A board diagram is a visual representation of a board game or a strategy game. It illustrates the layout of the board, including the placement of pieces, cards, and other game elements. Board diagrams are commonly used in game instructions, rulebooks, and strategy guides to help players understand the game’s mechanics and strategy.
The board diagram typically consists of a grid or a series of interconnected spaces that represent different areas or locations on the game board. Each space may contain images or symbols to represent specific game elements, such as player pieces, resource tiles, or action cards.
In addition to the board layout, a board diagram may also include annotations or labels to explain rules, actions, or outcomes associated with specific spaces or game elements. These annotations can be helpful for new players who are learning the game or for experienced players who want to develop advanced strategies.
Board diagrams can vary in complexity depending on the game. Some board games have simple diagrams with only a few spaces and pieces, while others have intricate diagrams with multiple levels, paths, and specialized spaces. The design of the board diagram can greatly influence the overall gameplay and player experience, as a well-designed diagram can enhance clarity, immersion, and strategic depth.
What is a board diagram and why is it important?
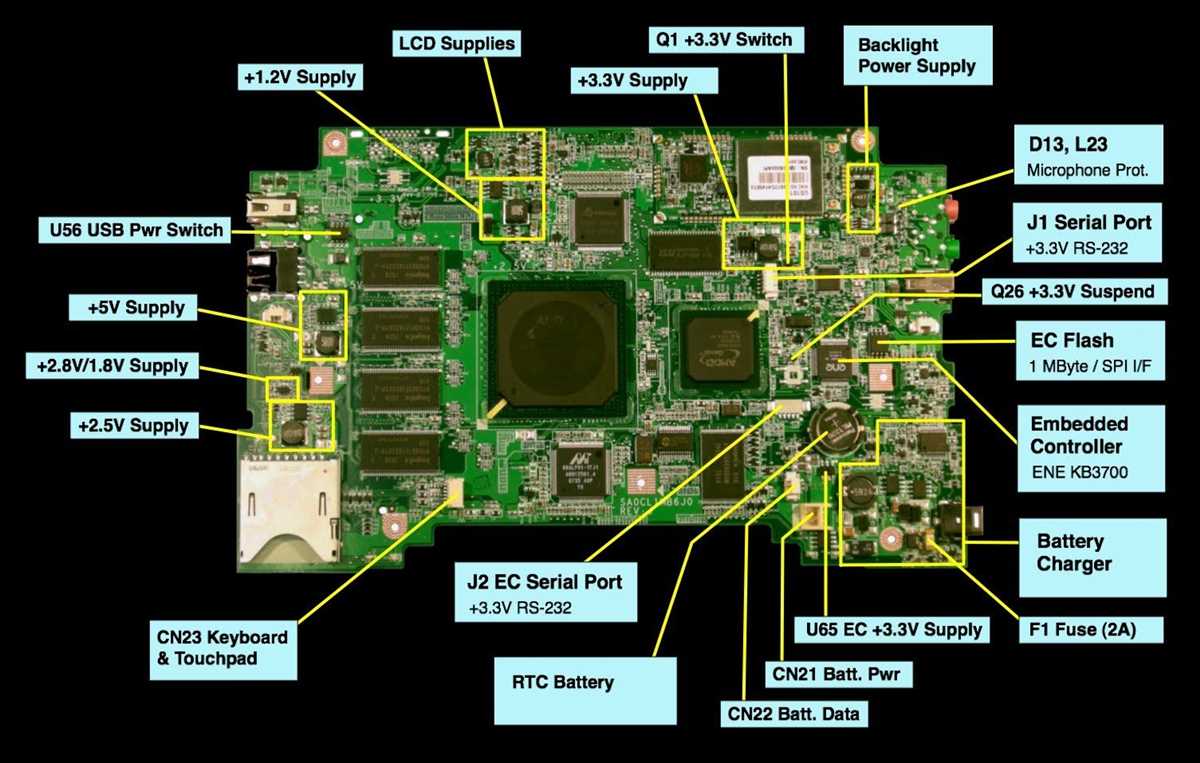
A board diagram is a visual representation of a board game or activity that lays out the rules, objectives, and components of the game in a clear and organized manner. It can be a schematic drawing, a flowchart, or even a table that helps players understand the gameplay and navigate through the various elements of the game.
