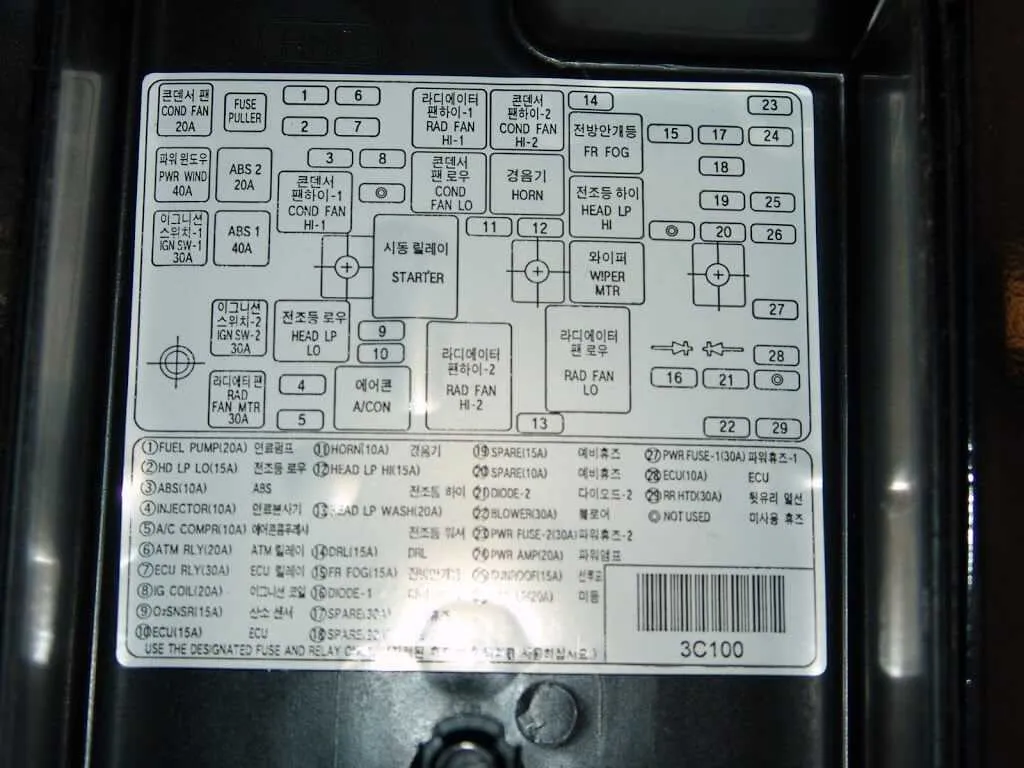
If you’re troubleshooting or maintaining the electrical components of your vehicle, locating and understanding the placement of each circuit is key. This guide provides a clear, step-by-step overview of the exact positions for relays, connections, and protected circuits. Start by referring to the primary panel located near the driver’s side or under the hood. Be sure to confirm the layout for your specific model to avoid any confusion with other configurations.
For interior electrical components: The main panel is typically situated beneath the dashboard, close to the driver’s side. Inside, you will find an organized system for controlling lights, entertainment units, and climate controls. If any of these features are malfunctioning, checking for a blown relay or disconnected wire should be your first step.
For engine bay components: A secondary unit in the engine compartment controls high-power circuits, such as the ignition system and air conditioning compressor. If your vehicle has started to show signs of electrical strain–such as dim lights or failure to start–inspect the power distribution block carefully for any potential issues.
Understanding these key locations will help you pinpoint electrical issues faster and keep your vehicle in optimal working condition. Be sure to double-check the individual relay and fuse ratings to avoid mismatches when replacing them.
Understanding the Electrical Component Layout for 2004 Models
Locate the main power distribution panel under the dashboard, typically on the driver’s side. Check the vehicle manual for precise location based on the make and model of your car. The schematic for electrical circuits is printed on the panel cover for quick reference.
Inspect each row of connections for a clear label of each section–typically marked as “A” through “F”. Ensure you understand the corresponding amperage values indicated for each section. This helps in identifying circuits such as lights, airbags, or power windows.
For troubleshooting, always use the vehicle’s wiring codes. Some circuits may be fused in groups for specific areas, like the HVAC system or audio components. Follow the color-coding and the current load for each circuit to address any issues quickly.
If you are replacing any protective elements, ensure the correct amperage rating is used. This prevents overloading and potential damage to the vehicle’s electrical system.
