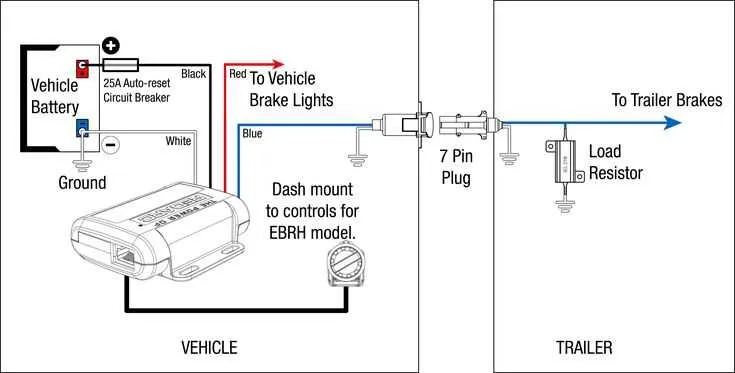
Ensure the correct installation of electrical connections to activate the stopping system on your towed unit. Start by securing a reliable ground connection between the towing vehicle and the towed unit’s frame. This will guarantee a consistent power flow for the braking mechanism.
Next, connect the power source from the vehicle to the braking controller using a dedicated wire, typically of 12V DC. This wire should be routed in a way that prevents damage during movement and should not interfere with any moving parts. Make sure to use an appropriate fuse to safeguard the system against electrical surges.
Important: Double-check the connections at both ends. Ensure that each wire is insulated properly to avoid short circuits. The power line for the braking system should be clearly marked for easy identification during troubleshooting or future upgrades.
Install the connector for the brake controller in a weatherproof enclosure to prevent moisture damage. Regularly inspect the system, especially the cable that runs between the two units, to ensure there are no frays or wear signs that could impair functionality.
Tip: Using color-coded wires for different functions (e.g., power, ground, signal) simplifies installation and future maintenance tasks.
Electrical Connection Guide for Towed Vehicle with Brake System
Ensure the correct connection of your towed vehicle’s brake system by following these essential steps. The key components that need to be linked are the brake controller, electric circuit, and connectors.
The brake controller must be linked to the 12V power supply from the towing vehicle. It connects to the main junction of the braking mechanism through a 7-pin or 13-pin connector, depending on the setup. Ensure all contacts are properly secured to avoid faults.
Proper grounding is critical for the effective operation of the system. The ground wire should be connected to the vehicle’s chassis and to the braking system’s frame. This ensures proper current flow for safe operation.
For electric brakes, the control wire from the towing vehicle must be connected to the brake mechanism, often through a dedicated plug. The current should activate the braking system in proportion to the towing vehicle’s braking force, ensuring synchronized stopping.
Verify that the signal wire is routed from the controller to the brake unit, ensuring clear communication between the two systems. If you are using a four-pin connector, additional wiring may be needed for enhanced stability and functionality.
Test the setup after installation to make sure all connections are functional. The braking system should activate when the towing vehicle’s brakes are engaged, providing seamless deceleration for both vehicles.
Step-by-Step Guide to Connecting Brake Lights
Start by locating the power source. Identify the positive wire from the vehicle’s electrical system that supplies current to the lights. Use a voltage tester to ensure proper voltage is available.
Next, connect the positive wire to the input terminal of the first light unit. Use high-quality connectors for a secure and corrosion-resistant connection. Make sure the wire is insulated properly to prevent short circuits.
Link the lights in sequence by connecting each light’s positive terminal to the next. Use a solid and reliable junction to maintain strong conductivity throughout the system.
For the negative connection, run a ground wire from the last light unit back to the vehicle’s chassis. Ensure the grounding point is clean, free from paint, and tightly secured to prevent poor connection.
Install a fuse or circuit breaker in line with the positive wire to protect the electrical system from overloads. Choose a fuse that matches the power rating of the entire light circuit to avoid unnecessary disruptions.
After completing the connections, test the system by activating the vehicle’s brake lights. Verify that all lights illuminate properly and that no flickering or malfunction occurs.
Ensure proper wire placement along the vehicle to avoid potential damage or wear. Secure wires using cable ties, keeping them away from moving parts or areas prone to heat.
Once verified, double-check all connections for security and continuity. Inspect the system periodically to maintain reliable function over time.
Identifying Components in the Brake System Circuit
Start by locating the power supply, usually a 12V connection, which powers the entire system. This is typically connected directly to the vehicle’s battery or a dedicated fuse. The next key component is the control unit, which receives signals from the towing vehicle’s braking mechanism. It is often placed near the battery or control box for ease of access.
The actuator, which controls the brakes’ response, is usually found along the axle. Ensure that the connections are secure and not exposed to weather damage. The sensor, which detects deceleration and sends feedback to the control unit, plays a critical role in activating the braking action. Position it near the hitch or coupling point for optimal functionality.
Check the grounding wire, which ensures proper electrical flow. This is typically connected to the frame of the vehicle or coupling system. A solid ground connection is crucial to prevent intermittent signals. Additionally, the signal wire that links the brake controller to the braking actuator must be intact, with no frays or signs of wear.
For the best results, regularly inspect the connector points to avoid corrosion, especially where components meet the vehicle. Tight, clean connections ensure that the system functions reliably under varying conditions.
Troubleshooting Electrical Issues in Brake Connections
First, verify the continuity of the circuit. Use a multimeter to check for any breaks in the path, especially between the power source and the connector points.
If no issues are found in the wiring, check for corrosion at the connection points. Clean all terminals and connectors using a wire brush or contact cleaner, ensuring a solid metal-to-metal connection.
Examine the ground connection closely. A poor ground can lead to malfunctioning of the electrical system. Make sure the ground wire is securely attached to a clean, rust-free metal surface.
If the power supply seems insufficient, check the fuse box for blown fuses or damaged relays. Replace any faulty components with the correct rated replacements.
- Test the voltage at each connector point to ensure it matches the required specifications.
- Inspect the condition of all cables for signs of fraying, kinking, or visible damage.
- If using a controller, ensure it is properly configured and synchronized with the electrical system.
Sometimes, faulty connectors or plugs may be the culprit. Test each connection for wear and tear, replacing any that show signs of degradation.
Lastly, ensure that all wiring is routed properly to avoid sharp bends that could lead to wear or intermittent connections. Use protective sheathing where necessary to safeguard the conductors.