Board diagrams are important because they provide a visual and concise overview of the game, making it easier for players to learn and remember the rules. By presenting the information in a structured and visually appealing way, board diagrams enhance the overall gaming experience and reduce the chances of confusion or misunderstandings.
The key components of a board diagram often include the game board itself, the pieces or tokens used, the spaces or areas on the board, and the actions or rules associated with each component. It may also include additional information such as scoring systems, turn order, and special instructions. By having all this information laid out in a single diagram, players can quickly reference and understand the various aspects of the game.
Furthermore, board diagrams can be especially valuable for complex or strategic games where there are multiple paths, options, or decision points. They provide a visual representation of the game’s mechanics and dynamics, allowing players to plan their moves, strategize, and anticipate the consequences of their actions.
In summary, a board diagram is an important tool in board game design and play. It helps players understand and remember the rules, enhances the overall gaming experience, and enables strategic decision-making. Whether you’re a beginner learning a new game or an experienced player looking to master a complex one, a well-designed board diagram can be a valuable resource.
The definition and purpose of a board diagram
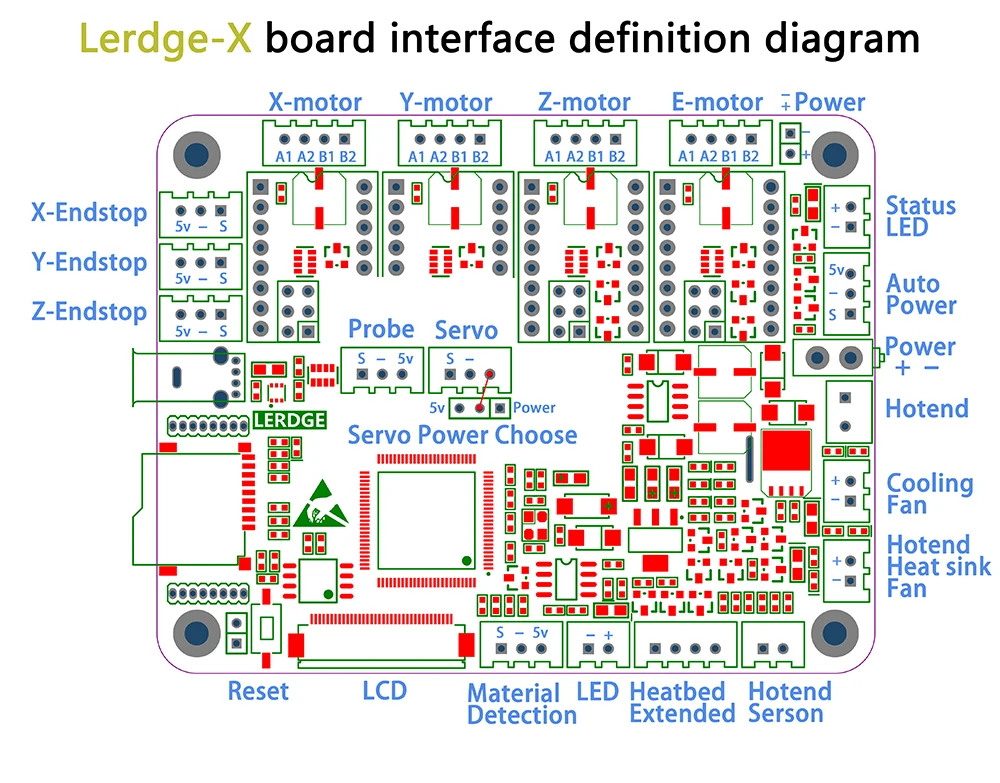
A board diagram is a graphic representation of the components and connections on a printed circuit board (PCB). It provides a visual overview of how different electronic components are arranged and connected on the board. It is an essential tool for designers, engineers, and technicians involved in the development and assembly of electronic devices.
