The brain is one of the most mysterious and complex organs in the human body. It is responsible for controlling our thoughts, emotions, movement, and many other important functions. To better understand the brain and its various regions, scientists and educators often use blank diagrams to study and teach about its structure and function.
A blank diagram of the brain is a visual representation that shows the different parts and regions of this intricate organ. It typically includes the major lobes, such as the frontal, parietal, temporal, and occipital lobes, as well as important structures like the cerebellum and brainstem. These diagrams are often used in neuroscience and psychology to help explain the functions and connections between different areas of the brain.
By using a blank diagram of the brain, researchers and educators can label and annotate the different regions to enhance understanding. This visual aid allows them to identify and discuss important structures, such as the motor cortex, sensory cortex, and hippocampus, which play key roles in controlling movement, sensation, and memory. The blank diagram also serves as a useful tool for medical professionals, as it can be used to pinpoint specific areas of the brain that may be affected by injury or disease.
Overall, a blank diagram of the brain is a valuable tool for scientists, educators, and medical professionals alike. It provides a clear and concise representation of the brain’s complex anatomy and allows for a deeper understanding of its structure and function. Whether used in a classroom setting or in a medical research lab, these diagrams play a crucial role in advancing our knowledge of the brain and all its wonders.
Blank Diagram of the Brain: A Comprehensive Guide
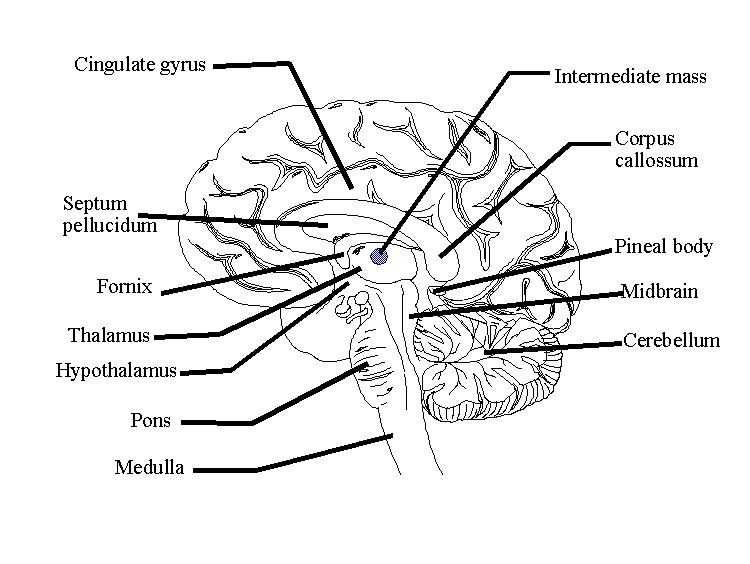
Understanding the structure and functions of the brain is fundamental to our understanding of human cognition, behavior, and overall well-being. A blank diagram of the brain serves as a valuable tool for studying and identifying the different regions and structures that make up this intricate organ. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the various parts of the brain and their functions.
Cerebrum: The cerebrum is the largest and most highly developed part of the brain. It is divided into two hemispheres, the left and right, which are responsible for a range of functions such as language, problem-solving, and sensory perception. The outer layer of the cerebrum, called the cerebral cortex, is responsible for higher-level thinking and conscious awareness.
Cerebellum: Located at the back of the brain, the cerebellum is responsible for coordination, balance, and fine motor skills. It receives sensory information from the body and helps to regulate movement and posture. Damage to the cerebellum can result in difficulties with coordination and balance.
Brainstem: The brainstem is located at the base of the brain and connects the cerebrum to the spinal cord. It is responsible for regulating vital functions such as breathing, heart rate, and blood pressure. The brainstem also plays a role in relaying sensory information between the brain and the rest of the body.
Thalamus: Situated deep within the brain, the thalamus serves as a relay center for sensory information. It receives sensory signals from the body and sends them to the appropriate areas of the cerebral cortex for processing. The thalamus is also involved in regulating sleep and wakefulness.
Hippocampus: Located within the temporal lobe, the hippocampus plays a crucial role in memory formation and spatial navigation. It helps to consolidate new memories and retrieve stored information. Damage to the hippocampus can result in memory impairments.
Amygdala: The amygdala is a small almond-shaped structure located deep within the brain. It plays a key role in processing emotions and regulating emotional responses. The amygdala is involved in fear conditioning and the formation of emotional memories.
This guide provides a basic overview of the various regions and structures of the brain. Understanding the functions of these different parts is essential for gaining insights into brain disorders and conditions and for advancing our knowledge of the human mind.
