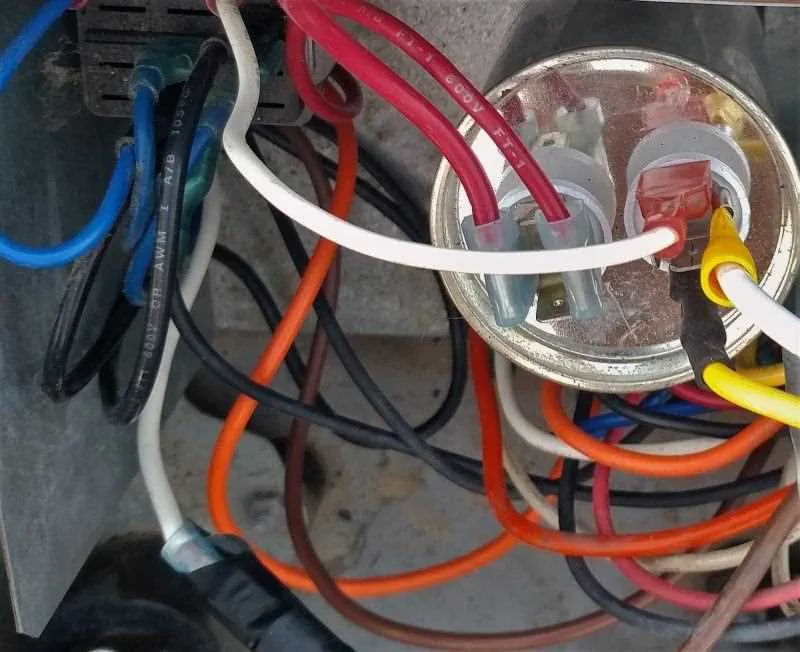
To effectively troubleshoot or upgrade the electrical setup of your HVAC system, it is crucial to understand how the key components are wired. One critical part to focus on is the component that stores and releases energy to assist the motor in starting up. If you notice issues with the motor not running or struggling to start, this part could be malfunctioning. It’s recommended to inspect its connections first.
Begin by locating the connections that feed power to the start-up mechanism. In most systems, this element is wired to two terminals: one for a direct power supply and another for a connection to the motor. Make sure to verify that the wires are securely attached and there is no visible corrosion or wear. If you detect any issues, a replacement or repair might be necessary to ensure proper operation.
For those with experience in electrical systems, double-check the orientation and polarity when reconnecting the unit. The motor and this electrical component are sensitive to miswiring, which can result in inefficient performance or total failure. Always refer to the specific model’s schematics for detailed information on the wiring sequence.
Understanding the Electrical Component for Cooling Units
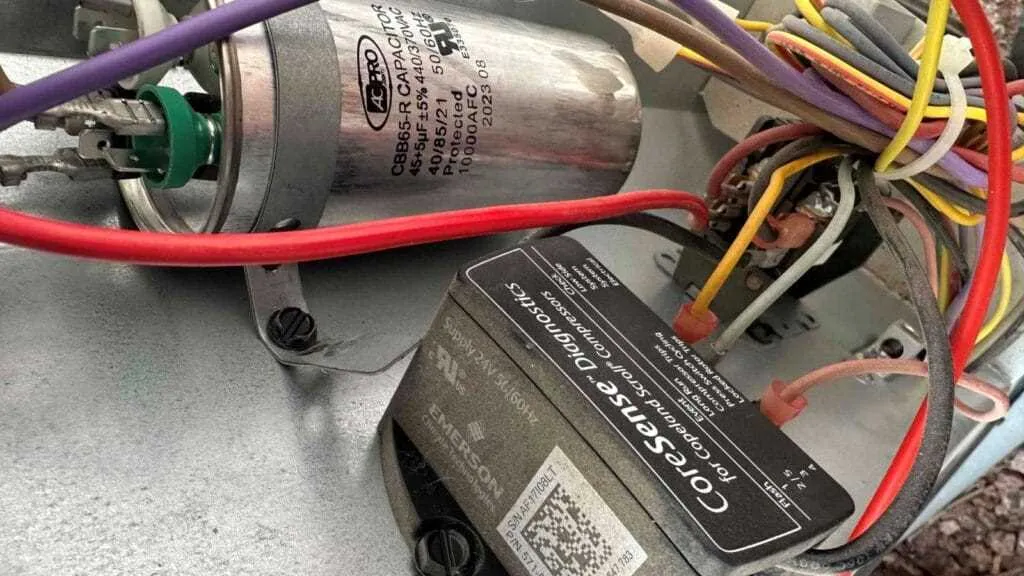

To ensure proper operation of cooling units, it’s vital to identify the role of key electrical parts like the starting and running elements. These devices manage the motor’s start-up and maintain optimal performance. One specific component, often linked to the system’s smooth functioning, is crucial for managing energy flow and preventing overloads.
