Diagram of crossing-over.
Note that while crossing over is shown here, for simplicity, between only one of the two chromatids of each chromosome, each. Diagram of crossing-over.
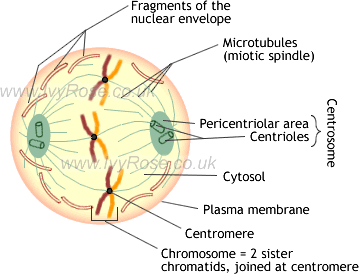
Note that while crossing over is shown here, for simplicity, between only one of the two chromatids of each chromosome, each. Definition: Mitosis is defined as the type of cell division by which a single cell divides in such a way as to produce two genertically identical “daughter cells”. Mitosis is the simplest of the two ways (mitosis and meiosis) in which the nucleus of a cell can divide – as part of.
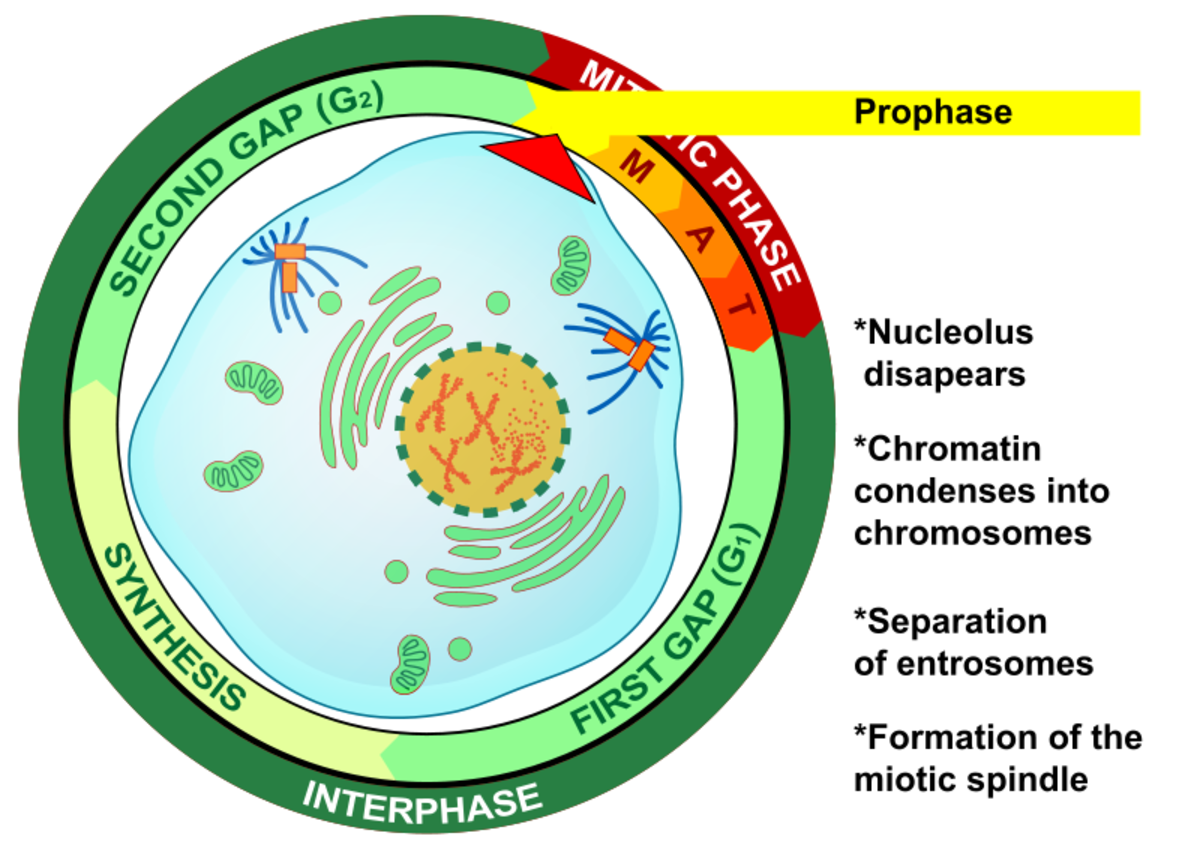
Diagram of crossing-over. Note that while crossing over is shown here, for simplicity, between only one of the two chromatids of each chromosome, each.
