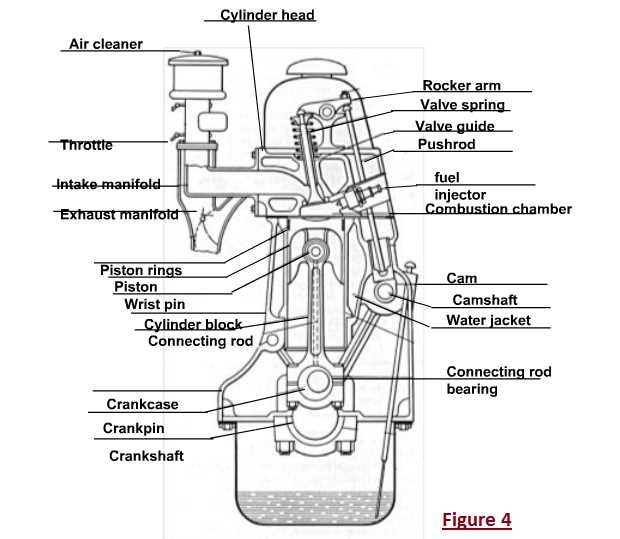
A diesel engine is a type of internal combustion engine that converts the chemical energy of fuel into mechanical energy. It is widely used in various applications, such as cars, trucks, ships, and power generation systems. Understanding the different parts of a diesel engine is crucial for its proper functioning and maintenance.
The main parts of a diesel engine can be categorized into two major groups: the external components and the internal components. The external components include the air intake system, the fuel system, and the exhaust system. These components are responsible for supplying air and fuel to the engine and removing the exhaust gases.
The internal components of a diesel engine include the cylinder head, the piston, the connecting rod, and the crankshaft. The cylinder head acts as a cover for the top of the cylinder block and houses the intake and exhaust valves. The piston moves up and down inside the cylinder, converting the energy from the combustion process into reciprocating motion. The connecting rod connects the piston to the crankshaft, which converts the linear motion of the piston into rotational motion.
Other important parts of a diesel engine include the camshaft, which controls the opening and closing of the valves, the fuel injectors, which inject fuel into the combustion chamber, and the turbocharger, which increases the engine’s power by compressing the air entering the cylinders. Understanding the function and interaction of these parts is essential for the efficient operation of a diesel engine.
Diagram of Diesel Engine Parts
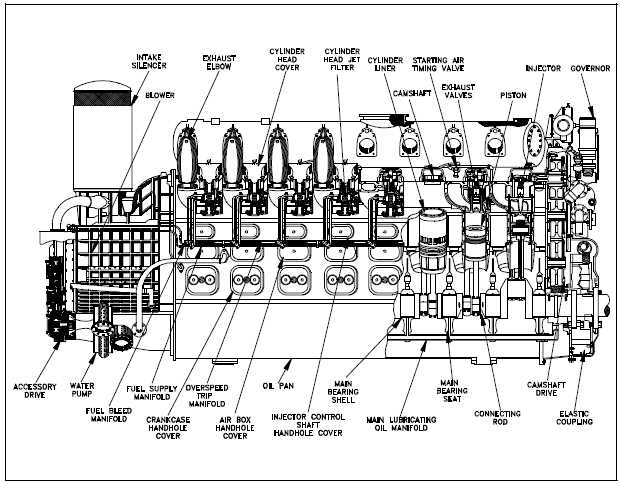
A diesel engine is a type of internal combustion engine that uses compression ignition to generate power. Understanding the different parts of a diesel engine can help provide a clearer picture of how it functions and the role each component plays in the overall operation.
1. Engine Block: The engine block is the main component of the diesel engine. It serves as the foundation for all other parts and houses the cylinders, crankshaft, and other major components.
2. Pistons: Pistons are cylindrical components that move up and down within the cylinders. They are connected to the crankshaft via connecting rods and transfer the force generated by the expanding gases during combustion to the crankshaft.