Locating and Identifying Fuses in the 2004 Model Fuse Box
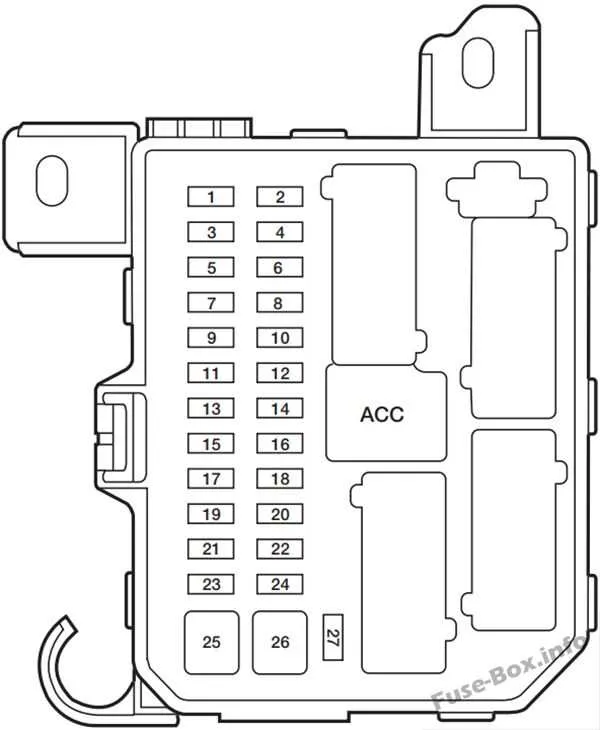
Start by accessing the main electrical panel located in the interior or engine compartment, depending on the vehicle model. Check the cover for a label or legend detailing the placement of each component. This label is essential for quickly finding the correct circuit and avoiding confusion.
When inspecting the interior unit, it is usually positioned beneath the dashboard on the driver’s side, near the lower section of the steering column. For the engine compartment unit, lift the hood and locate the assembly near the battery or near the front of the engine bay. Ensure the vehicle is turned off before proceeding.
Each component is typically housed within a plastic slot that can be removed for inspection. Use a fuse puller tool or a pair of needle-nose pliers to gently remove the element. Visually inspect the wire inside; a broken or discolored wire indicates a malfunctioning component. Always replace with a new part of the same amperage to avoid damage to the vehicle’s electrical system.
If the components are difficult to identify, a detailed map can usually be found within the owner’s manual, listing each component’s specific function. In case of uncertainty, it’s safer to consult this guide before attempting any replacements.
Understanding Fuse Assignments and Their Functions in a 2004 Vehicle’s Electrical System
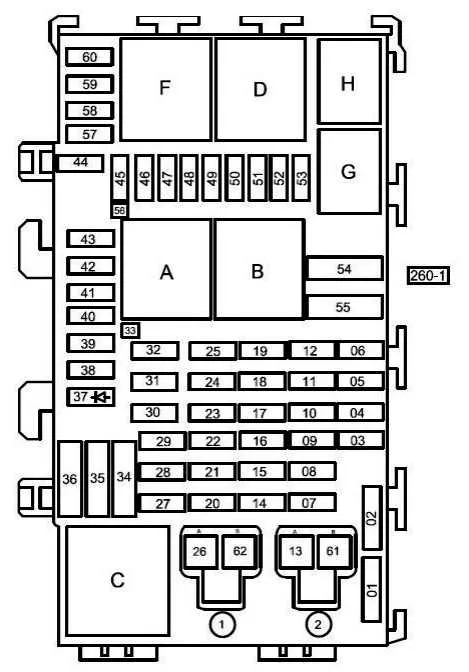
The distribution of electrical current in your car is carefully managed by the components in the panel. Each component is responsible for protecting specific circuits from damage due to overcurrent. If you’re troubleshooting or performing maintenance, identifying each component’s function is key. For instance, a fuse marked for “engine management” typically handles the power supply to critical engine systems, while one dedicated to “lighting” ensures that headlights and interior lights are protected from voltage spikes.
When dealing with individual circuits, make sure to check the amperage rating on each protection device. Using the wrong size can lead to electrical failure or even damage. A device dedicated to the air conditioning might have a 20-amp fuse, whereas the one for the radio could be rated at 10 amps. This difference is due to the varying electrical loads each component requires. Always replace with the same amperage to maintain safety and efficiency.