Understanding the Anatomy of the Brain
The brain is an incredibly complex and fascinating organ that plays a vital role in our daily lives. To truly understand its functions and how it influences our thoughts, emotions, and behaviors, it is important to have a basic understanding of its anatomy. By studying the structure of the brain, we can better comprehend its intricate workings and the connections between different regions.
One way to visualize the anatomy of the brain is through a blank diagram. This diagram typically includes various regions and structures, such as the cerebrum, cerebellum, brainstem, and different lobes of the cerebral cortex. Each of these regions has its own unique functions and contributes to the overall functioning of the brain. For example, the cerebrum is responsible for voluntary movements, sensory perception, and higher cognitive functions, while the cerebellum plays a role in balance, coordination, and motor control.
The cerebral cortex, which is the outer layer of the cerebrum, is particularly important for higher cognitive functions, such as language, memory, attention, and decision-making. It is divided into four lobes: the frontal lobe, parietal lobe, temporal lobe, and occipital lobe. Each lobe is associated with specific functions and interconnected with other regions of the brain.
Another essential structure of the brain is the brainstem, which connects the brain to the spinal cord. It regulates basic functions like breathing, heart rate, and blood pressure. The brainstem also serves as a relay center, transmitting information between the brain and the rest of the body.
By studying the anatomy of the brain, researchers and medical professionals can gain valuable insights into various neurological disorders and potentially develop new treatments. Understanding the intricate connections and functions of the brain can also help us appreciate its complexity and marvel at the wonders of the human mind.
Functions of Different Brain Regions
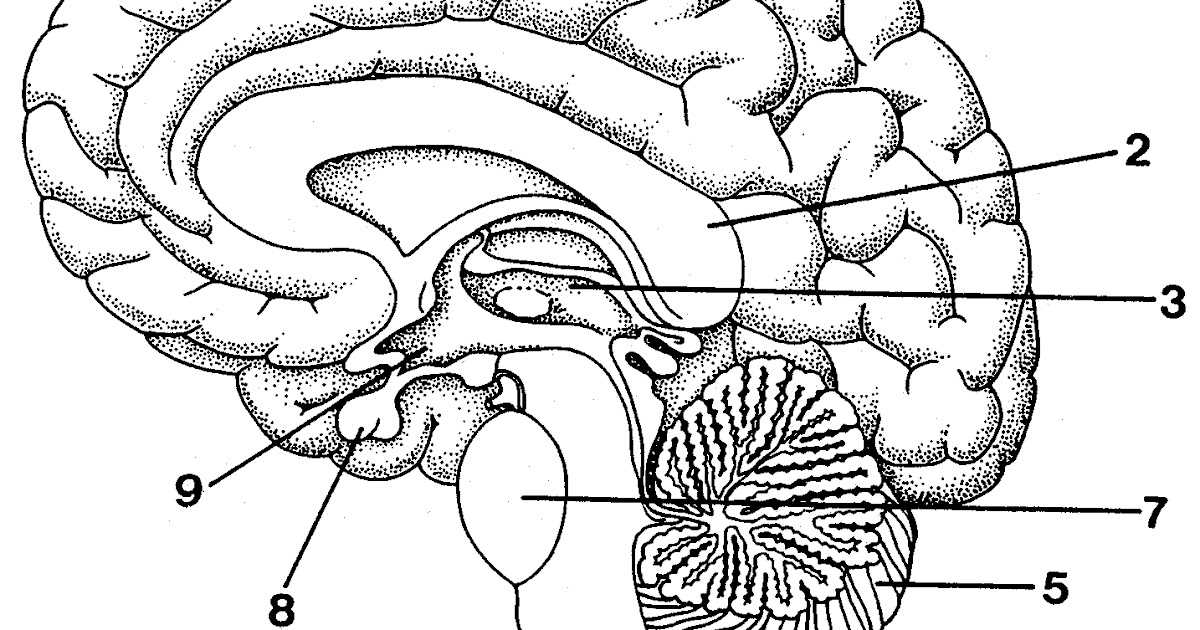
The human brain is a complex organ that consists of various regions, each responsible for specific functions. Understanding the functions of different brain regions is crucial to comprehending how the brain works and how it influences our thoughts, behaviors, and emotions.
Frontal Lobe: Located at the front of the brain, the frontal lobe is responsible for higher cognitive functions such as decision-making, problem-solving, and planning. It plays a crucial role in personality development, social behavior, and emotional control. Damage to this region can result in changes in mood, behavior, and personality.