In a board diagram, each component is represented by its symbol or footprint, which indicates its size, shape, and electrical characteristics. The connections between the components are represented by lines or traces, which show how the electrical signals flow through the board. The diagram also includes labels and annotations to provide additional information about the components and their functions.
The purpose of a board diagram is several-fold:
- Design and planning: A board diagram helps the designer in planning the layout of the PCB and deciding the optimal placement of components to ensure their proper functioning and minimize signal interference. It allows for the visualization of the overall structure and organization of the board, making it easier to identify potential design issues and optimize the design.
- Communication: A board diagram serves as a visual communication tool between the design team, manufacturing team, and other stakeholders. It allows them to understand and discuss the layout, connections, and functionality of the board, ensuring everyone is on the same page and reducing the chances of miscommunication or errors during the production process.
- Troubleshooting and debugging: In case of any issues or malfunctions with the PCB, a board diagram can be used as a reference to identify and locate the problem. By visually following the traces and connections, technicians can trace the flow of signals and identify any potential faults or errors in the circuit.
- Documentation: A board diagram is an important part of the documentation for the PCB. It provides a detailed record of the board’s layout, connections, and component placement, making it easier for future modifications, repairs, or reproductions of the board.
In summary, a board diagram is a crucial tool for the design, development, and assembly of electronic devices. It helps in planning, communication, troubleshooting, and documentation, ensuring the efficient and accurate production of PCBs.
How to Create a Board Diagram
Creating a board diagram is an essential step in the planning and organization of various projects, whether it’s a business strategy, a software development process, or a creative brainstorming session. A board diagram visually represents the different elements, tasks, or ideas involved in a project, helping to provide a clear and structured overview.
To create a board diagram, follow these simple steps:
- Identify the main components: Start by identifying the main components or categories that are relevant to your project. For example, in a business strategy diagram, these could include marketing, finance, operations, and human resources.
- Create columns and rows: Once you have identified the main components, create columns and rows to represent them on the board diagram. You can use a whiteboard, a piece of paper, or a digital tool for this purpose.
- Add tasks or ideas: Within each component, add the specific tasks or ideas that need to be included in the project. Use sticky notes, labels, or text boxes to represent these tasks or ideas.
- Connect the elements: Connect the different elements in the board diagram using lines or arrows to show relationships, dependencies, or progress. This helps to visualize how the various tasks or ideas are connected and how they contribute to the overall project.
- Add additional details: Depending on the complexity of the project, you can add additional details to the board diagram, such as due dates, priorities, or additional comments. These details help to provide more context and facilitate better project management.
By following these steps, you can create a clear and structured board diagram that helps you and your team stay organized, track progress, and effectively communicate the different aspects of your project.
Key elements of a board diagram
A board diagram is a graphical representation of a board or committee’s structure, roles, and responsibilities. It provides a visual overview of how the board is organized and how it functions. There are several key elements that are typically included in a board diagram.
1. Board members: The board diagram should identify all board members, including their names and roles. This helps to clarify who is responsible for decision-making and oversight within the organization. It should also indicate any committees or subcommittees that board members are a part of.
2. Board chairperson: The board chairperson is a key leadership role within the board. The diagram should clearly indicate who is serving as the board chairperson and their responsibilities.
3. Committees: Many boards have committees that focus on specific areas of the organization’s operations, such as finance, governance, or fundraising. The diagram should outline the different committees and their members, as well as their specific responsibilities and reporting lines.
4. Staff: The board diagram may also include key staff members who work closely with the board, such as the executive director or CEO. This helps to clarify the relationship between the board and staff and ensures that everyone understands their respective roles and responsibilities.
5. Reporting lines: It is important for the board diagram to show the reporting lines between different roles and committees. This helps to ensure clear lines of communication and accountability within the organization.