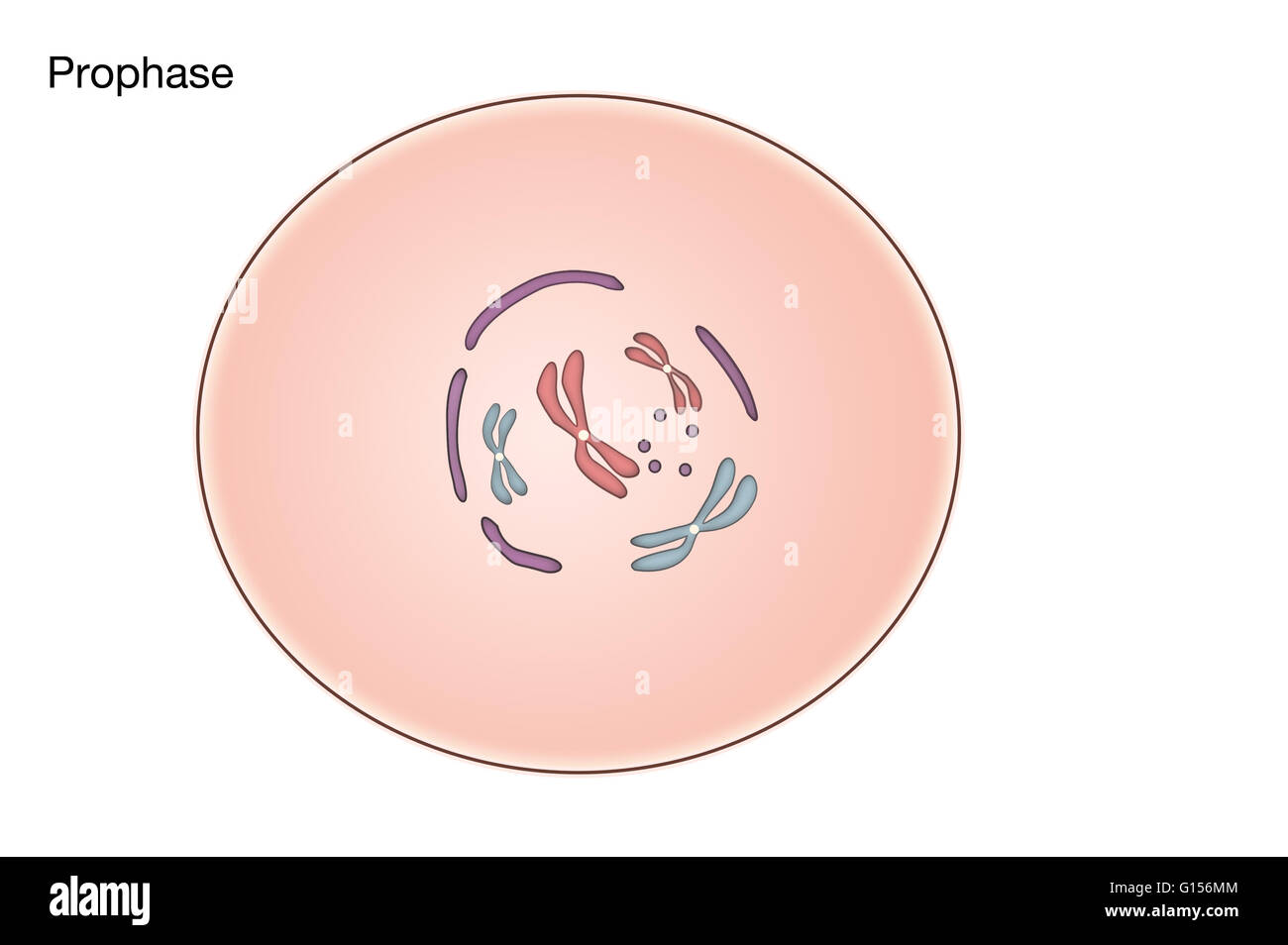
Prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Mitosis consists of four basic phases: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.