Parietal Lobe: Situated behind the frontal lobe, the parietal lobe is involved in processing sensory information from the body and integrating it with visual and auditory stimuli. It plays a vital role in spatial awareness, perception of touch, and understanding numbers. Damage to this region can lead to difficulties in spatial orientation and sensory processing.
Temporal Lobe: Located on the sides of the brain, the temporal lobe is responsible for processing auditory information, language comprehension, and memory formation. It is also involved in facial recognition and emotional responses. Damage to this region can cause difficulties in understanding spoken language, memory problems, and changes in emotional processing.
Occipital Lobe: Found at the back of the brain, the occipital lobe is primarily responsible for processing visual information. It helps in perceiving shapes, colors, and motion, and allows us to recognize objects and faces. Damage to this region can result in visual disturbances and difficulties in visual perception.
Brain Stem: Located at the base of the brain, the brain stem controls vital functions such as breathing, heart rate, and blood pressure. It connects the brain to the spinal cord and plays a crucial role in relaying sensory and motor information. Damage to this region can be life-threatening and lead to severe impairments in essential bodily functions.
Cerebellum: Situated at the lower back of the brain, the cerebellum is responsible for coordinating voluntary movements, maintaining balance and posture, and regulating muscle tone. It plays a vital role in motor learning and fine motor skills. Damage to this region can result in difficulties in coordination, balance, and precision movements.
With the brain consisting of numerous interconnected regions, each with its unique set of functions, it is truly a marvel of nature. By understanding the functions of these different brain regions, researchers can gain insights into various neurological disorders, develop targeted treatments, and ultimately improve the quality of life for individuals affected by these conditions.
Importance of a Blank Diagram for Studying the Brain
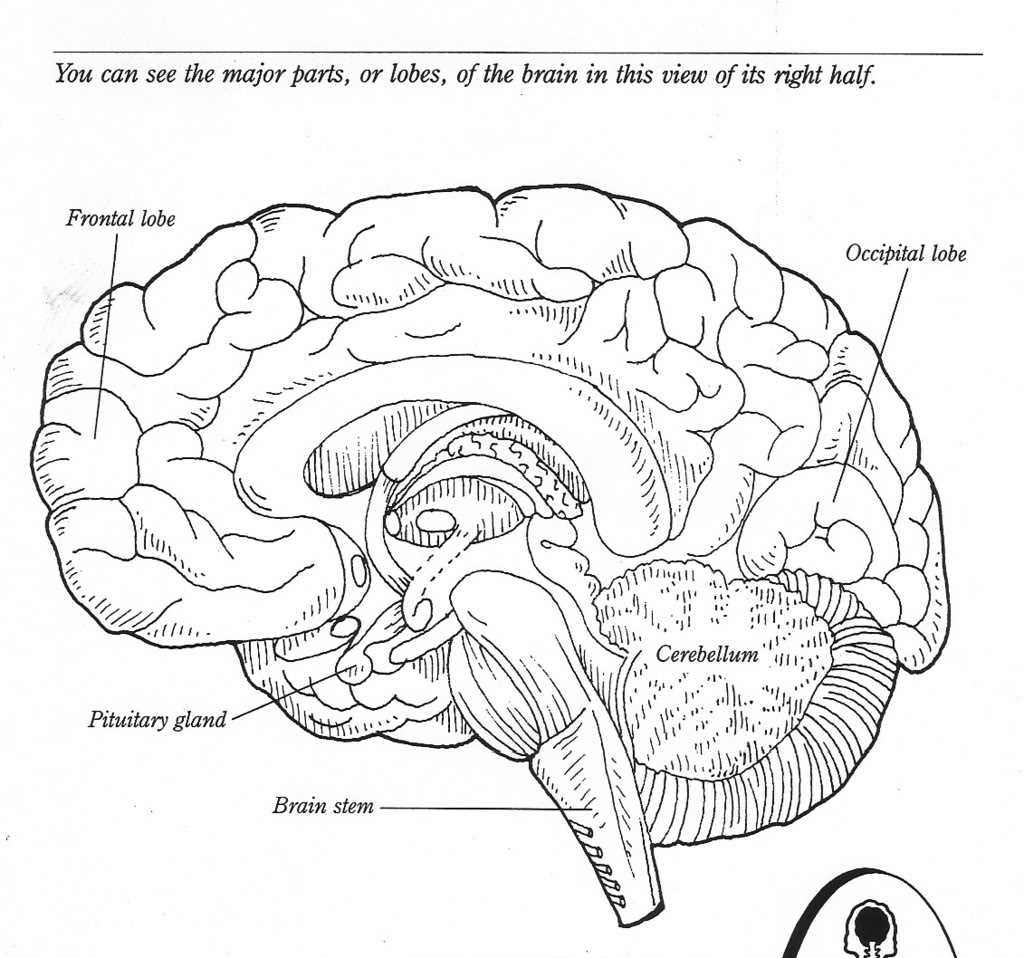
A blank diagram of the brain is an essential tool for studying and understanding its complex structure and functions. This diagram provides a visual representation of the different regions and parts of the brain, allowing researchers, scientists, and students to identify and label specific areas accurately.
