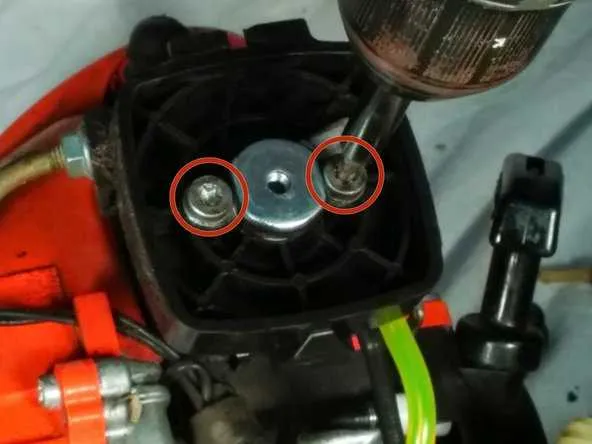

When working on maintenance or repairs, having a clear and detailed layout of a tool’s internal components is crucial. This helps ensure that each part is correctly identified and replaced when necessary. Whether you’re fixing the cutting mechanism, adjusting the fuel system, or troubleshooting electrical issues, understanding the full structure of the equipment speeds up the process and reduces the likelihood of errors.
Understanding the assembly of the machine starts with visualizing the core sections. First, focus on the main housing, which contains the drive shaft, gear mechanism, and ignition system. Each segment has specific parts that wear out over time, such as drive belts and spark plugs. Knowing the exact configuration and the order in which the parts interact will save valuable time during reassembly.
Next, inspect the cutting mechanism, which typically includes the spool and cutter head. Pay attention to how each piece connects, as improper alignment can lead to poor performance or damage. This component is especially prone to wear from continuous friction, so replacing worn parts promptly will maintain optimal functionality.
Another area that requires close attention is the power unit, where you’ll find the carburetor, fuel lines, and air filter. Any clogs or leaks here can drastically affect performance. A thorough understanding of how these elements connect and function together is essential for proper maintenance and repair.
Detailed Breakdown of Trimmer Components
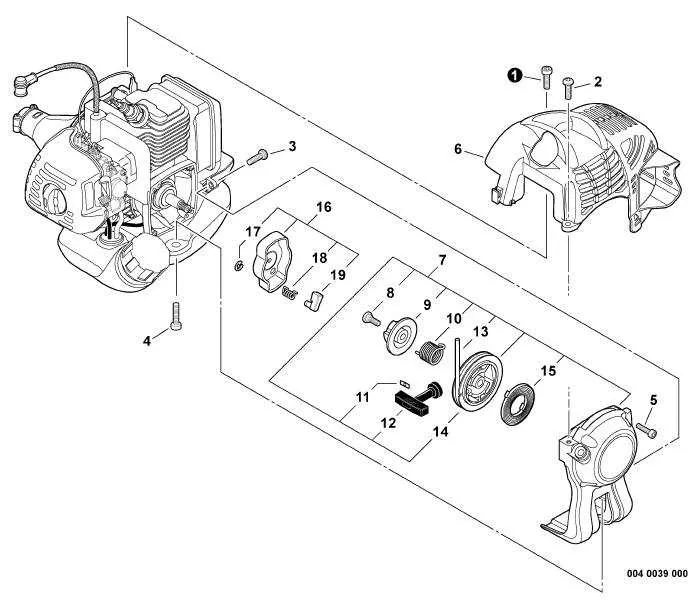
For efficient maintenance or repair of your trimmer, start by consulting the component layout for easy identification. It helps in understanding the function of each part and ensures quick troubleshooting.
The motor assembly is central to the system’s operation, providing the necessary power to the string or blade mechanism. Around the motor, check the air filter and spark plug. A clogged filter can lead to poor engine performance, while a worn spark plug causes misfiring. Replace these parts regularly to avoid starting issues.
Inspect the spool area where the line is wound. If the line is incorrectly loaded or damaged, it could result in uneven cutting. Regularly check for wear, especially if the trimmer is used in tough conditions like heavy grass or thick weeds. The line feed system should also be kept clear of debris to ensure smooth operation.
Examine the handle and shaft, ensuring that all components are tightly fastened. Loose parts can lead to vibrations, making the trimmer harder to control and potentially damaging other components over time. Pay attention to the trigger mechanism, which should move smoothly without sticking.
Don’t forget about the guard that protects both the user and the motor. Ensure it is securely in place and free from cracks or excessive wear. This part plays a crucial role in reducing debris ejection, especially in dense vegetation.
