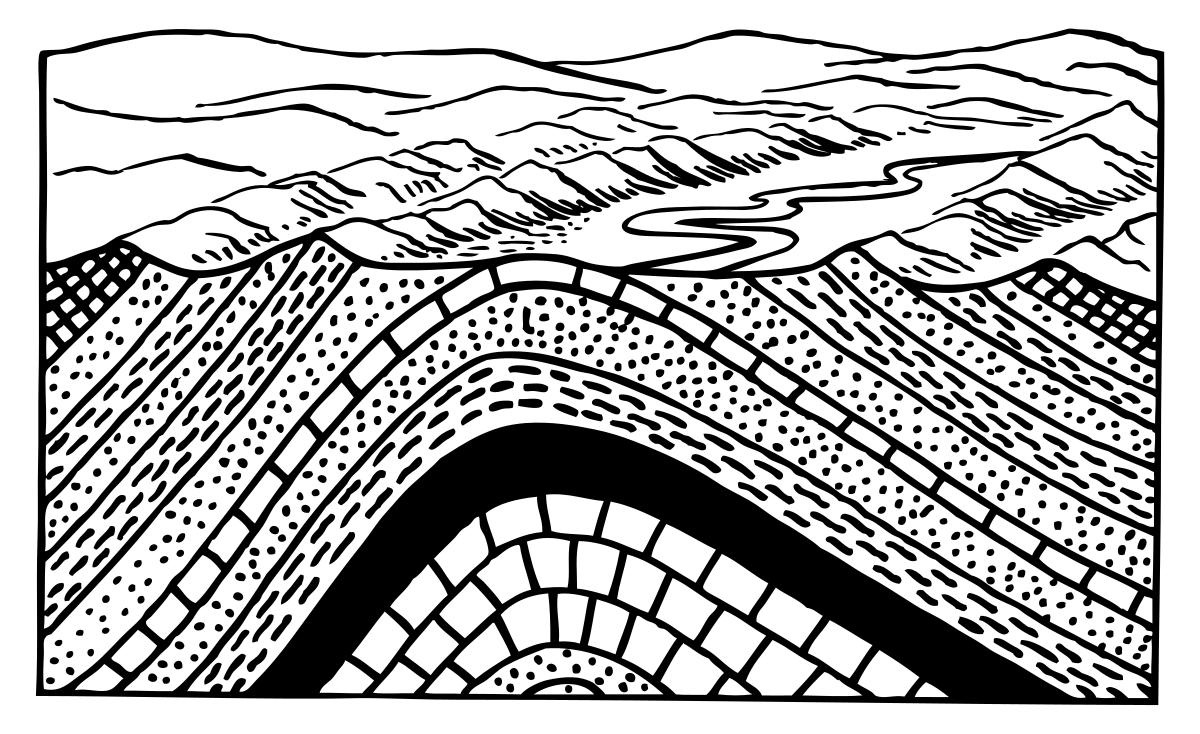
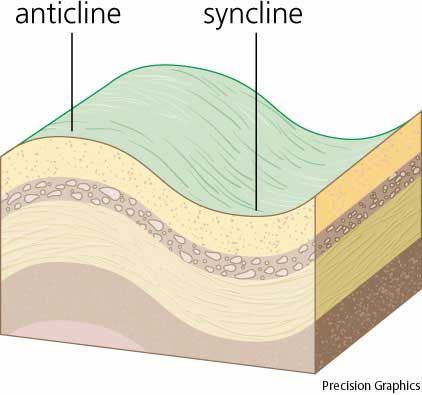
Diagram of an anticline.
In structural geology, an anticline is a fold that is convex up and has its oldest beds at its core. The term is not to be confused with.
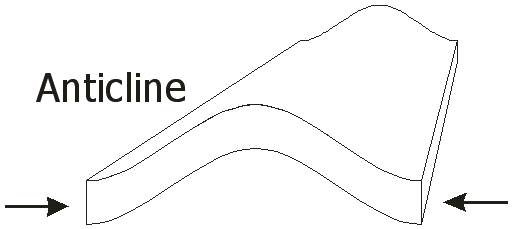
Diagram of an anticline. In structural geology, an anticline is a fold that is convex up and has its oldest beds at its core. The term is not to be confused with.