Several circuits are often grouped together to share a protection device. For example, a pair of circuits used for the windshield wipers and washers may be linked to one fuse. In such cases, if either component encounters a malfunction, the fuse will blow to prevent further damage to the system.
Referencing a layout that shows each component’s allocation is essential when performing checks or replacements. Note that some fuses are responsible for high-priority systems such as airbags or the braking system, which must not be neglected in case of malfunction. Regularly inspect and test these components to ensure reliable operation.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting for the Electrical Panel in a 2004 Vehicle Model
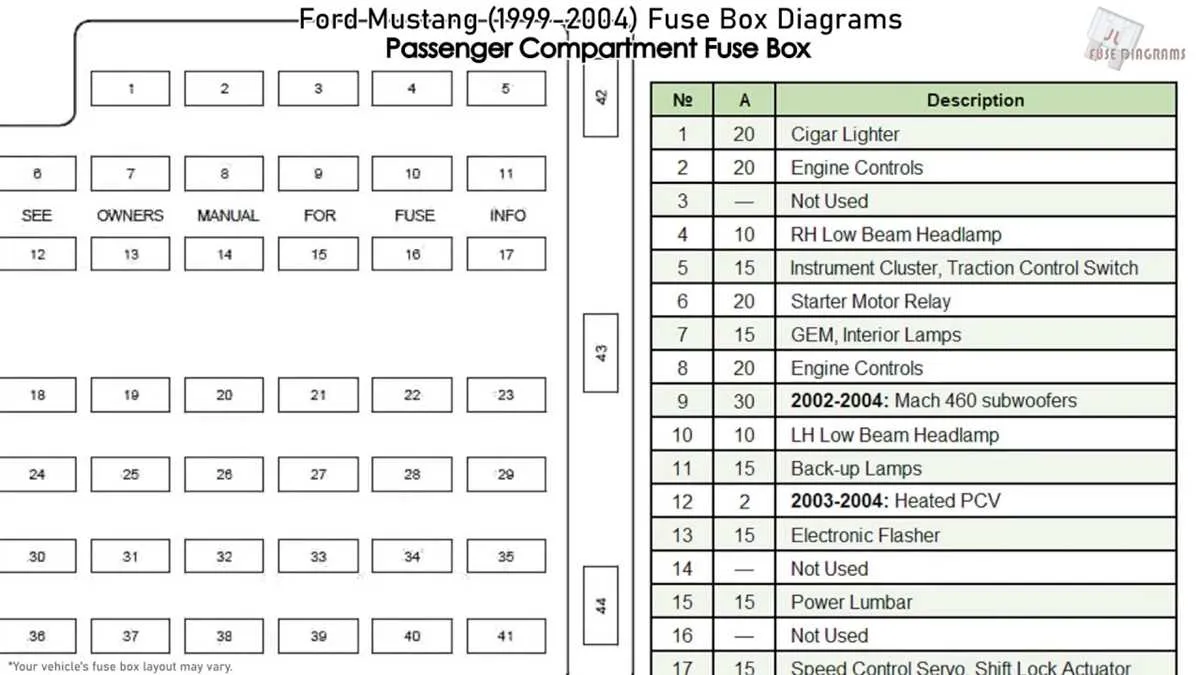
If electrical components stop working or malfunction, it’s likely caused by problems within the panel that distributes power to various parts of the vehicle. Here’s how to diagnose and fix common issues:
- Blown Connections: Inspect the metal strips inside the panel. A loose or burnt strip often causes circuits to stop working. Replace any damaged strips and check the affected system to see if the issue resolves.
- Loose or Corroded Terminals: If the electrical contacts seem worn out or corroded, clean them with a contact cleaner or replace the connectors. Loose terminals often prevent proper conductivity and cause power loss to certain features.
- Malfunctioning Relays: A faulty relay could cause intermittent electrical failures. To test, remove the relay and swap it with a similar one. If the issue is resolved, replace the faulty relay with a new one.
- Damaged Wires: Damaged or frayed wires can cause a short circuit. Inspect the wiring for visible signs of wear or damage. If you find any, rewire the affected area or repair the broken wires with electrical tape or connectors.
- Overloaded Circuits: Excessive power draw can overload the panel, causing it to stop working or malfunction. Check for any aftermarket accessories that might be drawing too much power, and disconnect them temporarily to see if the issue resolves.
Before making any repairs, always disconnect the vehicle’s battery to avoid shock hazards. If issues persist after addressing these common causes, seek professional help to prevent further damage to the vehicle’s electrical system.