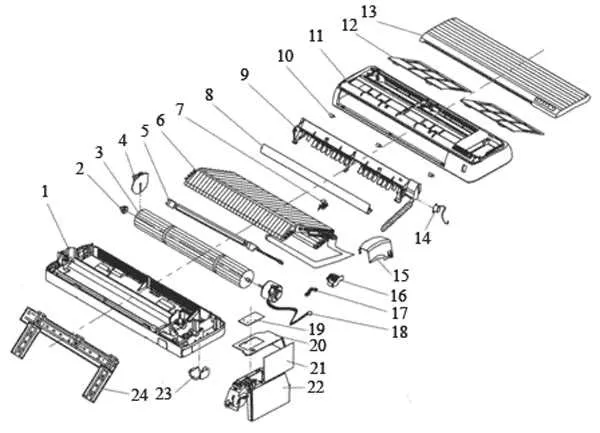
For efficient maintenance and troubleshooting, familiarize yourself with the internal structure of the system. Proper knowledge of its layout will help identify potential issues more quickly, ensuring faster repairs.
Thermal control system: The core elements regulating temperature flow include a compressor, expansion valve, and evaporator coil. Each component plays a crucial role in managing the system’s efficiency and temperature regulation.
Fluid circulation system: The pump and condenser are responsible for moving refrigerant throughout the system. Understanding the placement and function of these components is vital when diagnosing leaks or blockages.
Electrical system: Key electrical components like the control board, relays, and sensors work in tandem to regulate the system’s operation. Identifying their connections and wiring patterns can simplify troubleshooting and ensure proper power distribution.
Be sure to also check ductwork and filters, which directly impact airflow and overall performance. Regular inspection of these elements can prevent common problems, like poor air circulation or inefficient cooling.
Essential Components of a Cooling System
For efficient cooling, ensure the following key elements are in optimal working condition:
Compressor: This is the heart of the system, responsible for pressurizing and circulating refrigerant. If it malfunctions, the entire system may fail to function properly. Regular maintenance and timely lubrication are essential for its longevity.
Evaporator Coil: Located inside the indoor unit, it absorbs heat from the air. Dust buildup can reduce its efficiency, so clean it regularly. Make sure the coil is free from debris and the refrigerant levels are correct.
Condenser Coil: Found in the external unit, it releases the heat absorbed inside. Overheating can occur if the coil is obstructed, so keep the area clear of leaves and dirt to maintain airflow.
Expansion Valve: This component regulates the flow of refrigerant into the evaporator. Blockages or leaks can disrupt this flow, causing performance issues. Regular inspections help avoid potential problems.
Fan: Both indoor and outdoor fans are critical for air movement. Check them regularly for wear and tear. A malfunctioning fan can cause the system to overheat or perform inefficiently.
Drainage System: Ensure that the condensation is draining properly. Blockages in the drainage lines can lead to water damage or poor performance, so clean them periodically.
By regularly checking and maintaining these components, you can significantly extend the life of your cooling system and ensure it runs efficiently throughout the year.
Understanding Key Components of an AC System
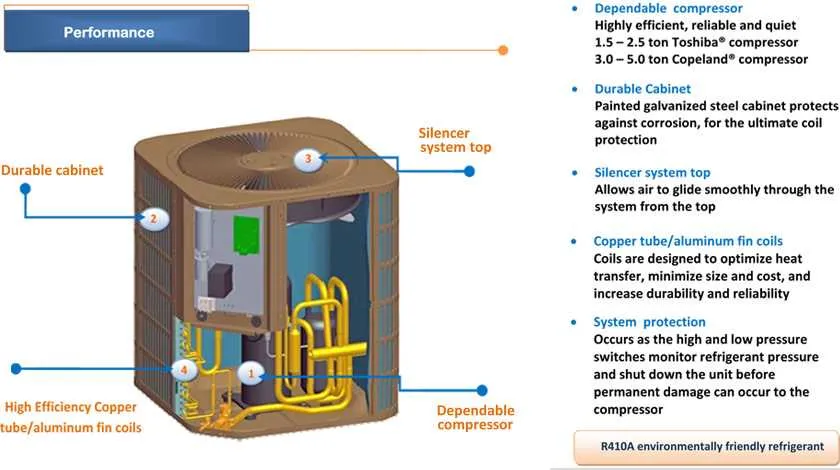
To ensure efficient cooling, it’s essential to understand the main components of your system. Below is a breakdown of crucial elements that contribute to its functionality:
- Compressor: This component circulates refrigerant through the system. Its role is critical in increasing the refrigerant’s pressure, which enables it to release heat outside the space.
- Evaporator Coil: Located inside, this coil absorbs heat from the indoor environment. The refrigerant flows through the coil, turning into a gas as it collects heat, thus cooling the space.
- Condenser Coil: Found outside, it helps expel the absorbed heat from the refrigerant. The gas condenses back into a liquid state as it cools down, releasing energy to the environment.
- Expansion Valve: This component controls the flow of refrigerant into the evaporator coil. It reduces the pressure of the liquid refrigerant, allowing it to expand and cool down.
- Blower Fan: It circulates air over the evaporator coil, ensuring even distribution of cool air throughout the room.
- Thermostat: This regulates the temperature by controlling the operation of the compressor and fan. It ensures the desired climate is maintained inside the space.
Each of these elements works in harmony to maintain a consistent and energy-efficient environment. Regular maintenance of these parts will extend the lifespan and performance of your system.
