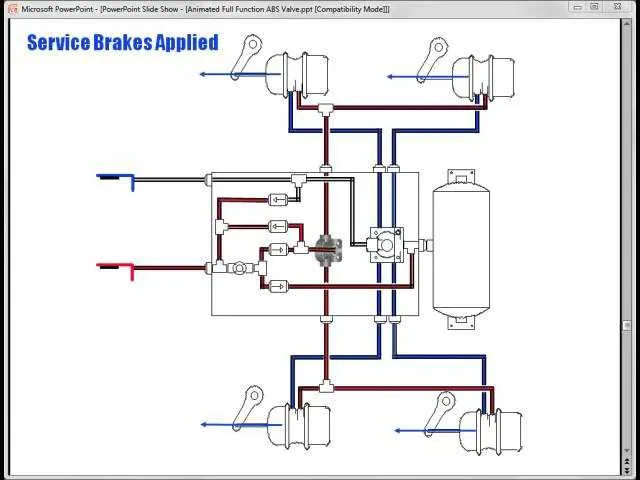
For reliable performance and safety, the pneumatic braking setup in hauling units requires a precise and well-understood design. It is crucial to ensure proper maintenance and checks to avoid failures that could compromise safety. To achieve this, focus on the following components: the compressor, valves, reservoirs, and the connections that regulate pressure throughout the vehicle. Each part plays a significant role in controlling the pressure required to slow down or stop a heavy load effectively.
Start by regularly inspecting the pressure gauges to ensure optimal function of the pneumatic setup. If the pressure falls below the required levels, a malfunction in the compressor or leakage in the pipes could be the cause. Additionally, valve blockages can disrupt air flow, leading to delayed response times or even failure to engage the stopping mechanism when needed. Keep these parts clean and free of debris to maintain smooth operation.
The reservoirs must be checked for condensation buildup, as moisture can lead to corrosion or freezing in colder environments, ultimately compromising the braking force. Inspecting and replacing faulty components regularly can help prevent serious accidents. When in doubt, refer to manufacturer guidelines to confirm the recommended specifications for pressure levels and maintenance schedules.
Understanding the Pneumatic Stopping Mechanism for Heavy Vehicles
For optimal performance, ensure the correct integration of components like the compressor, reservoir, and control valves. Each element plays a vital role in maintaining effective deceleration, especially when handling significant loads.
The compressor should be capable of producing sufficient pressure, which is stored in the reservoirs for later use. Always check the capacity to avoid insufficient force. If the pressure drops too low, it can lead to malfunction during activation.
When setting up the pressure regulators, ensure they are calibrated to avoid over- or under-pressure situations. Incorrect settings can lead to inconsistent response times or unnecessary wear on components.
Regularly inspect the distribution lines for any leaks, as even minor air loss can severely affect stopping power. Tighten or replace connections as necessary to maintain system integrity.
Testing the valve mechanisms regularly is crucial. Their job is to manage airflow to the braking components. Misalignments or wear can cause delayed or uneven force application, affecting control during operation.
Ensure that all pneumatic lines are clear of debris, and that the filters are clean. Blockages in the airflow paths can drastically reduce performance, increasing stopping distances.
Lastly, always verify that the pushrod, actuator, and other mechanical linkages are in good condition and properly adjusted to ensure responsive stopping when required.
Understanding the Components of an Air Brake System in Trailers
Ensure regular inspection of the compressor and reservoir for optimal pressure storage. The compressor should be able to build pressure efficiently, while the reservoir must maintain enough air volume to prevent system failures during operation.
Check the valve assembly for proper sealing and functionality. A malfunctioning valve can lead to delayed response times or failure to engage braking mechanisms when required.
Ensure that the hoses and connections are tightly sealed and free from damage. Leaks in these areas can cause pressure drops, leading to reduced efficiency. Use quality rubber or reinforced hoses for durability in varying environmental conditions.
Monitor the relay and modulation valves for any signs of wear. These components regulate pressure distribution and control, essential for maintaining balanced stopping power across all wheels. Inconsistent pressure levels can cause uneven wear on the wheels or, worse, total system failure.
Test the mechanical components, like chambers and actuators, to confirm they move freely without obstruction. Sticking components can compromise the braking performance and response time. Ensure that seals and diaphragms are in good condition to prevent air loss.
Examine the gauge readings regularly to ensure the correct pressure is being maintained throughout the operation. Consistent pressure readings indicate that all components are functioning within designed parameters.
Keep the control valve clean and functioning correctly. It directs the pressure into the necessary components to activate the stopping mechanism. A malfunction here could lead to unresponsiveness or inconsistent action when engaging the brakes.
How to Identify Common Issues in Trailer Pneumatic Diagrams
Check for leaks and improper connections in the pneumatic components by inspecting the layout closely. Leaks often show up at connectors, valves, and hoses. If the vehicle is losing pressure or not holding it, this could point to a faulty part or poor sealant application.
- Inspect the coupling points for visible wear or cracks.
- Look for damaged or corroded fittings that may cause air loss.
- Verify that all components are properly aligned to avoid miscommunication between parts.
Ensure the valves are functioning as expected. An improperly calibrated valve can result in uneven pressure distribution, leading to malfunction. Listen for abnormal sounds or erratic pressure readings during testing.
- Check that the valves open and close smoothly.
- Confirm the pressure settings match the specifications for each component.
- Look for blockages or debris in valve lines.
Examine the pneumatic storage tank for dirt or water accumulation. Contaminants can block airflow or cause rust, which interferes with the system’s performance.
- Ensure that the drain valve is functioning properly.
- Inspect for moisture buildup or discoloration inside the tank.
- Check the integrity of tank seals to prevent leaks.
Monitor the performance of the exhaust valves. If there is inconsistent discharge of air or excessive noise, this could be an indication of malfunctioning exhaust components.
- Confirm the exhaust valves are releasing air at the correct intervals.
- Inspect for signs of wear or blockages in exhaust ports.
- Check for proper mounting to ensure correct airflow.
Regularly test the pneumatic pressure and response times to identify issues early. Slow response or pressure fluctuations often indicate a problem with one of the key components.
Step-by-Step Guide to Troubleshooting Trailer Braking Mechanisms
Start by inspecting the compressor. Ensure it’s functioning properly by checking pressure levels. If the gauge shows inconsistent readings or low pressure, it might indicate an issue with the compressor or the air intake valves. Replace any damaged components immediately.
Next, check the hoses for leaks. Even small holes or loose fittings can cause pressure loss. Run a soapy water solution over the hoses and connections to detect escaping air. If bubbles appear, replace the affected hose or tighten the fitting.
Examine the control valve for correct operation. Ensure the valve responds promptly when the pedal is engaged. If it’s sluggish or unresponsive, clean or replace it as necessary to restore proper functioning.
Inspect the release mechanism. When not engaged, it should remain fully open, allowing for full pressure transfer. If it’s sticking or doesn’t fully release, clean and lubricate the moving parts to prevent corrosion buildup.
Look at the chamber for damage or contamination. A malfunctioning diaphragm can lead to irregular engagement. Ensure the unit is free from debris or leaks. Replace any components showing signs of wear.
Finally, test the connection between the tractor and the unit. Check for tight, secure fittings and ensure the lines are free from blockages. Perform a manual test by engaging the unit at various speeds to ensure consistent responsiveness.