6. External stakeholders: The board diagram may also include external stakeholders, such as funders, advisors, or community representatives. This helps to demonstrate the board’s connection to the broader community and its relationships with key partners.
Overall, a board diagram is a useful tool for visually representing the structure and function of a board. It helps to ensure clear communication, accountability, and understanding of roles within the organization.
Benefits of using a board diagram
A board diagram, also known as a board chart or a board plan, is a useful tool for visualizing information and data in a clear and organized manner. It involves the use of a board or a large sheet of paper where information is displayed using graphics, diagrams, and text. There are several benefits of using a board diagram:
- Visual representation: A board diagram allows for the visual representation of complex information, making it easier to understand and interpret. By using graphics, diagrams, and color coding, it becomes possible to highlight important points, connections, and relationships, which may not be easily conveyed through text alone.
- Collaboration and communication: A board diagram serves as a visual aid during meetings, presentations, and discussions, enabling effective collaboration and communication among team members. It provides a common ground for everyone to contribute, share ideas, and brainstorm solutions.
- Organizational tool: The use of a board diagram helps in organizing and structuring information. It allows for the categorization of data into different sections or sections, making it easier to navigate and comprehend. It also facilitates quick retrieval of data, as everything is visually laid out in one place.
- Decision-making: A board diagram aids in decision-making processes by providing a comprehensive overview of information. It allows decision-makers to evaluate options, compare alternatives, and weigh pros and cons. By visualizing the data, it becomes easier to identify patterns, trends, and outliers, enabling informed and strategic decisions.
- Flexibility and adaptability: A board diagram can be easily modified and updated as needed. Information can be added, removed, or rearranged without the need for complex software or technical skills. This flexibility allows for the diagram to adapt to changing circumstances, ensuring that it remains relevant and up-to-date.
In summary, a board diagram is a powerful tool for organizing, visualizing, and communicating information. It enhances collaboration, supports decision-making, and provides a clear and concise representation of complex data. Whether used in business, education, or personal projects, a board diagram offers numerous benefits and can greatly improve the understanding and effectiveness of the information being conveyed.
Examples of board diagrams in different industries
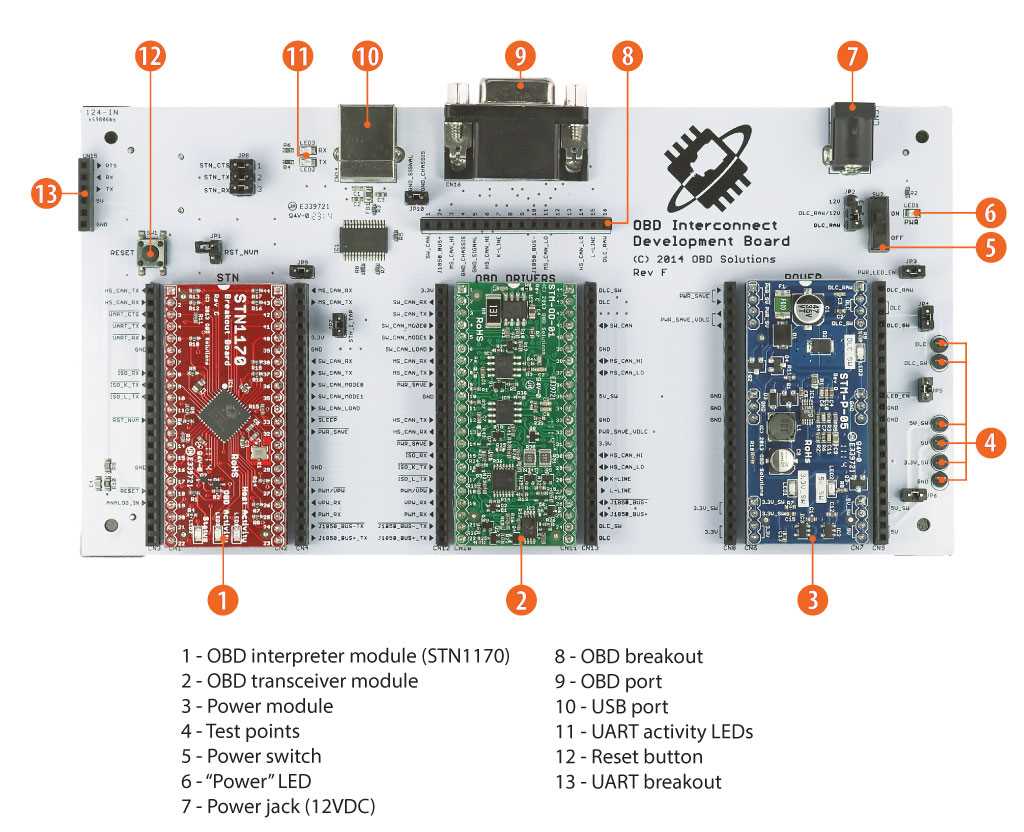
A board diagram is a powerful visual tool that is widely used in various industries to convey complex information and make informed decisions. It helps to illustrate the relationships, interactions, and components of a system or process. Here are some examples of board diagrams used in different industries.
