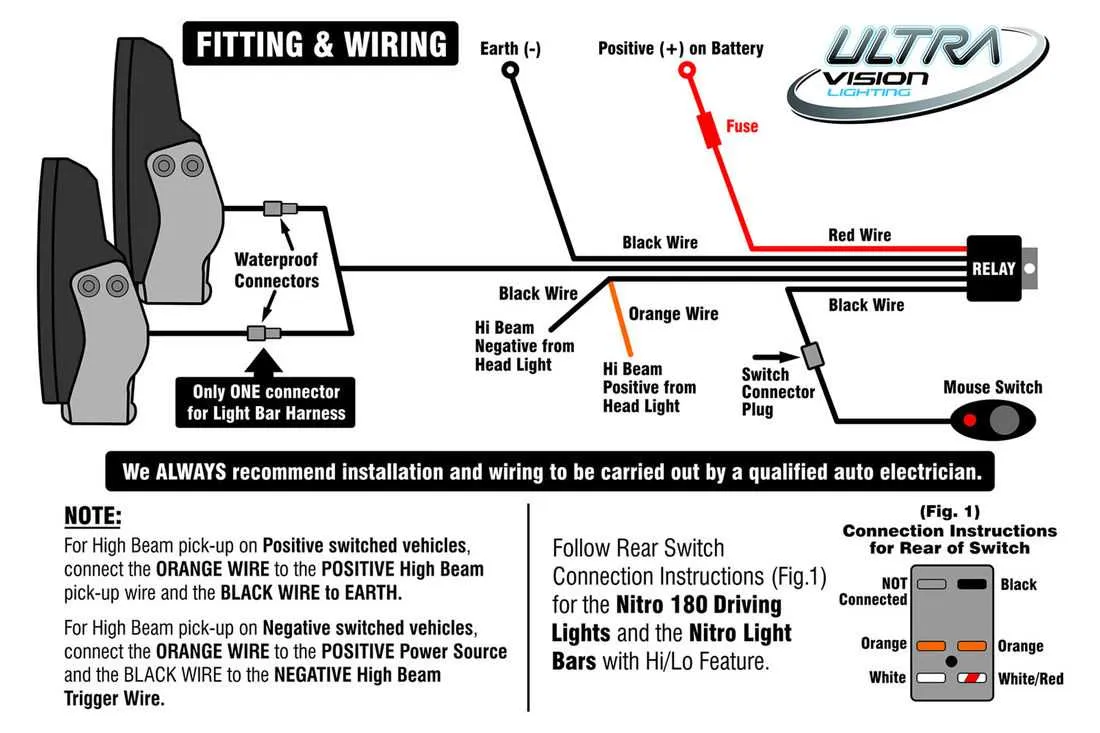
For optimal connection of your high-power illuminators, connect the positive terminal of the power source to the positive terminal of the unit, ensuring secure and insulated contacts. The negative terminal should be linked to the ground point, typically a metal chassis or another grounding location. Use 12-gauge or thicker wire for main connections to prevent voltage drops and ensure durability in harsh environments.
Always include a fuse rated for the appropriate current draw in the positive lead, ideally placed near the power source. This safeguards the system from potential electrical surges. Additionally, incorporate a relay to handle the switching mechanism efficiently. Ensure the relay is rated for the total current the setup will draw and place it as close as possible to the power source for minimal voltage loss.
If you plan to integrate an on/off switch, use one that is rated for the current and voltage of your system. For longer wiring runs, consider upgrading to a larger gauge wire, like 10-gauge, to minimize power loss over distance. Keep the wiring organized, and use zip ties to prevent accidental short circuits. To increase the lifespan of the illuminators, check the wiring regularly for wear or damage and replace any compromised components immediately.
Understanding the Basic Wiring Components for LED Bar Lights
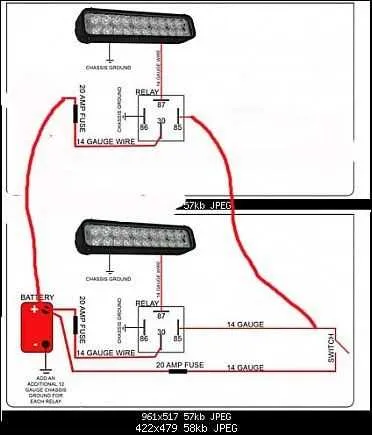
The power source is the starting point when setting up your fixture. Ensure that the voltage and amperage match the specifications of the unit you’re working with. Using an adapter that converts your supply to the appropriate level is crucial to prevent damage.