Finally, inspect the drive system, whether it’s a flexible shaft or direct drive. Any irregular noise or vibration may indicate a misalignment or a worn-out bearing. Ensure that all connections are tight and lubricated to prevent friction and extend the lifespan of the tool.
Identifying Key Components in the Manual Breakdown
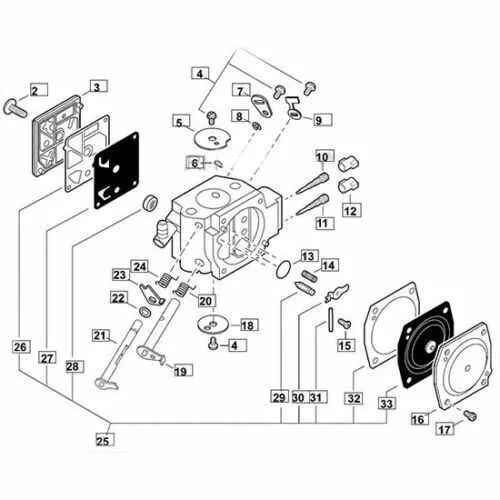
To quickly identify the most crucial elements of your device, focus on the following components and their roles in its functionality. These are often the parts that require frequent maintenance or replacement.
| Component | Function | Maintenance Tip |
|---|---|---|
| Motor | Drives the entire system. Converts fuel or battery energy into motion. | Ensure air vents are clear to prevent overheating. Regularly check for spark plug wear. |
| Cutting Head | Responsible for trimming grass and small plants. Features rotating blades or lines. | Replace cutting lines regularly. Inspect for cracks or damage to blades. |
| Throttle Control | Regulates speed and power output of the motor. | Lubricate periodically to ensure smooth operation. Test responsiveness to ensure it adjusts properly. |
| Fuel Tank | Stores fuel, ensuring a steady flow to the motor. | Inspect for leaks. Use stabilizer to prevent fuel degradation in long-term storage. |
| Handle | Provides stability and control during use. | Check for cracks or wear in the handle material. Tighten any loose screws for added safety. |
| Air Filter | Prevents debris from entering the engine, ensuring efficient performance. | Clean or replace regularly to prevent clogging and engine strain. |
Understanding these key elements will allow you to quickly troubleshoot issues and perform necessary maintenance. Regular inspection of these components ensures a longer lifespan and smoother operation of the equipment.
How to Use the Diagram for Maintenance and Repair
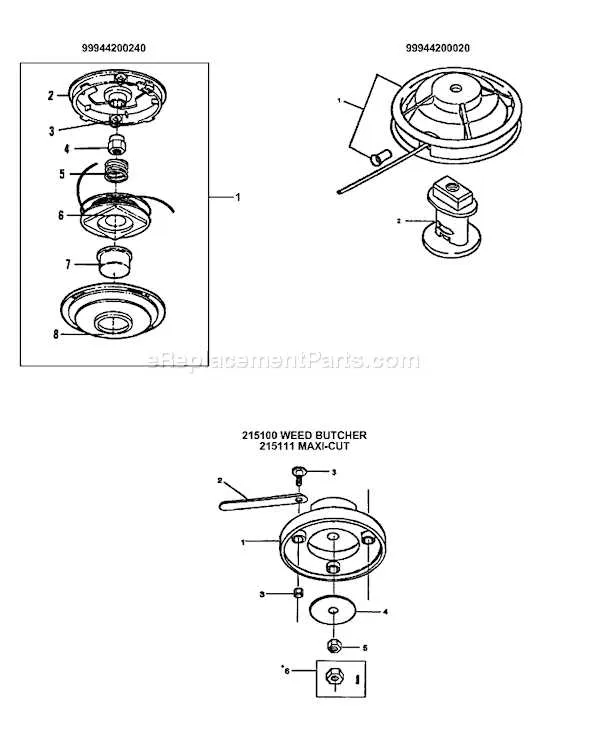
Start by locating the specific section in the visual reference that corresponds to the malfunctioning component. Identify the part by matching the item’s description with its labeled number. This will guide you to its location and function within the assembly.
When performing regular maintenance, such as cleaning or lubrication, check the components highlighted for wear. Cross-reference them with the illustration to ensure correct reassembly after maintenance. Regularly inspecting moving parts, like the shaft or housing, helps in detecting signs of damage or wear.
For repairs, use the diagram to disassemble the unit carefully. Follow the sequence shown in the visual, noting any special tools or techniques required for specific parts, like screws or locking mechanisms. Ensure that each part is replaced or fixed with the correct version to avoid incompatibility or malfunction.