When handling installation or troubleshooting, make sure the connection follows the manufacturer’s guide. Always check the terminals to ensure they are correctly wired, as improper connection can cause failure or inefficient operation. The component in question often comes in either a dual or single configuration, each serving distinct roles in motor regulation.
For optimal performance, replace defective or worn-out units promptly, as they can cause excessive current draw or motor stalling. It is important to use a replacement with the same specifications as the original to avoid system malfunctions. Testing with a multimeter will help you determine if the component is functioning as expected.
Check the voltage rating on your replacement unit to confirm compatibility. Ensure proper alignment of the terminals to prevent short circuits, which could damage the rest of the system. Also, ensure the device is securely mounted to avoid any vibrations that could affect its operation or lead to wear over time.
How to Identify the Correct Component for Your System
First, locate the part number printed on the old unit. This will help you find the correct replacement. Ensure that the voltage rating matches the original. For example, if your previous unit is rated for 370V, you should choose a replacement with the same or higher voltage. Using a lower voltage rating can lead to failure.
Next, check the microfarad (uF) rating. This indicates the capacity of the part to store energy. The exact value should match the original. If the values differ, it could impact performance and efficiency. If you’re unsure, consult the equipment’s manual for the specific microfarad value needed.
Verify the physical dimensions of the replacement. The component should fit properly within the system’s enclosure. If necessary, measure the height and width to ensure compatibility.
Pay attention to the type of terminal connections required. Some systems use a different terminal configuration than others, so confirming this beforehand will prevent installation issues.
If in doubt, check the manufacturer’s specifications or consult a professional for assistance. Using the wrong part can damage your system or reduce its efficiency over time.
Steps to Safely Install a Power Storage Unit in a Cooling System
Follow these precise steps to ensure proper installation of a power storage component:
- Turn off the power supply: Disconnect the system from the electrical source. Ensure that the main switch is turned off, and verify with a voltage tester.
- Discharge the existing unit: Prior to removing the old component, discharge any stored energy by shorting the terminals with an insulated tool.
- Identify connection points: Examine the connections, noting which wires go to the terminals. Take a photo or label the wires for reference.
- Remove the old component: Carefully disconnect the wires from the terminals, taking care not to damage any components. Remove the faulty unit and set it aside.
- Check the new unit: Before installation, confirm the specifications of the replacement, such as voltage and capacitance. Compare these to the requirements of the system.
- Install the new unit: Attach the wires to the appropriate terminals on the new component. Tighten the connections to avoid loose contacts.
- Secure the component: Mount the new unit in the designated space. Ensure it is positioned securely to prevent movement during operation.
- Reconnect the power: Turn on the power supply, and double-check the connections for any signs of overheating or incorrect installation.
- Test the system: Power up the system and monitor for proper functionality. Listen for unusual sounds and check for efficient operation. If necessary, adjust the settings.
Always follow the manufacturer’s guidelines when working with electrical components. If unsure, consult a professional for assistance.