Connectors are used to link the various parts of the setup. Quick connectors, like waterproof ones, provide ease of installation while protecting against moisture and dirt. If you’re using a strip, make sure the connections are secure to avoid flickering or malfunctioning.
Fuses act as safety components, protecting against short circuits and power surges. Ensure the fuse rating matches the electrical load; an under-rated fuse can blow easily, while an over-rated one might fail to protect the system properly.
Resistors help regulate current flow to prevent excessive energy consumption. They should be placed at the right position in the circuit to ensure longevity of your equipment. Always double-check the resistance value against the system’s needs.
Switches and controllers allow for operation and control of brightness or patterns. A dimmer switch or a multi-function controller can add versatility, but make sure it’s compatible with your setup’s specifications.
For mounting and placement, using the correct brackets and fasteners is essential. Over-tightening can damage components, while under-tightening may lead to instability or the fixture shifting.
Step-by-Step Guide to Connecting a Light Strip to a Vehicle’s Power System
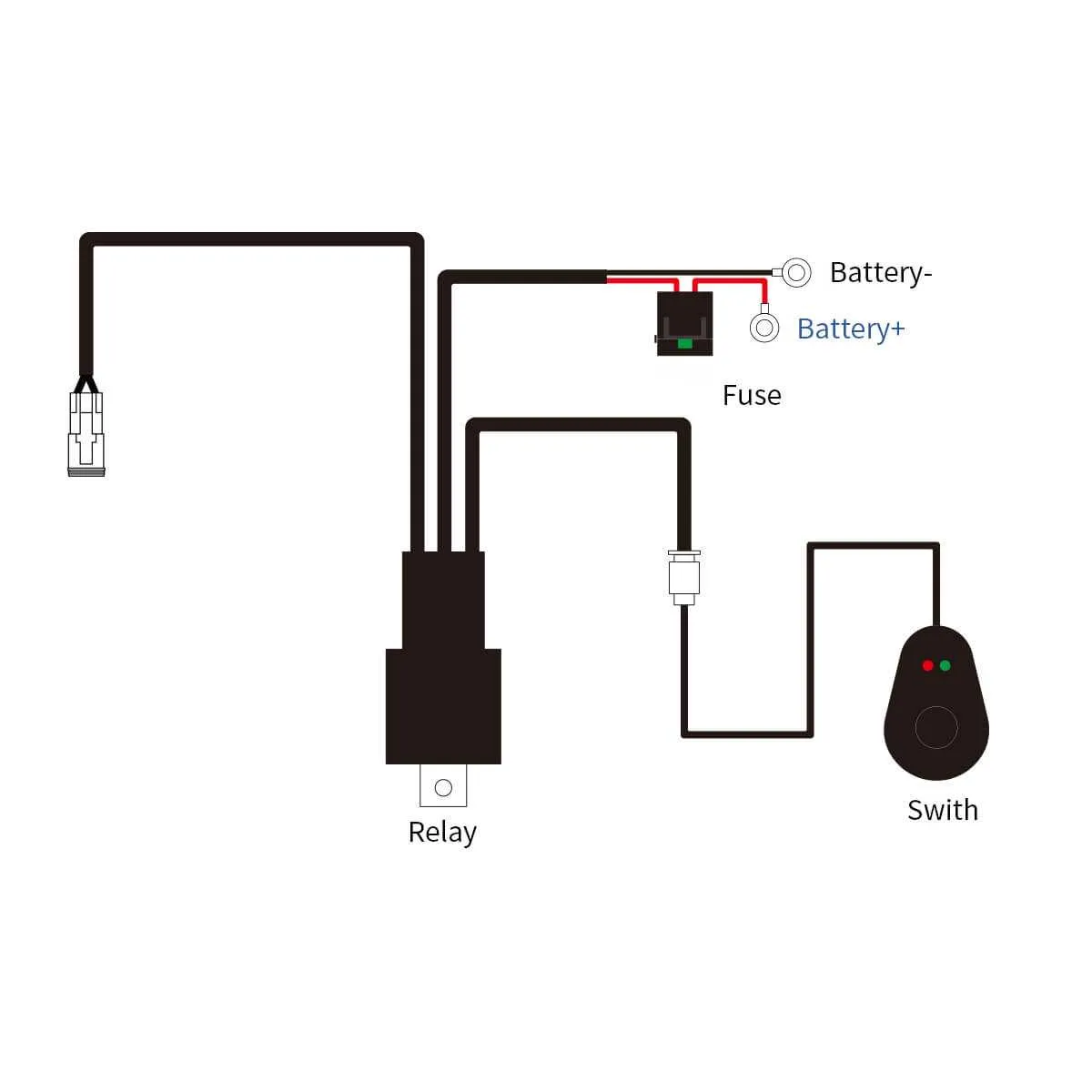
1. Disconnect the Vehicle Battery
Start by removing the vehicle’s battery terminal to ensure safety while handling the electrical components. This minimizes the risk of shorts and electric shocks during installation.
