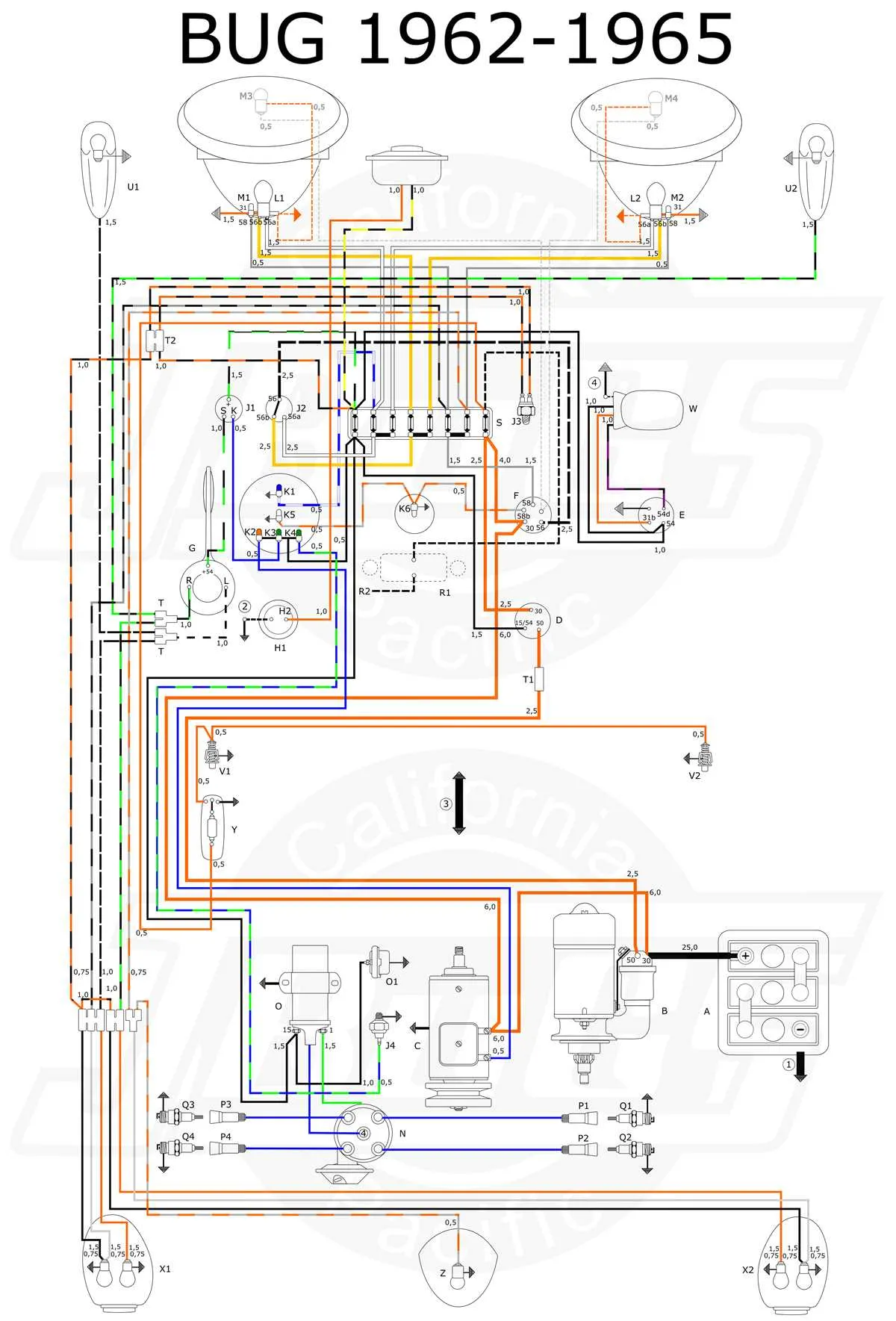
When dealing with electrical issues in older models, it’s crucial to identify the correct layout of the system. Begin by locating the central electrical panel, which is responsible for distributing power to various circuits. Understanding the placement of connectors and relays will save you significant time when troubleshooting. Ensure that all terminals are clean and corrosion-free, as this can affect the overall performance.
Refer to a detailed schematic to pinpoint where each component connects within the vehicle’s electrical framework. The diagram will indicate the precise configuration of the system, showing both the main connections and auxiliary units. Pay attention to color codes for wires, as they simplify the identification process for each function.
Before you start any repair or replacement, it’s wise to disconnect the main power source to avoid any electrical shorts or accidents. Always check for consistency in the flow of current after completing a job. If issues persist, revisit the schematic to verify that all components are properly linked, ensuring everything is connected according to specifications.
Using the correct reference guide will help you avoid common mistakes and improve the efficiency of your work. A reliable schematic is an essential tool in diagnosing faults and performing repairs without unnecessary complications.
Electrical System Overview
For efficient troubleshooting, always begin by checking the main electrical distribution panel under the dashboard. The first row of connections typically handles the essential components such as headlights and interior lights. If you encounter issues with the electrical systems, focus on the 10A and 15A slots as these often regulate key functions like the ignition system and windshield wipers.
For power distribution, pay close attention to the relays located in the secondary panel. These manage high-demand systems like the engine control unit (ECU) and climate control. Ensure these relays are securely fastened and functioning properly. If necessary, use a multimeter to check for continuity and verify the integrity of the connections.
