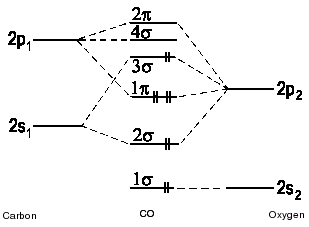
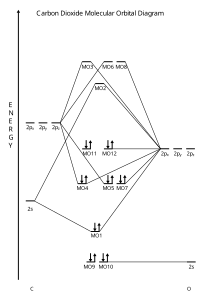
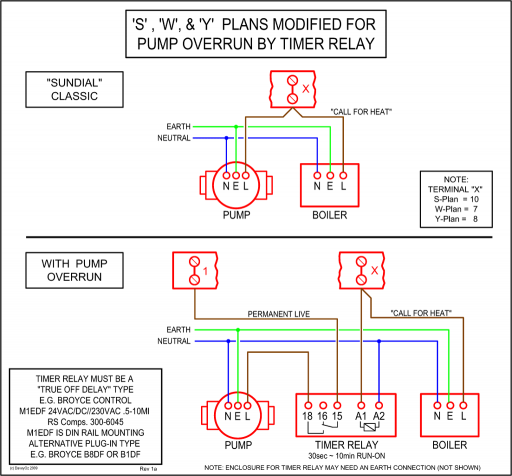
Hey I was wondering if anyone could explain/help me understand the molecular orbital diagram of CO, this the energy level diagram I have copied out of my. A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining MO diagrams can explain why some molecules exist and others do not.
. combinations such as CO and NO show that the 3σg MO is higher in energy.
Mulliken came up with theory known as Molecular Orbital Theory to explain questions like above. According to Molecular .

Molecular Orbital Diagram for CO. Hey I was wondering if anyone could explain/help me understand the molecular orbital diagram of CO, this the energy level diagram I have copied out of my.
The electronic configuration of carbon and oxygen atom are 1s²2s²2p² and 1s²2s²2p⁴ respectively. There are 4 electrons in the outer shell of carbon and 6.A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) molecular orbital method in particular.
EXAMPLE #2: Carbon Monoxide, CO Recall: The MO energy level diagram for O 2 is not the same as the MO energy level diagram for the C 2 gas phase fragment. This is also true for molecular orbitals.
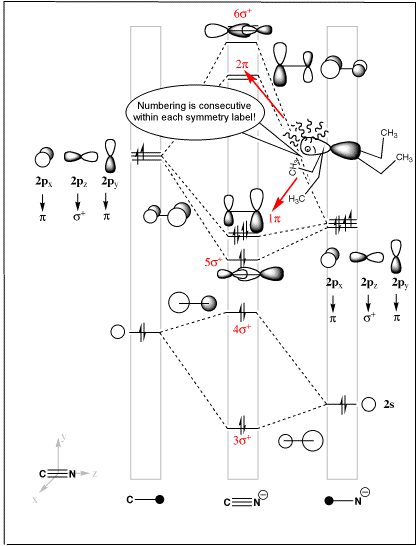
• All Molecular Orbital Nodes must be symmetrically disposed. Molecular orbitals in Carbon Monoxide CO.