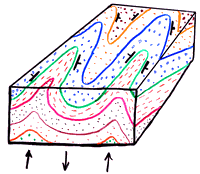
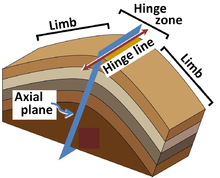
This Diagram depicts some of the differences between Asymmetrical, Symmetrical, and Folds typically occur in anticline-syncline pairs. Cross-sectional diagram of an anticline. Anticline exposed in road cut (small syncline visible at far right).
Note the man standing in front of the formation, for scale. New Jersey, U.S.A..
In structural geology, an anticline is a type of fold that is an arch-like shape and has its oldest. Domes resemble anticlines, but the beds dip uniformly in all directions away from the center of the structure.
Domes are Dome (Diagram by Phyllis Newbill).GEOLOGIC STRUCTURESCRUSTAL DEFORMATION. This photo shows deformation of rocks resulting in folded structures–internal Earth forces can cause such geologic structures to form–geologic structures can harbor important energy sources and valuable mineral ore deposits.
Anticline · is a. Acetate 54 (Figure ) Syncline and Anticline.
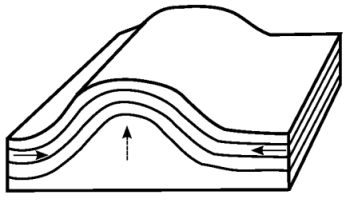
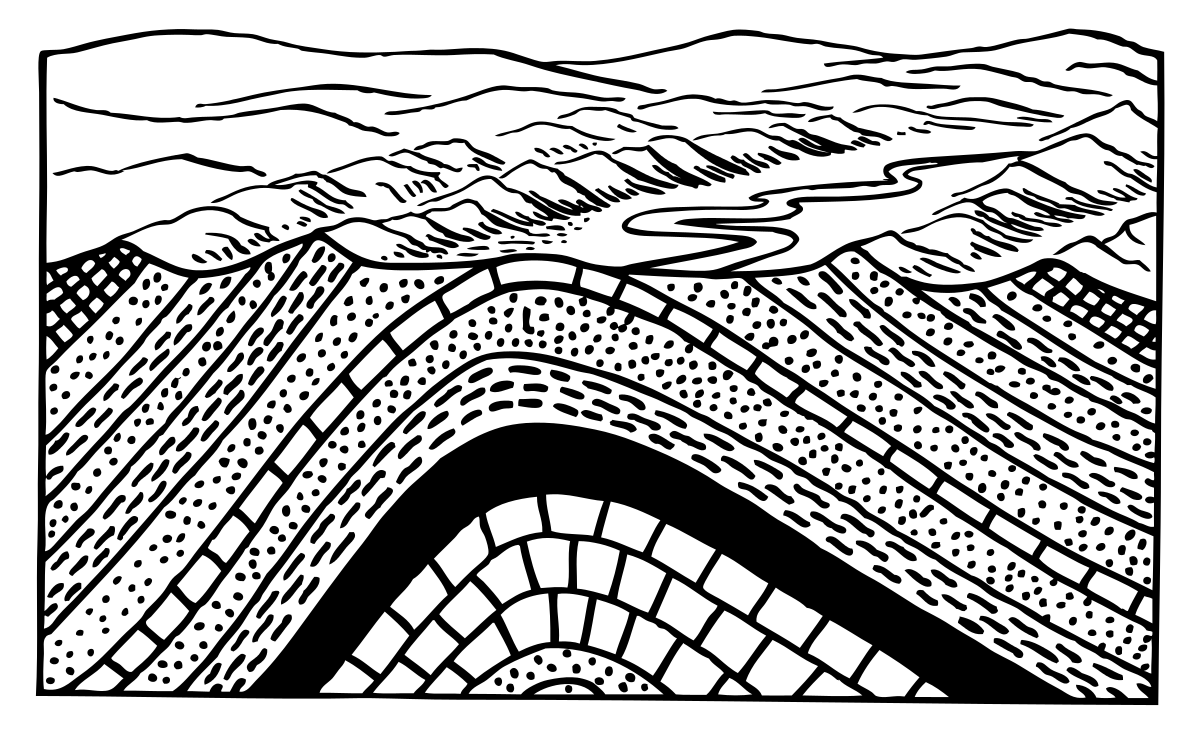
C West Publishing Company. This diagram depicts an adjacent ANTICLINE and SYNCLINE with their .