2. Identify the Power Source
Locate a suitable power source in the vehicle, such as the fuse box or directly from the battery. The connection must provide a steady 12V DC current for optimal functionality. Use a voltage tester to confirm the power source’s output before proceeding.
3. Run the Power Cables
Route the positive and negative cables from the power source to the installation location. Ensure cables are secure and away from moving parts or sources of heat. Use cable ties to avoid any loose wiring.
4. Install the Relay
The relay allows for an on/off switch to control the power to the unit. Connect the relay to the positive cable, ensuring it is securely mounted to avoid shifting during operation. Make sure to use a relay that matches the amperage rating of your equipment.
5. Connect the Switch
Install the switch in a convenient location, such as on the dashboard or near the driver’s seat. Run a wire from the switch to the relay’s control input terminal. This wire will allow you to activate the system when needed.
6. Attach the Ground Wire
For proper functioning, connect the negative cable to a solid grounding point on the vehicle’s frame or chassis. Ensure the connection is clean and free of rust or paint for maximum conductivity.
7. Secure the Unit
Fix the light assembly in place using appropriate mounts. Double-check the positioning to avoid obstruction of other vehicle systems and ensure it’s protected from road debris and weather conditions.
8. Test the System
Reconnect the vehicle battery and test the entire system. Flip the switch to check if the unit operates correctly. If there are issues, double-check connections and verify all wiring is in place and functioning properly.
9. Finalize the Installation
Once verified, tidy up all wiring, ensuring no exposed parts are left. Secure the cables along the vehicle’s frame to prevent wear or accidental damage during operation.
Troubleshooting Common Electrical Problems with Auxiliary Lighting Strips
When encountering issues with your auxiliary lighting setup, it’s essential to focus on the most frequent culprits. Follow these steps for a precise diagnosis:
- Inconsistent Power Supply: Ensure a steady connection to the power source. Test the voltage output and check for any signs of instability. If voltage is low, inspect the battery or relay system for faults.
- Loose or Corroded Connections: Inspect all terminals and connectors. Corrosion or loose connections can prevent proper operation. Clean connectors with contact cleaner and tighten connections for a secure fit.
- Short Circuits: If the system flickers or doesn’t function, there might be a short circuit. Use a multimeter to check for continuity and identify any areas where wiring is improperly grounded.
- Overheating Components: Excessive heat can damage the internal components. Ensure the auxiliary lighting unit has adequate ventilation and isn’t subjected to prolonged use without cooling periods.
- Incorrect Fuse Rating: Double-check the fuse ratings for compatibility with your setup. An incorrect rating can lead to blown fuses or insufficient power delivery. Replace with the recommended fuse value.
- Defective Control Switch: A malfunctioning switch can lead to intermittent performance. Test the switch with a multimeter to ensure it’s operating correctly and replacing it if necessary.
By systematically checking these factors, you’ll be able to identify and resolve most common electrical issues swiftly, ensuring your setup operates without a hitch.