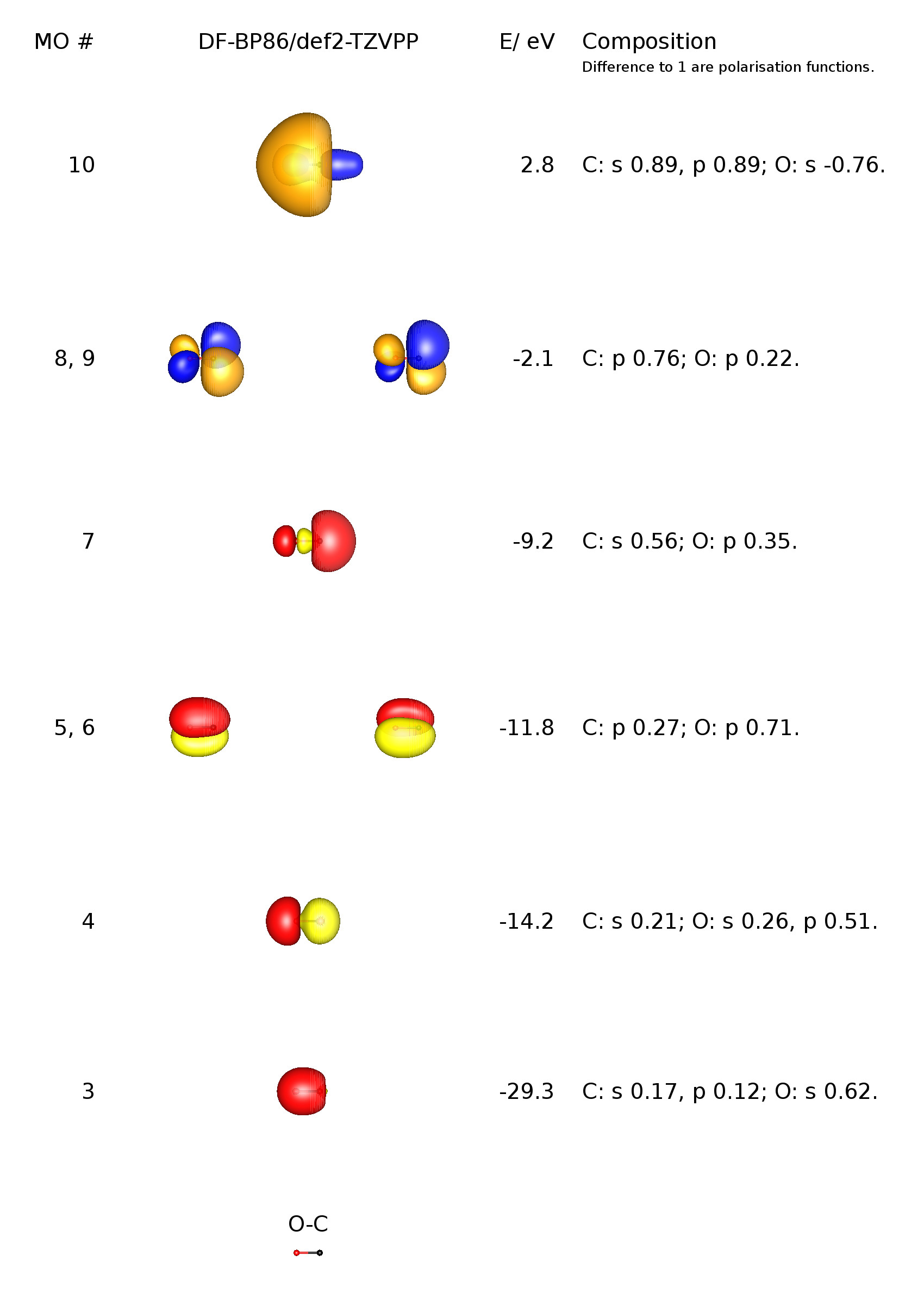
Background: Click on the CO molecular orbitals in the energy level diagram to display the shapes of the orbitals. Explore bonding orbitals in other small molecules.
Hydrogen | Fluorine | Nitrogen. Carbon monoxide strips oxygen off metal oxides, reducing them to pure metal in high temperatures, forming carbon dioxide in the process.
Carbon monoxide is not usually supplied as is, in gaseous phase, in the reactor, but rather it is formed in high temperature in presence of oxygen-carrying ore, carboniferous agent such as coke and high temperature. When acting as a ligand to a metal centre, carbon monoxide is capable of forming a metal-carbon σ bond via donation of a lone pair from carbon.
It can also accept π-electron density from filled d-metal orbitals into the CO π antibonding orbital.Molecular orbital diagram – WikipediaInteractions between Carbon Monoxide Molecular Orbitals and Metal d Orbitals