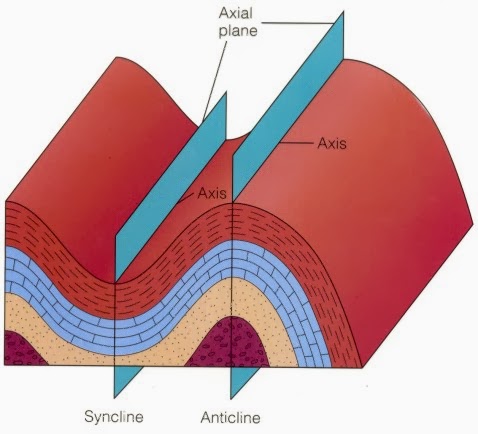
Diagram of an anticline. In structural geology, an anticline is a fold that is convex up and has its oldest beds at its core. The term is not to be confused with antiform, which is a purely descriptive term for any fold that is convex up. Diagram of an anticline.
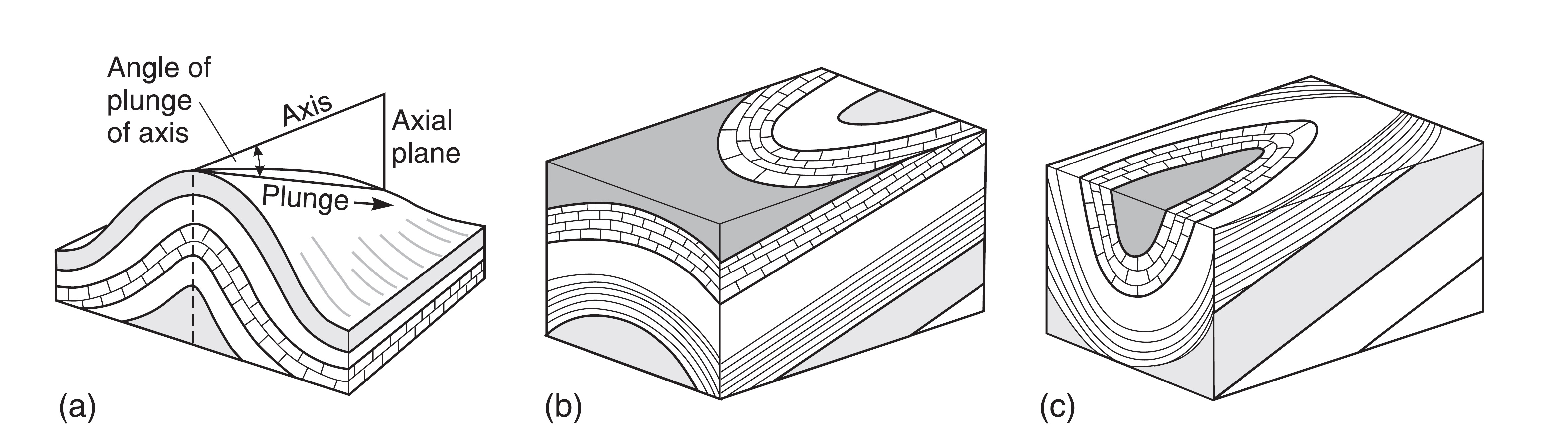
In structural geology, an anticline is a fold that is convex up and has its oldest beds at its core. The term is not to be confused with antiform, which is a purely descriptive term for any fold that is convex up.
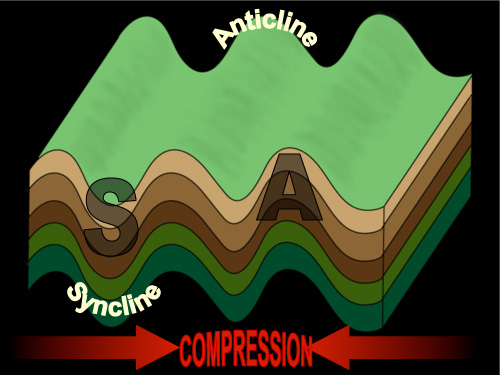
Geologic Structures (Part 5) Anticlines and Synclines • Anticlines and synclines are the up and down folds that usually occur together and are caused by compressional stress. Anticline and syncline (Diagram by Phyllis Newbill) Anticlines are folds in which each half of the fold dips away from the crest.Richard Harwood’s Courses: Physical Geology Structural GeologyAnticline | Geology Wiki | FANDOM powered by Wikia
