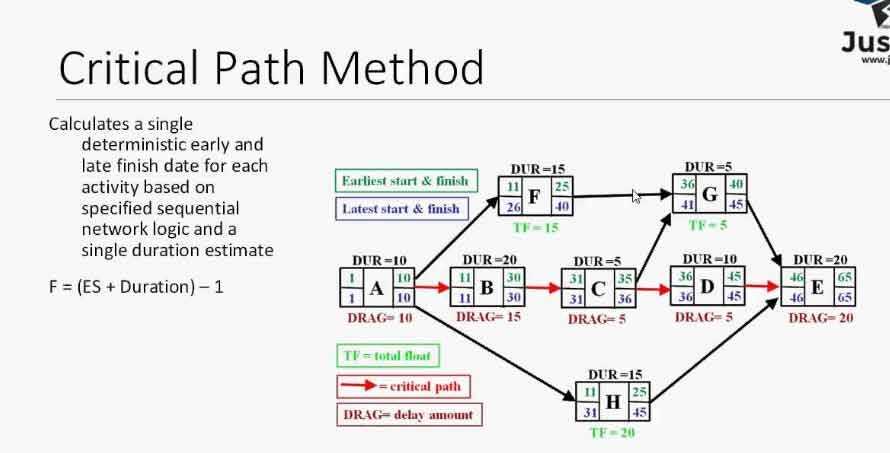
The Critical Path Method (CPM) is a project management technique that helps in planning and scheduling activities in a project. It is used to determine the longest sequence of activities that must be completed in order to finish the project as early as possible. The CPM is widely used in industries such as construction, engineering, and information technology.
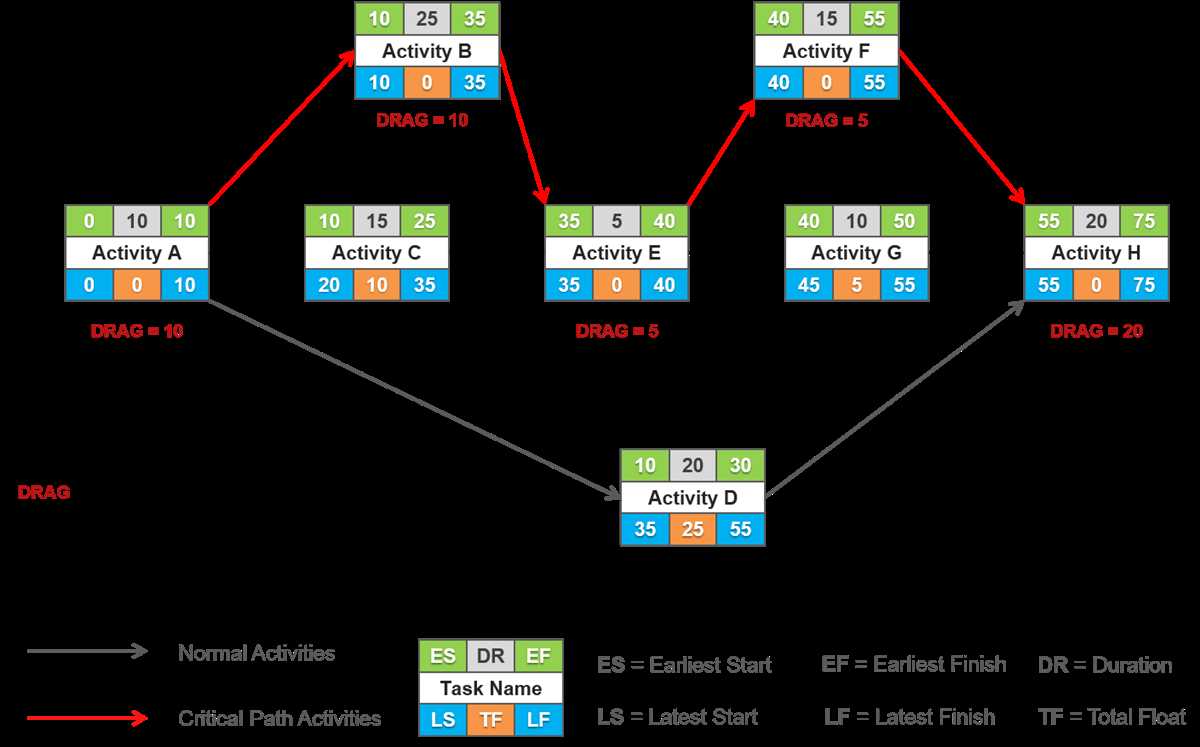
The CPM diagram is a visual representation of the project schedule. It consists of a network of nodes and arrows, where each node represents an activity and each arrow represents the dependency between activities. The diagram helps project managers to identify the critical path, which is the sequence of activities that will take the longest time to complete. By focusing on the critical path, project managers can allocate resources and prioritize tasks effectively to ensure the project is completed on time.