1. Information Technology
In the IT industry, board diagrams are commonly used to map out the architecture and infrastructure of computer systems, networks, and software applications. These diagrams help IT professionals understand the flow of data, identify potential bottlenecks, and optimize system performance. Examples of board diagrams in IT include network diagrams, server diagrams, and database diagrams.
2. Manufacturing
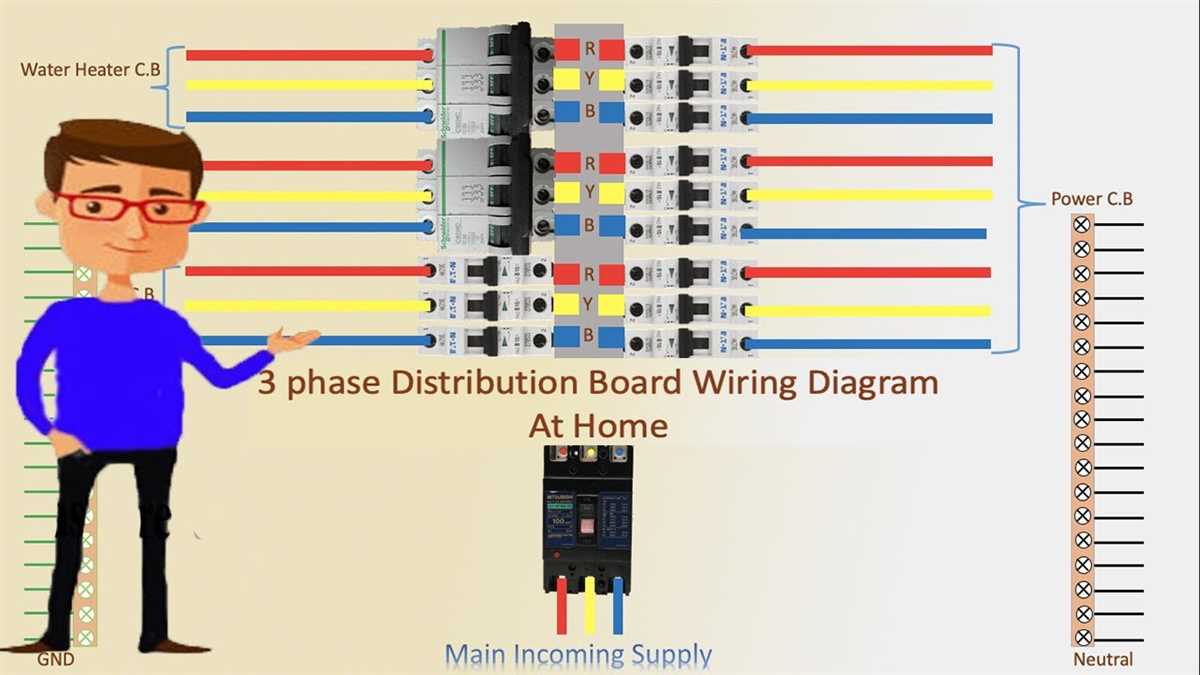
In the manufacturing industry, board diagrams are essential for optimizing production processes, improving efficiency, and ensuring quality control. These diagrams depict the different stages of production, workflow, and equipment layout. Examples of board diagrams in manufacturing include process flowcharts, assembly line diagrams, and value stream maps.