Troubleshooting Common Issues with Electrical Components in Cooling Systems
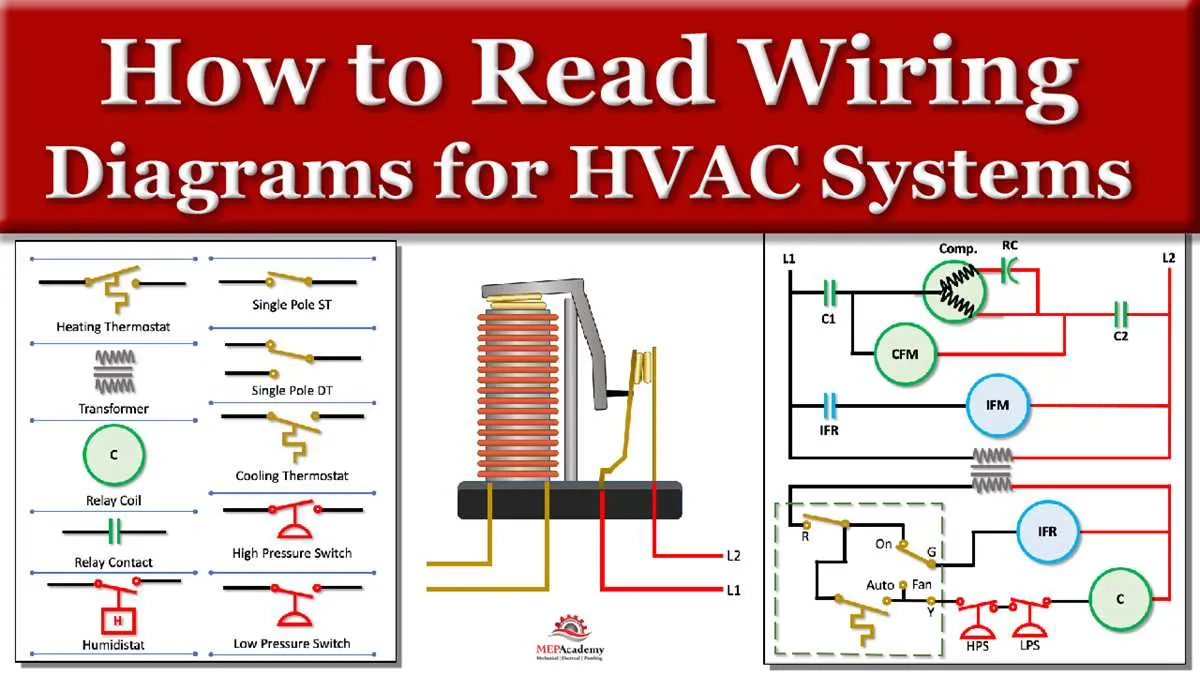
If the unit is not starting or operating inefficiently, check the component that stores energy for starting and running the motor. First, inspect for visible signs of damage, such as bulging or leakage. If the component appears deformed, it is likely faulty and should be replaced.
Measure the voltage across the terminals using a multimeter. A healthy component should show a resistance reading of near zero ohms initially, then gradually increase as the capacitor charges. If the reading remains unchanged or shows an open circuit, it may have failed.
Another critical check is to test the motor’s startup performance. If the motor struggles to start or doesn’t run at full speed, it may be a sign that the energy-storing part is no longer capable of providing the necessary boost. Replace the faulty part and confirm the motor starts smoothly after installation.
Verify the integrity of the electrical connections. Loose or corroded terminals can prevent the system from operating correctly. Tighten connections and clean corrosion from the terminals before proceeding with further troubleshooting.
If your unit works intermittently or shuts off unexpectedly, a weak or failing component may be unable to maintain consistent performance. Consider replacing the part to restore optimal functionality, especially if you notice inconsistent running cycles or erratic performance.
Finally, ensure the system is properly sized. Overloading the cooling unit can cause undue stress on the internal components, including the one responsible for motor support. Double-check the specifications and ensure that the part matches the unit’s requirements for optimal operation.