One of the primary reasons why a blank diagram is crucial for studying the brain is that it helps in learning about the different lobes and their functions. The brain is divided into four main lobes: frontal, parietal, temporal, and occipital. Each lobe has specific functions, such as the frontal lobe controlling decision-making and problem-solving, while the parietal lobe is responsible for processing sensory information. With a blank diagram, it becomes easier to study and remember these different functions by labeling the corresponding areas in the diagram.
The blank diagram also serves as a valuable tool for understanding the brain’s interconnectedness and how information is processed. By labeling the different pathways and structures in the diagram, researchers and students can visualize how signals are transmitted and received within the brain. This understanding is crucial in studying neurological disorders and developing treatments.
Furthermore, a blank diagram allows for a more interactive and hands-on approach to learning about the brain. By filling in the labels and coloring different regions, students can actively engage with the material and enhance their understanding. Additionally, using a blank diagram as a study tool enables self-assessment and memorization of brain structures, facilitating a more comprehensive and effective learning experience.
In conclusion, a blank diagram of the brain plays a vital role in studying its structure and functions. It provides a visual representation of the different lobes, pathways, and structures, helping students and researchers understand the brain’s complexity and interconnections. By utilizing a blank diagram, individuals can enhance their learning experience and gain a deeper understanding of the brain’s functioning.
How to Create and Use a Blank Diagram of the Brain
Creating and using a blank diagram of the brain can be a useful tool for studying and understanding the different regions and functions of the brain. By having a visual representation, you can easily label and identify the various parts of the brain, making it easier to comprehend and remember the complex structure.
To create a blank diagram of the brain, you can start by finding an anatomically correct reference image of the brain. This image can be downloaded or printed from reputable sources such as medical textbooks or online educational websites. Ensure that the image is clear and detailed for accurate labeling.
Once you have the reference image, you can use a graphic editing software or drawing program to remove any labels or text from the image. This will create a blank canvas where you can add your own labels and descriptions. Alternatively, you can print the image and use a pen or marker to erase any existing labels.
When labeling the diagram, it is essential to use clear and concise descriptions for each part of the brain. You can use a different color or font size for each label to ensure clarity and visibility. Additionally, it is helpful to include a key or legend that explains the meaning of each label.
To make the most of your blank diagram of the brain, you can use it for various purposes. For example, you can use it as a study aid by testing yourself or others on the different parts and functions of the brain. You can also use it as a teaching tool by presenting the diagram to others and discussing the various aspects of the brain.
- Use flashcards or quizzes to test your knowledge of the brain regions.
- Create a study guide by writing detailed descriptions or mnemonic devices next to each label on the diagram.
- Compare your blank diagram with labeled diagrams to check your understanding and accuracy.
Overall, creating and using a blank diagram of the brain can greatly enhance your understanding and retention of this complex organ. It provides a visual representation that allows for detailed examination and labeling of its different regions. Incorporating this tool into your study or teaching routine can greatly improve your knowledge and comprehension of the brain.