How to Identify and Troubleshoot Common AC Component Failures
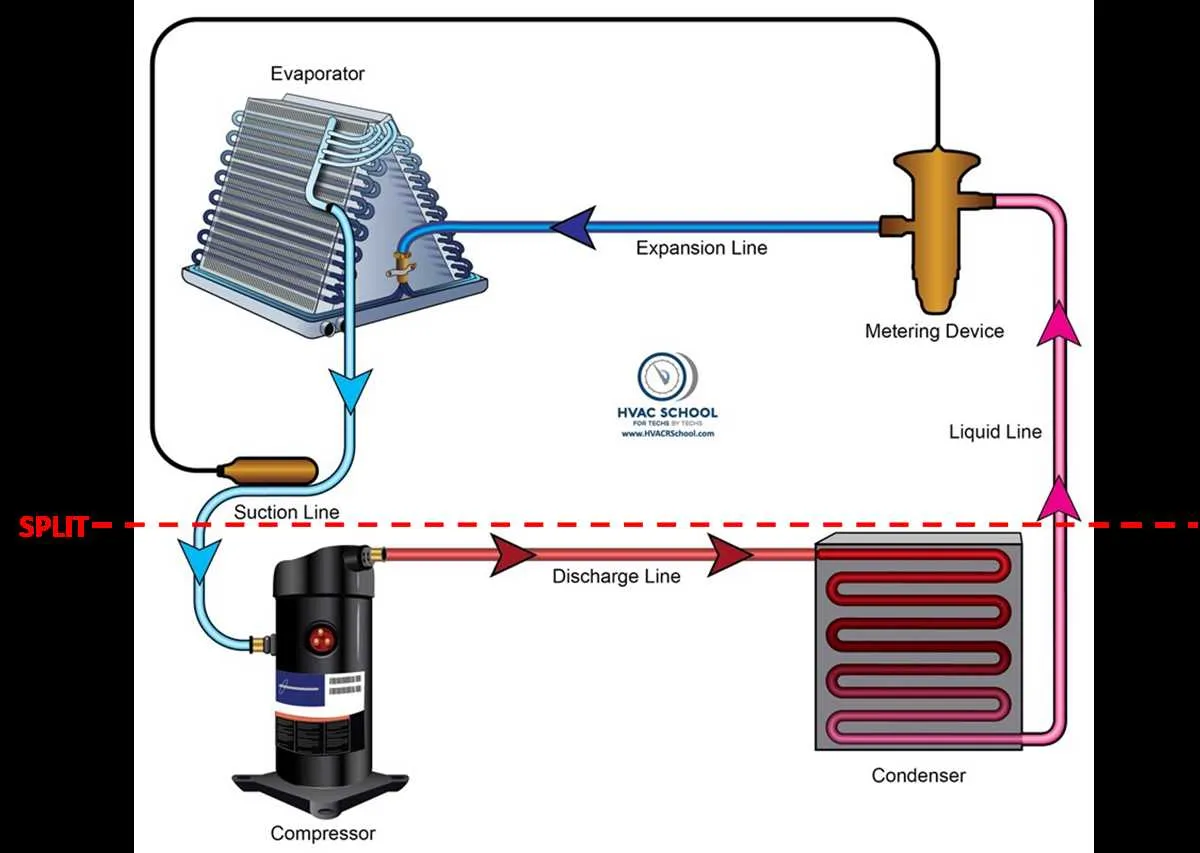
If the system is blowing warm air, check the compressor. A malfunctioning compressor often causes the refrigerant to stop circulating, leading to inefficient cooling. Listen for unusual noises–grinding or squealing sounds may indicate worn-out bearings or faulty internal components.
For reduced airflow, inspect the fan motor. If the fan blades aren’t spinning or the motor seems to be struggling, it could be a sign of electrical issues or mechanical failure. Ensure there’s no obstruction in the airflow path, and the motor wiring is intact.
Inconsistent temperature control may stem from a faulty thermostat. A malfunctioning sensor or incorrect calibration can cause erratic cooling cycles. To troubleshoot, calibrate the thermostat according to the manufacturer’s instructions or replace it if it no longer provides accurate readings.
Leaks or moisture around the evaporator coil are often a result of clogged drain lines. Over time, debris can accumulate in the drainage system, leading to water pooling. Inspect and clear any blockages to restore normal drainage and prevent potential water damage.
If the system isn’t turning on, check the circuit breaker and fuse. A blown fuse or tripped breaker could be caused by a power surge, so reset or replace them as needed. Also, verify the electrical connections to ensure they’re secure and free of damage.
Detailed Overview of Electrical Connections in Cooling Systems
For effective installation and troubleshooting of electrical systems, always ensure that the power supply is properly isolated before working with connections. In systems utilizing compressors and fans, check that the wiring is correctly matched to the voltage ratings of the components. Incorrect voltage can cause overheating or complete system failure.
The control board typically acts as the central hub, with relays and terminals routing power to critical components such as compressors and motors. Double-check that each terminal is securely fastened and that wire insulation is intact to prevent short circuits.
When installing capacitors, pay close attention to polarity, as incorrect connection can damage the capacitor and other associated parts. Ensure grounding connections are clear and unbroken to avoid potential electrical hazards or equipment malfunction.
Use appropriately rated fuses or circuit breakers in all power lines to protect components from voltage spikes or overloads. Verify the ratings align with the current requirements of each specific electrical component in the system.
In multi-phase systems, ensure that all phases are balanced to prevent under or overloading of circuits. Imbalance can lead to reduced efficiency or even system failure. Regularly inspect all connections for signs of wear, corrosion, or overheating, which can indicate underlying electrical issues.