3. Healthcare
In the healthcare industry, board diagrams are used to visualize patient care processes, medical procedures, and hospital operations. These diagrams help healthcare professionals identify areas for improvement, streamline processes, and enhance patient safety. Examples of board diagrams in healthcare include patient flow diagrams, surgical flowcharts, and medication administration charts.
4. Project Management
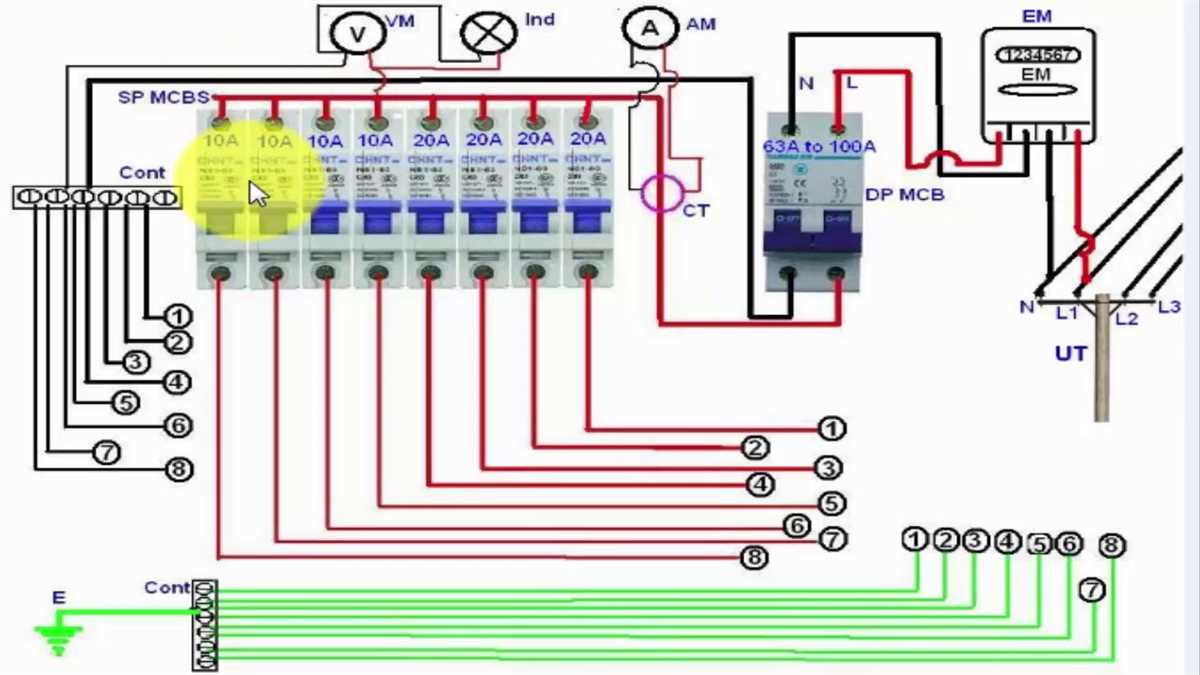
In project management, board diagrams are widely used to plan, track, and communicate project progress. These diagrams provide a visual representation of project activities, dependencies, and timelines. Examples of board diagrams in project management include Gantt charts, PERT charts, and swimlane diagrams.
5. Marketing
In the marketing industry, board diagrams play a crucial role in visualizing marketing strategies, customer journeys, and campaign plans. These diagrams help marketers understand target audience segments, plan marketing activities, and analyze the effectiveness of marketing campaigns. Examples of board diagrams in marketing include customer journey maps, marketing funnel diagrams, and campaign performance dashboards.