3. Crankshaft: The crankshaft converts the linear motion of the pistons into rotational motion. It is connected to the pistons via connecting rods and provides power to the engine’s drivetrain.
4. Cylinder Head: The cylinder head sits on top of the engine block and houses the combustion chambers. It contains valves, fuel injectors, and other components necessary for the combustion process.
5. Valves: Valves control the flow of air and exhaust gases into and out of the combustion chambers. The intake valves allow air to enter the cylinder, while the exhaust valves allow exhaust gases to exit.
6. Fuel Injectors: Fuel injectors spray fuel into the combustion chambers at a precise moment during the engine’s compression stroke. This fuel mixes with the compressed air and is ignited, resulting in combustion and the release of energy.
7. Glow Plugs: Glow plugs are used in diesel engines to preheat the combustion chambers, especially during cold starts. They help ensure proper ignition of the fuel-air mixture by heating the air in the cylinders.
8. Turbocharger: A turbocharger is a device that increases the air intake pressure in the combustion chambers. It uses the engine’s exhaust gases to drive a turbine, which compresses the incoming air, leading to improved combustion efficiency and increased power output.
9. Cooling System: The cooling system in a diesel engine helps regulate the temperature and prevent overheating. It typically includes a radiator, coolant, water pump, and fan to dissipate heat generated during operation.
10. Lubrication System: The lubrication system ensures proper lubrication and reduces friction between moving parts. It includes an oil pump, oil filter, and various oil passages that distribute lubricating oil to critical engine components.
Conclusion
Knowing the different parts of a diesel engine and their functions can provide valuable insights into its operation and maintenance. From the engine block and pistons to the fuel injectors and cooling system, each component plays a crucial role in the overall performance and longevity of the diesel engine.
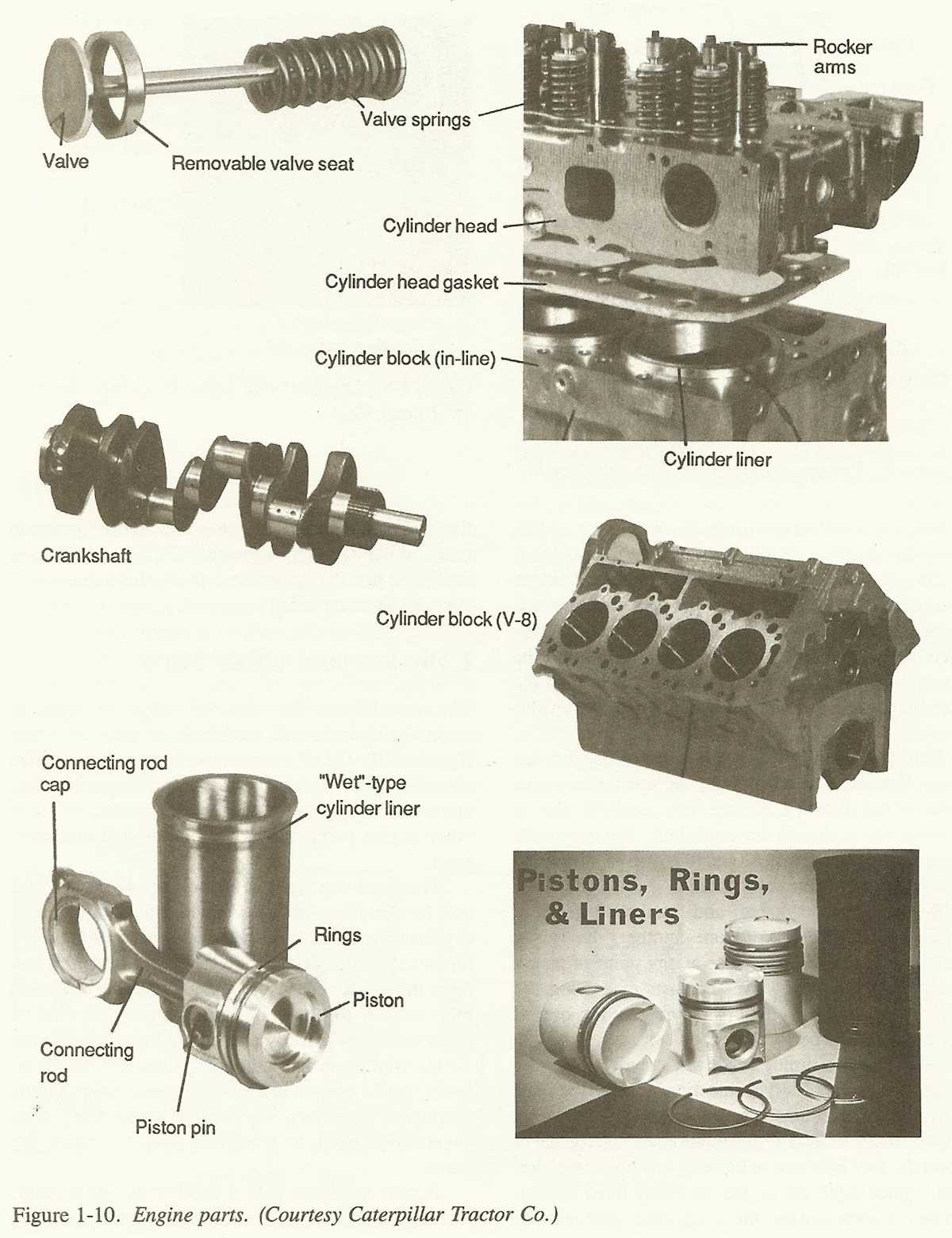
Engine Block
The engine block, also known as the cylinder block, is the main structural component of a diesel engine. It is typically made of cast iron or aluminum and houses the cylinders, crankshaft, camshaft, and other vital components of the engine.