The CPM diagram also helps project managers to identify slack or float time, which is the amount of time an activity can be delayed without delaying the project. Activities that are not on the critical path have slack time, while activities on the critical path have zero slack time. By understanding the slack time, project managers can better manage risks and make informed decisions to keep the project on track.
Critical Path Method Diagram
The Critical Path Method Diagram (CPM) is a project management technique used to determine the most efficient sequence of activities needed to complete a project. It is a visual representation of the project’s activities, their dependencies, and their durations. The CPM diagram helps identify the critical path, which is the longest sequence of activities that determines the earliest possible project completion date.
The CPM diagram consists of nodes, which represent the activities, and arrows, which depict the dependencies between the activities. Each node is labeled with the activity name and its duration. The arrows indicate the flow of the project, connecting the activities in the order they need to be completed. The CPM diagram also includes the early start (ES) and early finish (EF) times, which represent the earliest possible start and finish of each activity, and the late start (LS) and late finish (LF) times, which represent the latest allowable start and finish of each activity without delaying the project.
The critical path is determined by calculating the total duration of each path in the CPM diagram and identifying the path with the longest duration. The activities on the critical path have zero total float, meaning that any delay in their completion would directly impact the project’s overall duration. By focusing on the critical path, project managers can allocate resources and prioritize activities to ensure timely project completion. The CPM diagram also helps identify non-critical activities that have total float, providing flexibility in scheduling and resource allocation.
Key Components of a CPM Diagram:
- Activities: Represented by nodes and labeled with activity name and duration
- Dependencies: Represented by arrows and show the order in which activities need to be completed