Overall, board diagrams are versatile tools that can be applied in various industries to simplify complex information, improve decision-making, and enhance organizational efficiency.
Tips for effectively using board diagrams
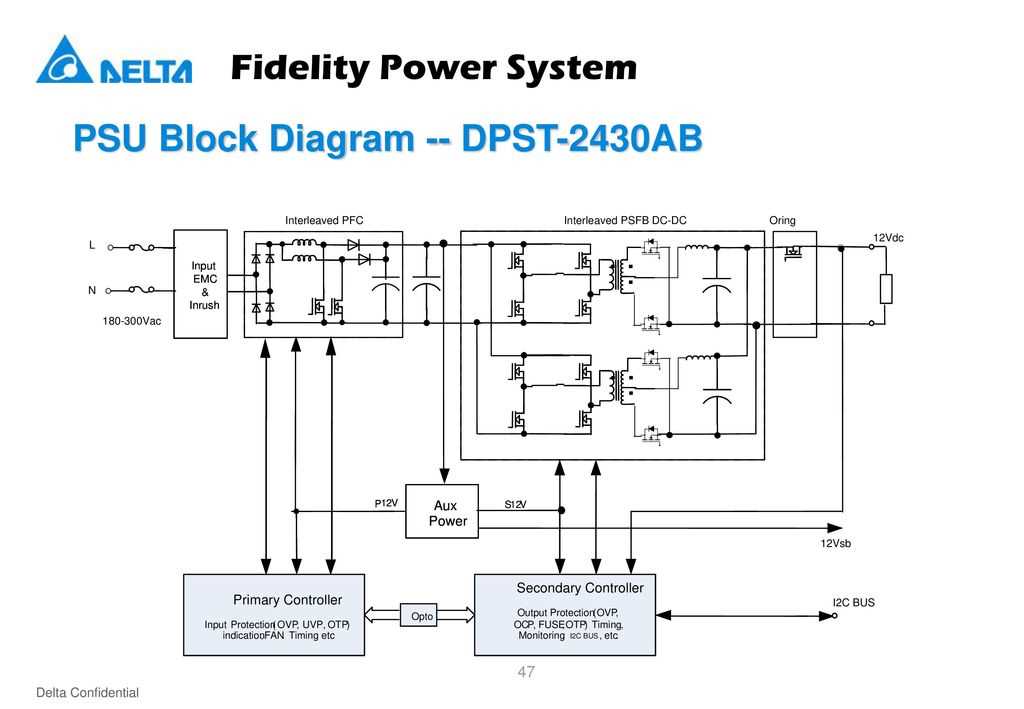
Board diagrams are powerful tools for visualizing and organizing information. Here are some tips to help you effectively use board diagrams:
- Keep it simple: Try to keep your board diagrams simple and clutter-free. Focus on representing the essential elements and relationships without overwhelming the viewer.
- Use clear labels: Make sure to use clear labels for each element in your board diagram. This will help the viewers understand the content and make connections between different components.
- Consider the layout: Think about the best layout for your board diagram. Arrange the elements in a logical manner that reflects their relationships and makes it easier for viewers to navigate through the diagram.
- Use different colors and shapes: Utilize colors and shapes to distinguish between different elements or categories in your board diagram. This can help make the diagram more visually appealing and aid in comprehension.
- Provide explanations and context: Include short explanations or descriptions alongside your board diagram to provide additional context. This can help viewers understand the purpose and significance of the elements represented.
- Update and revise: Board diagrams are not set in stone. They can evolve and change as new information or insights arise. Regularly update and revise your board diagrams to ensure they remain accurate and relevant.
- Collaborate and share: Board diagrams are excellent tools for collaboration and sharing ideas. Share your board diagrams with colleagues or team members to gather feedback and foster discussions.
By following these tips, you can effectively utilize board diagrams to communicate and visualize information in a clear and organized manner.