Common Uses of a Blank Brain Diagram in Education and Research
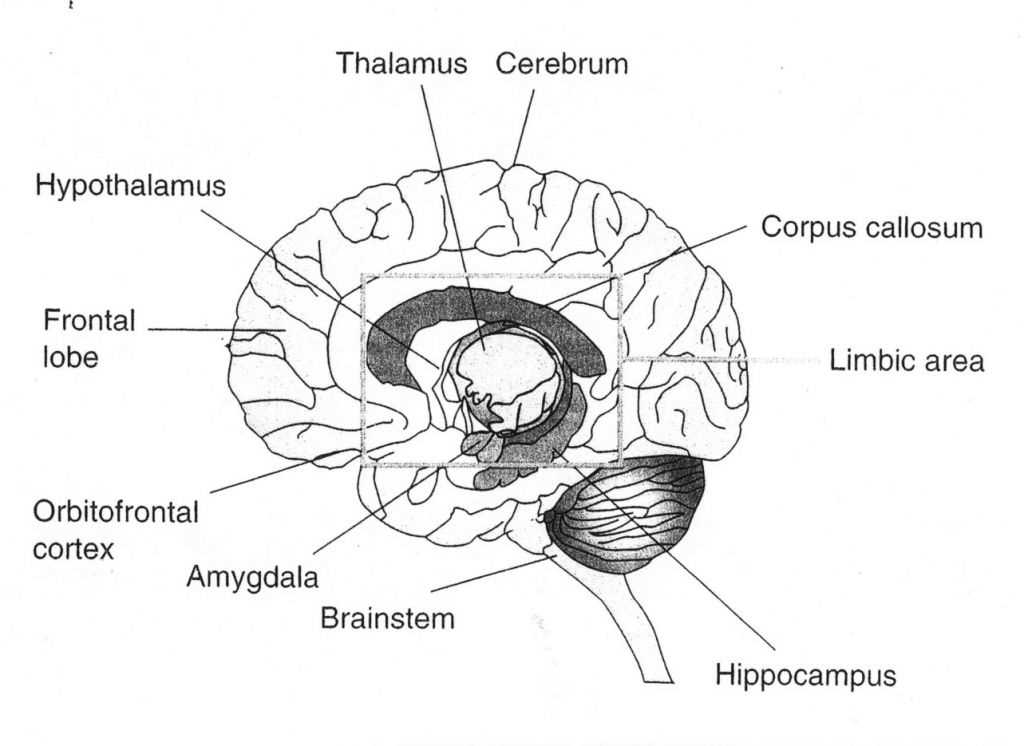
A blank brain diagram is a powerful tool that is extensively used in education and research. It offers a visual representation of the brain’s structure, helping students and researchers understand the complex organization of the brain and its various regions.
1. Education: In education, a blank brain diagram is commonly used as a teaching aid. It allows educators to introduce students to the different parts of the brain and their functions. By labeling the diagram, students can develop a better understanding of how different areas of the brain contribute to specific cognitive processes and behaviors.
2. Neuroscience Research: Blank brain diagrams are crucial in neuroscience research. Researchers often use them to map and identify brain structures and regions. By referencing the blank diagram, researchers can accurately label and analyze the specific areas of the brain that are involved in various cognitive processes, neurological disorders, and brain imaging studies.
3. Psychological Studies: Psychologists also use blank brain diagrams to study how brain functions relate to psychological processes. By labeling the diagram with different cognitive functions, researchers can visually represent the brain areas responsible for memory, attention, emotions, language, and perception. This aids in the development of theories and models that explain the relationship between brain structure and psychological processes.
4. Medical Education: In medical education, a blank brain diagram is utilized to teach students about the anatomy of the brain. By labeling the diagram, medical students can learn about the different lobes, gyri, and sulci of the brain, as well as the major blood vessels and cranial nerves. This helps students understand the structure and function of the brain, which is essential for diagnosing and treating neurological disorders.
5. Communication and Collaboration: A blank brain diagram also serves as a visual communication tool in collaborative research settings. Researchers can use the diagram to present and discuss their findings, facilitating a better understanding and exchange of ideas among team members. The diagram provides a common reference point, allowing researchers to collectively interpret and analyze data.
In conclusion, a blank brain diagram is a versatile tool that finds widespread use in education and research. Its visual representation of the brain helps with understanding brain structure, mapping brain regions, studying psychological processes, teaching medical anatomy, and facilitating communication among researchers. By utilizing a blank brain diagram, individuals can enhance their knowledge and contribute to advancements in neuroscience and related fields.
Q&A:
What is a blank brain diagram used for?
A blank brain diagram is used to label and identify different parts of the brain.
How is a blank brain diagram used in education?
In education, a blank brain diagram is used as a learning tool to help students understand the anatomy and functions of the brain.
What are the benefits of using a blank brain diagram in research?
Using a blank brain diagram in research allows researchers to visually analyze and identify different brain regions and their functions.
Can a blank brain diagram be customized for specific purposes?
Yes, a blank brain diagram can be customized by adding additional labels or annotations to suit specific educational or research needs.
Are there any other common uses of a blank brain diagram?
Yes, a blank brain diagram can also be used as a reference tool in medical settings for neurosurgeons and other healthcare professionals.
What is a blank brain diagram used for in education?
A blank brain diagram is often used in education to help students learn and understand the different parts of the brain. It allows them to label and identify the various regions and structures of the brain.
How is a blank brain diagram useful in research?
In research, a blank brain diagram can be used as a visual tool for scientists to map and study the functions of different areas of the brain. It can also be used to document and record findings during experiments or studies.