- Early Start (ES): The earliest possible start time of an activity
- Early Finish (EF): The earliest possible finish time of an activity
- Late Start (LS): The latest allowable start time of an activity without delaying the project
- Late Finish (LF): The latest allowable finish time of an activity without delaying the project
- Total Float: The amount of time an activity can be delayed without delaying the project
- Critical Path: The longest sequence of activities that determines the earliest possible project completion date
What is the Critical Path Method?
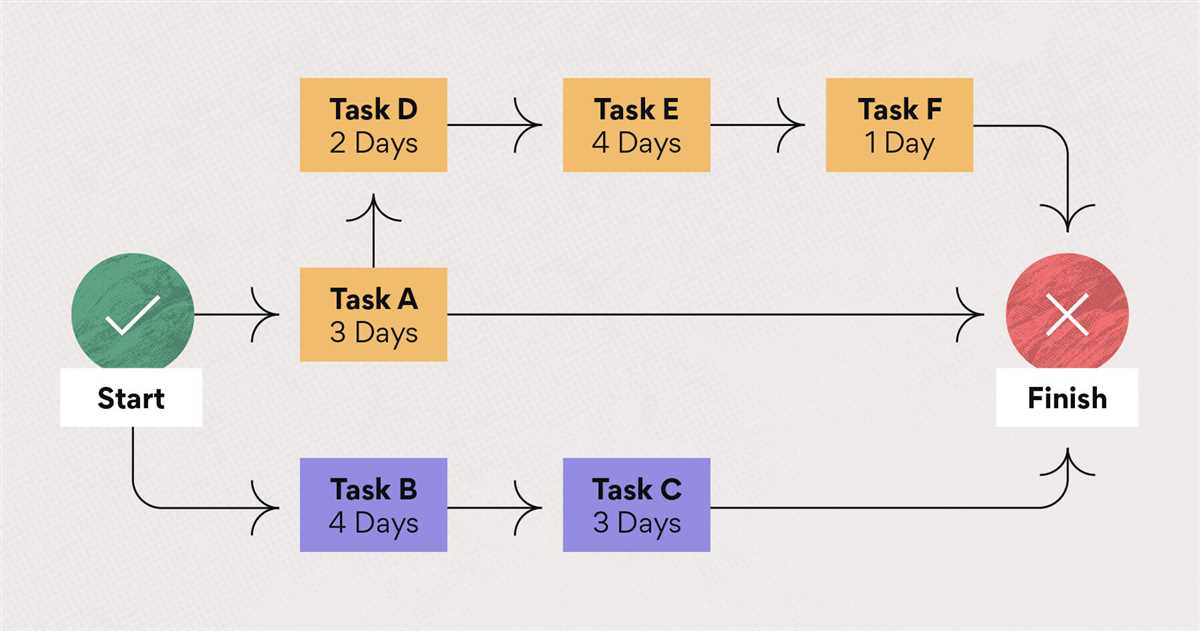
The Critical Path Method (CPM) is a project management technique used to schedule and plan complex projects. It helps project managers identify the most crucial tasks and activities that must be completed in order to meet the project deadline. The CPM provides a visual representation, called a CPM diagram, that outlines the sequence and interdependence of all tasks and activities.
The CPM diagram consists of nodes, which represent tasks, and arrows, which depict the dependencies and relationships between tasks. Each task on the diagram is assigned a duration, which represents the time needed to complete that particular task. By analyzing the CPM diagram, project managers can determine the critical path, which is the longest sequence of dependent tasks that determines the minimum time required to complete the project.
The Critical Path Method is vital in project management as it allows project managers to identify potential bottlenecks and delays in the project schedule. By focusing on the critical path tasks, project managers can allocate resources and manage the project timeline more effectively. The CPM also helps in estimating the project duration and identifying tasks that can be expedited or delayed without affecting the overall project deadline.
How Does the Critical Path Method Work?
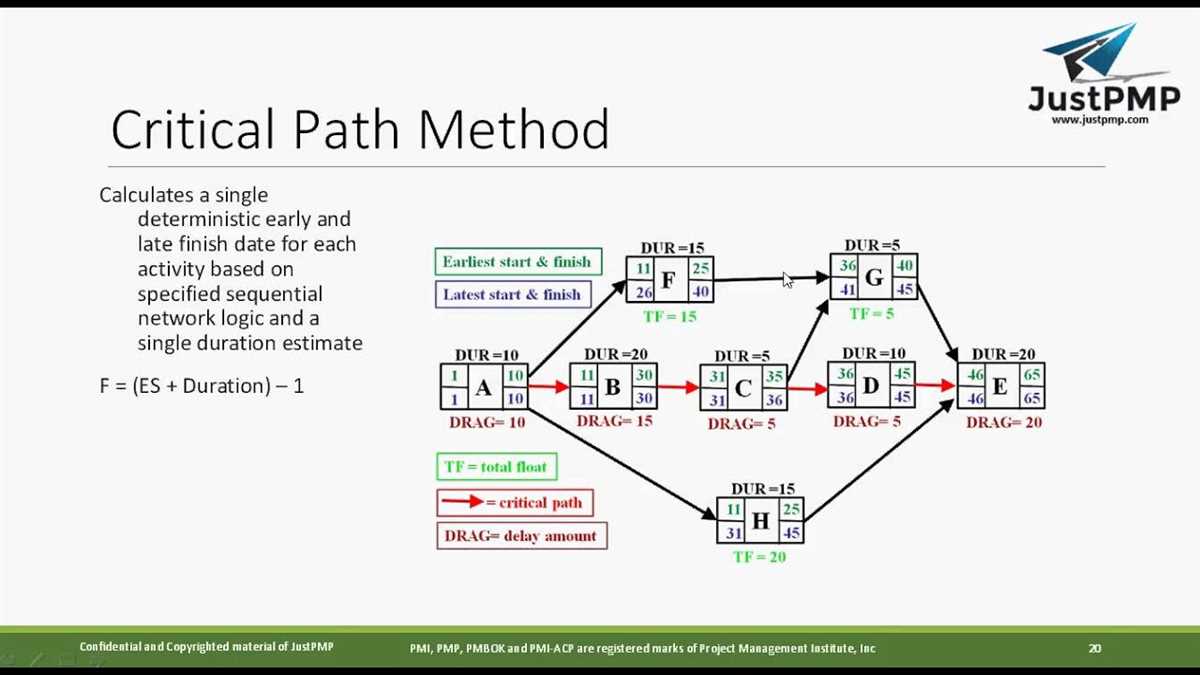
The Critical Path Method (CPM) is a project management technique that helps in planning and scheduling complex projects. It identifies the critical tasks that directly impact the project’s end date and determines the shortest possible time needed to complete the project.