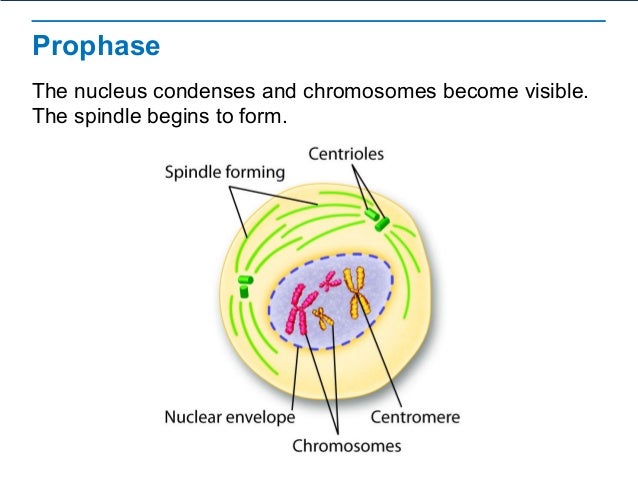
These phases occur in strict sequential order, and cytokinesis – the process of dividing the cell contents to make two new cells – starts in anaphase.Diagrams of Mitosis – the process of cell division via mitosis occurs in a series of stages including prophase, metaphase, Anaphase and Telophase. It is easy to describe the stages of mitosis in the form of diagrams showing the dividing cell(s) at each of the main stages of the process.
During prophase I the two members of each homolog pair become intimately associated along their entire lengths (that is, they “synapse”) to form a structure known as a tetrad (or bivalent). In the upper diagram two tetrads are represented as two x-shaped chromosomes associated side by side.
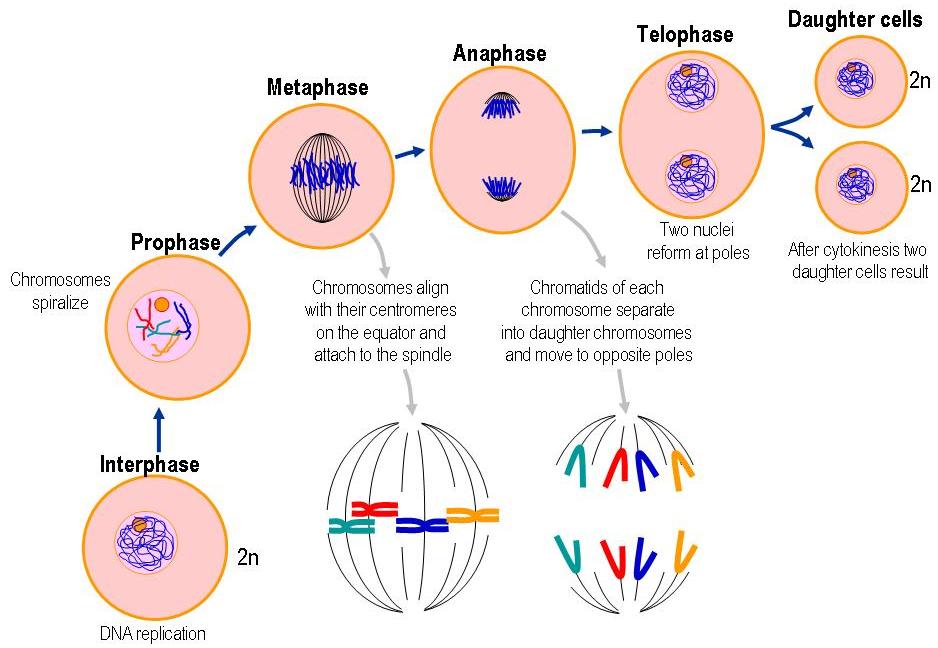
Interphase Prophase Prometaphase The cell prepares for mitosis. At this stage, the chromosomes are not clearly visible.
The chromosomes, pairs of sister chromatids, condense and become visible. Meanwhile, the nucleolus and nuclear envelope disappear. Each step of meiosis has stages just as in mitosis but is named with a number after every stage to signify the step; so there will be prophase 1 (to signify prophase stage of meiosis 1); metaphase 1 (to signify metaphase stage of meiosis 1) while metaphase II (or metaphase 2) refers .

Prophase 2: DNA does not replicate. Metaphase 2: Chromosomes align at the equatorial plate.
