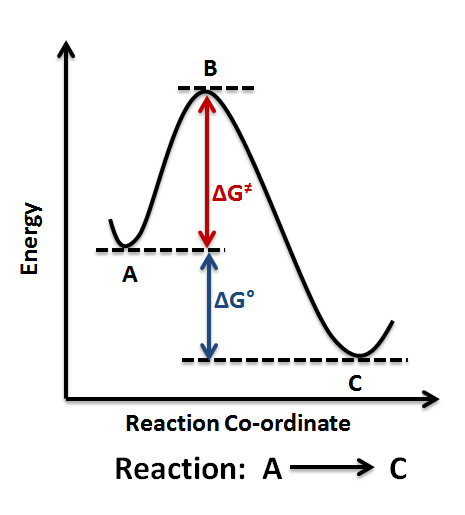
The fully filled in reaction coordinate diagram is displayed below.
Potential Energy Diagrams – Chemistry – Catalyst, Endothermic & Exothermic Reactions
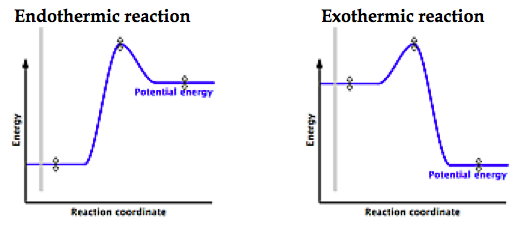
This reaction is also exothermic because the energy of the products is lower than that of the. A reaction coordinate diagram shows the energy changes that take place in each of Do not confuse these terms with exothermic and endothermic, which are.
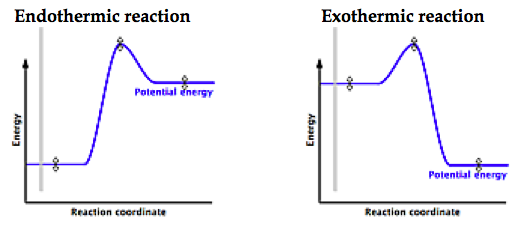
Exothermic Reaction. Endothermic Reaction.
Reaction Coordinate Diagram. Energyproducts > Energyreactants.
Energyproducts < Energyreactants. A typical reaction coordinate diagram for a mechanism with a single step is ΔE on the diagram, determines whether the reaction is exothermic or endothermic.
This is an example of an exothermic reaction. Exothermic reactions: Heat is released. .
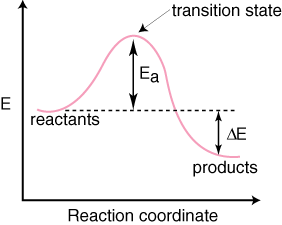
Energy diagrams for endothermic and exothermic reactions.You may recall from general chemistry that it is often convenient to describe chemical reactions with energy diagrams. In an energy diagram, the vertical axis represents the overall energy of the reactants, while the horizontal axis is the ‘reaction coordinate’, tracing from left to right the progress of the reaction from starting compounds to final products. This is an example of an endothermic reaction.
In Julie’s case, when calcium chloride was dissolved in water, the system released heat into the surroundings, the flask, and thus the flask felt hot. This is an example of an exothermic reaction. 1! Energy/Reaction Coordinate!
Diagrams! Thermodynamics, Kinetics!
Dr. Ron Rusay” A Reaction Coordinate (Energy) Diagram Thermodynamic Quantities Gibbs standard free energy change (ΔGo) Enthalphy (ΔHo): the heat given off or absorbed during a reaction.
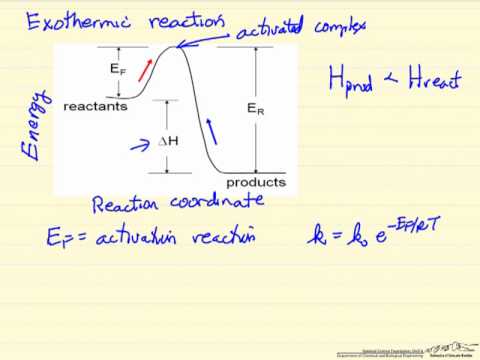
And a reaction coordinate diagram where the energy level of B ends up lower than A is exothermic (delta E is negative): Activation Energy The activation energy is important in a reaction. A reaction coordinate diagram can also be used to qualitatively illustrate kinetic and thermodynamic control in a reaction.
Energy profile (chemistry)
Figure 9:Kinetic and Thermodynamic Control: A. Product B is both the kinetic and thermodynamic product and B. Product A is the kinetic product while B is the thermodynamic product.Energy profile (chemistry) – WikipediaSparkNotes: Reaction Kinetics: Reaction Mechanisms: Mechanisms of Chemical Reactions