To start with, the project manager creates a list of all the activities and their dependencies. The activities are then arranged in a flowchart, known as a network diagram. Each activity is represented by a node, and the arrows show the dependencies between the activities. The CPM algorithm then calculates the earliest and latest possible start and finish times for each activity based on their dependencies and duration.
The critical path is the longest sequence of activities that determines the project’s completion time. It consists of activities with zero slack, which means any delay in these activities will directly affect the project’s end date. The project manager focuses on these critical activities and ensures they are completed on time.
The CPM also helps in determining the float or slack time for non-critical activities, which are activities that can be delayed without affecting the project’s end date. This allows the project manager to prioritize these activities and allocate resources accordingly.
In summary, the Critical Path Method is a powerful tool for project planning and scheduling. It helps in identifying the critical tasks and allocating resources efficiently to ensure the project’s successful completion within the specified time frame.
Benefits of Using the Critical Path Method
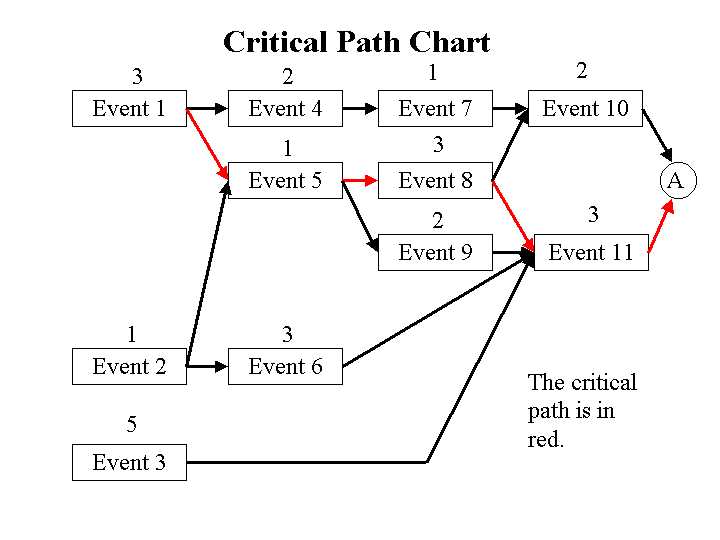
The Critical Path Method (CPM) is a project management technique that helps in planning and scheduling complex projects. It is used to determine the longest sequence of activities and the shortest project duration, which then becomes the critical path. The CPM provides several benefits to project managers and stakeholders.
1. Accurate Project Planning
By analyzing and sequencing different activities, the CPM helps project managers to create an accurate project plan. It enables them to identify the tasks that are critical to the project’s timeline and prioritize resources accordingly. With a detailed plan in place, it becomes easier to allocate resources effectively and ensure timely completion of the project.
2. Efficient Resource Allocation
The CPM allows project managers to identify activities that can be executed in parallel, reducing the total project duration. By understanding the dependencies between activities, resources can be allocated efficiently, minimizing idle time and maximizing productivity. This results in cost savings and improves overall project efficiency.
3. Improved Coordination and Communication
With a visual representation of the project activities and their dependencies, the CPM makes it easier for project teams to understand the project scope and workflow. It fosters better coordination and communication among team members and stakeholders, enabling them to work together towards achieving project objectives. This reduces misunderstandings and ensures smooth project execution.
4. Effective Risk Management
The CPM helps project managers to identify potential risks and their impact on the project timeline. By analyzing the critical path, they can identify activities that have little or no slack and are prone to delays. This enables them to develop mitigation strategies and allocate additional resources to minimize the impact of risks on project completion. Effective risk management reduces the chances of project delays and cost overruns.