For diagnostic purposes, ensure that the connections on the auxiliary panel are free of corrosion. Any sign of moisture buildup or rust should prompt a cleaning and re-tightening of the terminals. Faulty grounding can often lead to malfunction in the rear lights and electrical locks, so always check grounding straps and connections.
Finally, remember that issues with certain accessories or audio systems can stem from a weak or overdrawn connection in the power feeds. If accessories aren’t functioning properly, isolate the specific circuits and inspect the wiring for shorts or fraying, especially where wires exit the main connection terminals.
How to Identify the Electrical Component Location in a Volkswagen Beetle
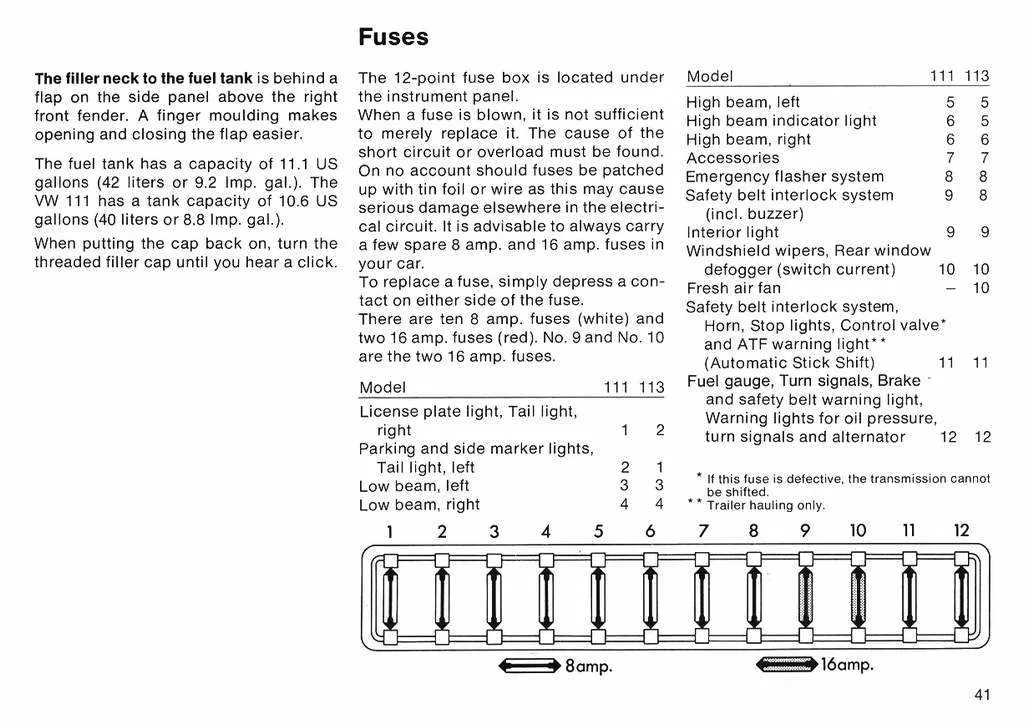
To find the electrical control unit in your vehicle, start by checking beneath the dashboard on the driver’s side. You may need to remove the panel beneath the steering wheel to access it. Another key location is near the battery under the hood; this area contains a secondary setup for larger components. Inspect the fuse connections on the driver’s side kick panel, as these often house additional parts for specific circuits. Finally, consult your vehicle manual for exact details on placement for your specific model year.
Note: Make sure to disconnect the vehicle’s battery before handling any electrical components to avoid short circuits or damage to the system. If you are unsure about the locations, reference the vehicle manual or seek professional assistance.
Understanding the Function of Each Fuse in the Vehicle
Check your car’s manual for a detailed guide on each protective component’s location and function. Knowing the specific amperage rating is key when replacing any of these components, as improper replacements can cause malfunction or even damage the electrical system. Below is a breakdown of typical functions:
15A: Often powers the headlights or rear lights, ensuring proper illumination for driving. It’s crucial for nighttime visibility.
20A: Controls the radio, air conditioning, and sometimes the dashboard lights. If the car’s entertainment system or ventilation system stops working, this is the first to check.
25A: Generally supplies power to the ignition or central locking system. A blown component here could indicate issues with starting the engine or securing the vehicle.
30A: Powers larger electrical systems such as the cooling fans or fuel system. A failure can lead to overheating or fuel delivery issues.
10A: Often linked to the horn or indicators. If these fail to function properly, inspect this section first.
5A: Usually assigned to smaller accessories, such as the interior lights or sensors. A blown unit may result in a lack of interior lighting or sensor malfunctions.
Always use the appropriate amperage when replacing any unit to maintain the vehicle’s safety standards. Don’t bypass or try to replace it with a higher-rated one as it could lead to severe electrical damage.
Steps to Replace a Blown Fuse in Your Car
To replace a damaged electrical component, follow these steps:
- Locate the fuse panel – Typically, it is found under the dashboard or near the driver’s side. Check the manual for its precise location.
- Turn off the ignition – Ensure the car is completely powered off before working with electrical parts.
- Identify the faulty circuit – Check the label on the panel for the circuit that needs replacement. It will usually show which device is affected.
- Remove the damaged part – Use a fuse puller or a pair of needle-nose pliers to safely take out the blown component.
- Check the new part’s specifications – Ensure the replacement is of the same amperage rating as the old one.
- Insert the new component – Place it into the same slot, making sure it is securely seated.
- Test the system – Turn the ignition back on to confirm the issue is resolved and the circuit is functioning.
If the new part blows quickly, there may be an underlying issue in the electrical system that requires further investigation.