Tip: After reassembling, compare the overall structure with the reference to confirm all parts are correctly aligned. Regularly check fastenings and connections to prevent loose components during use.
Utilizing the visual guide ensures efficient troubleshooting, reduces the chances of errors, and speeds up the repair process, saving both time and cost.
Ordering Replacement Components Based on the Schematic
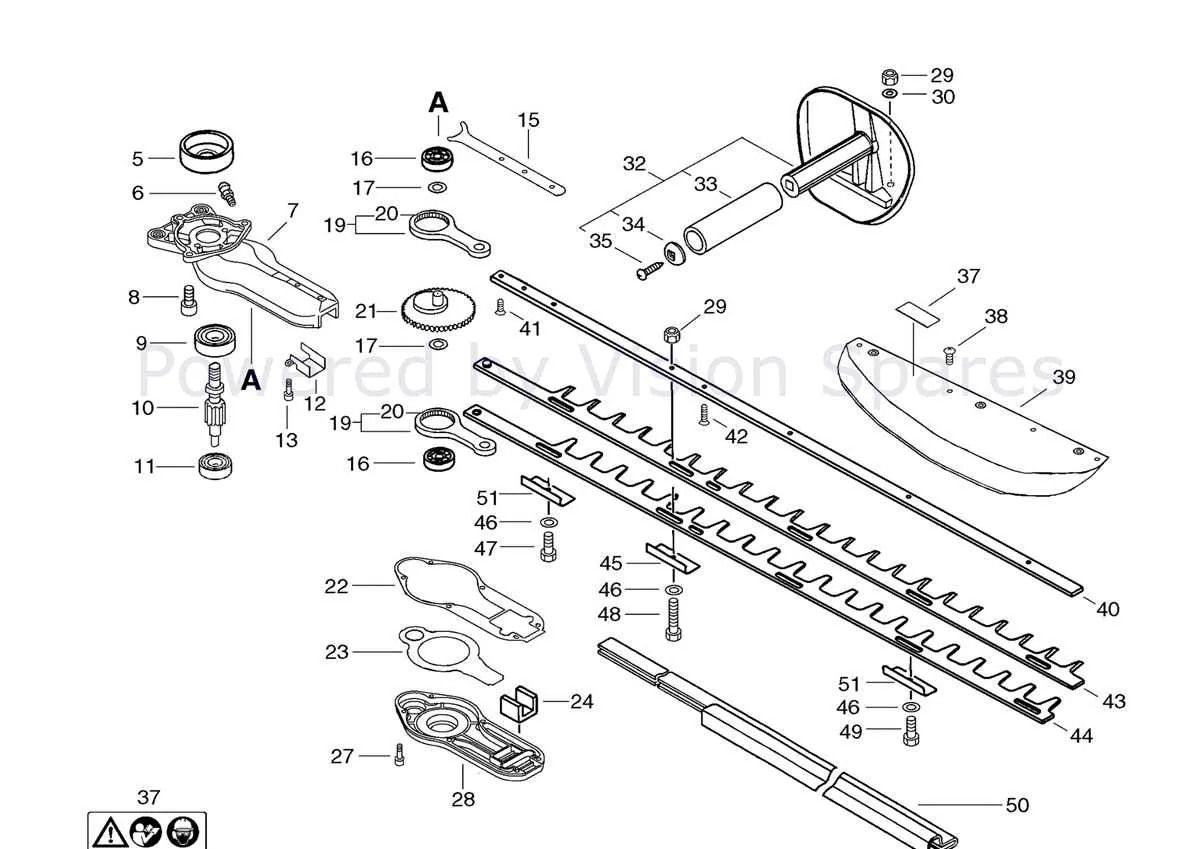
To ensure accurate replacements, follow these steps when ordering individual components from the schematic:
- Identify the specific item by referencing its part number in the chart.
- Double-check the compatibility of the replacement with your current model.
- Consult the manual or online resources for detailed specifications, such as size or material type.
- Order from authorized retailers or the manufacturer’s official website to avoid counterfeit items.
- Consider purchasing in bulk for frequently replaced components, as this can reduce overall costs.
When placing your order, it’s helpful to:
- Use the exact part code for faster processing and accuracy.
- Verify the quantity needed, especially for small components like screws or washers.
- Check for available warranties or return policies on ordered items.
If unsure about a specific part, contacting customer support or a technician with model details may be necessary to avoid errors.