5. Real-time Project Tracking
The CPM provides a framework for tracking the progress of individual activities in real-time. As the project progresses, project managers can compare the actual progress against the planned milestones and identify any deviations. This allows for timely course correction and helps in keeping the project on track towards successful completion. Real-time tracking also improves transparency and accountability within the project team.
In conclusion, the Critical Path Method offers several benefits for project managers and stakeholders. It facilitates accurate project planning, efficient resource allocation, improved coordination and communication, effective risk management, and real-time project tracking. By leveraging the CPM, project managers can increase their chances of delivering projects on time, within budget, and with the desired quality.
Common Applications of the Critical Path Method
The Critical Path Method (CPM) is a project management technique that helps in planning and scheduling complex projects. It is widely used in various industries and has proven to be an effective tool in ensuring successful project completion. Here are some common applications of the Critical Path Method:
1. Construction Projects
The construction industry heavily relies on the Critical Path Method for efficient project planning and management. By identifying the critical tasks and their interdependencies, project managers can allocate resources effectively, determine the project duration, and minimize delays. CPM helps construction companies stay on track, meet deadlines, and deliver projects within budget.
2. Engineering Projects
Engineering projects often involve multiple tasks and dependencies that need careful planning and coordination. The Critical Path Method allows engineers to determine the most efficient sequence of activities, estimate project duration, and identify bottlenecks or potential issues. It helps in optimizing the use of resources, managing risks, and ensuring timely project completion.
3. Information Technology Projects
In the dynamic and rapidly evolving field of information technology, the Critical Path Method is a valuable tool for project managers. It helps them prioritize tasks, manage dependencies, and allocate resources effectively. By identifying the critical path, IT projects can be completed with minimized risks and delays, ensuring successful implementation and deployment.
4. Event Planning
Event planning requires meticulous coordination of multiple tasks and resources. The Critical Path Method is used to create a detailed schedule, identify critical tasks, and determine the most efficient sequence of activities. By effectively managing the critical path, event planners can ensure the smooth execution of an event, minimize potential delays, and deliver a successful outcome.
5. Manufacturing and Production Projects
In manufacturing and production projects, the Critical Path Method is used to optimize workflow and minimize production time. By identifying the critical tasks and their dependencies, project managers can allocate resources efficiently and streamline the production process. CPM helps in reducing bottlenecks, maximizing productivity, and ensuring timely delivery of products.
In conclusion, the Critical Path Method is widely used in various industries and project types to effectively plan, schedule, and manage complex projects. Its applications range from construction and engineering projects to event planning and manufacturing. By utilizing CPM, project managers can optimize resource allocation, identify critical tasks, and ensure successful project completion.
Limitations of the Critical Path Method
The Critical Path Method (CPM) is a powerful tool for project management that helps identify the critical tasks and sequence of activities required to complete a project. However, like any method, the CPM has its limitations, which need to be considered when applying it to real-world projects.
Here are some of the limitations of the CPM:
- Assumption of independent and deterministic activities: The CPM assumes that activities are independent of each other and have fixed durations. In reality, dependencies and uncertainties often exist, leading to variations in activity durations and potential delays.
- Lack of flexibility: The CPM provides a rigid schedule, with no flexibility for changes or unforeseen circumstances. It does not account for dynamic changes in project requirements or external factors that may impact the project timeline.
- Complexity: The CPM can become complex and challenging to manage for large and highly interconnected projects. As the number of activities and dependencies increase, the calculations and analysis become more complicated, requiring specialized software and expertise.
- Focus on time: The CPM primarily focuses on project timelines and critical paths, neglecting other important aspects such as resource allocation, costs, and quality. It may not provide a comprehensive view of the project and its overall performance.
- Overemphasis on critical tasks: The CPM prioritizes critical tasks, leading to a heavy focus on those activities. This may overlook the significance of non-critical tasks that can still impact project progress and outcomes.
Despite these limitations, the CPM remains a valuable technique for project planning and scheduling. It helps identify the critical tasks and their sequence, enabling project managers to allocate resources effectively and identify potential risks. However, it is important to acknowledge the limitations and consider them alongside other project management methodologies and techniques to ensure successful project execution.