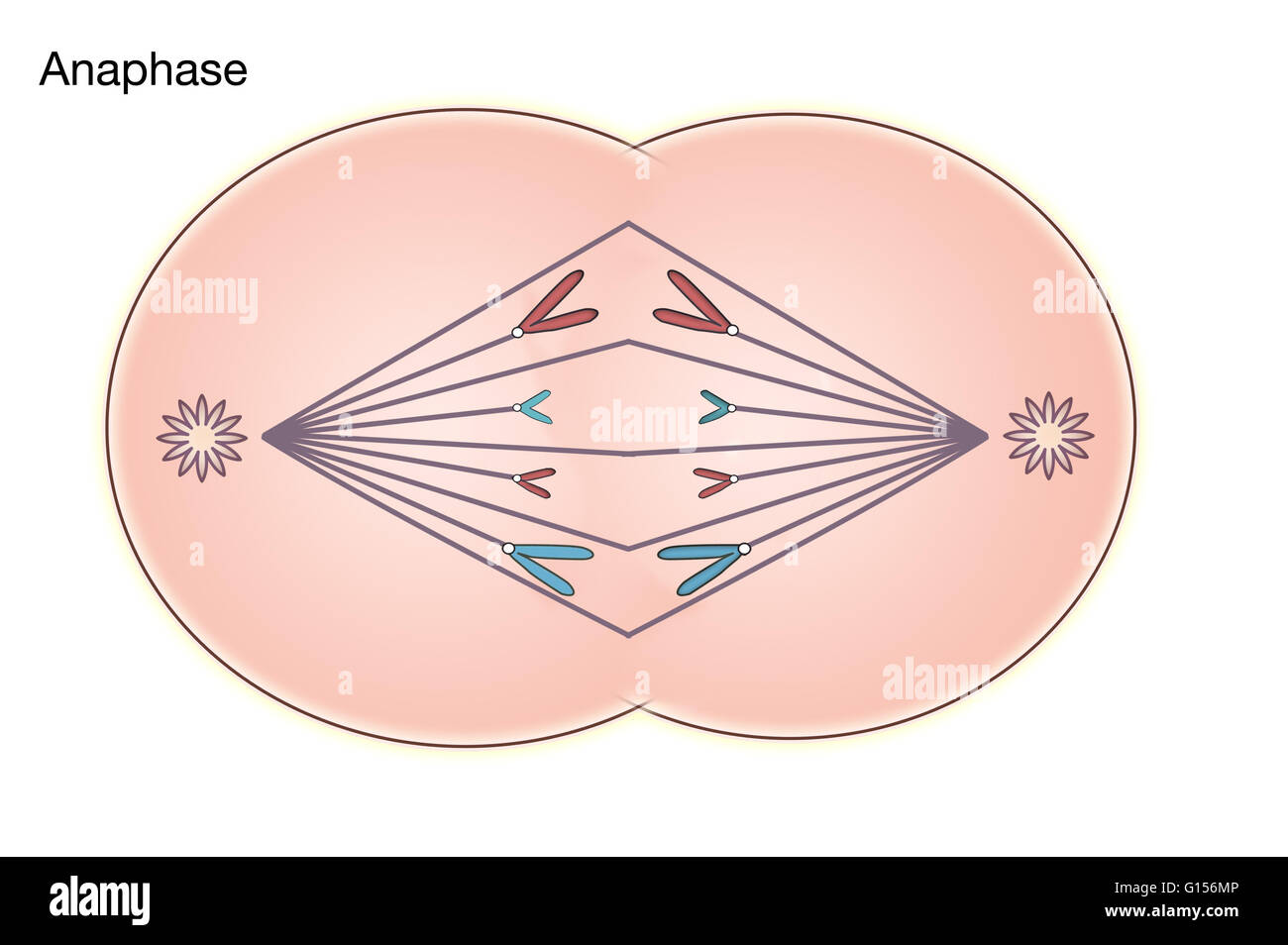
Anaphase 2: Centromeres divide and sister chromatids migrate separately to each pole. Telophase 2: Cell division is complete.
Four haploid daughter cells are obtained. One parent cell produces four daughter cells.Prophase – WikipediaProphase I – Stages of Meiosis – Online Biology Dictionary