The engine block is responsible for enclosing and supporting the cylinders, which are where the combustion process takes place. It provides a rigid structure that can withstand the high pressures and temperatures generated during combustion. The block also contains coolant passages and oil galleries that allow for the circulation of coolant and lubricating oil to keep the engine running smoothly.
Cylinder Head
The cylinder head is a crucial component of a diesel engine, as it forms the top part of the combustion chamber. It is typically made of cast iron or aluminum and is bolted onto the engine block. The cylinder head plays a vital role in sealing the combustion chamber and housing various important components.
Mechanical Properties:
The cylinder head is designed to withstand high temperatures and pressures generated by the combustion process. It must be strong and durable to endure the repeated explosions that occur in the cylinders. The material used for the construction of the cylinder head is chosen based on its ability to dissipate heat effectively and resist deformation.
- Cooling System: The cylinder head contains passages and channels for the circulation of coolant, which helps to regulate the temperature of the engine. These passages ensure that the excessive heat generated during combustion does not damage the cylinders or other engine components.
- Valvetrain: The cylinder head houses the intake and exhaust valves, along with their associated components. It provides a platform for these valves to open and close at the proper timing, allowing the intake of fresh air and expelling exhaust gases. The valvetrain is responsible for the efficient flow of air and fuel in and out of the combustion chamber.
- Gasket Sealing: The cylinder head is sealed against the engine block using a cylinder head gasket. This gasket ensures that the combustion chamber remains airtight and prevents any leakage of gas or coolant. It also acts as a barrier between oil and coolant passages, preventing cross-contamination.
- Combustion Chamber: The shape and design of the combustion chamber in the cylinder head greatly influence the engine’s performance and efficiency. It determines factors such as compression ratio, swirl, and turbulence, which impact fuel combustion and power output.
In summary, the cylinder head is a critical component of a diesel engine, responsible for sealing the combustion chamber, housing the valvetrain components, facilitating coolant circulation, and providing a platform for efficient fuel combustion. Its design and material play a crucial role in the engine’s overall performance and reliability.
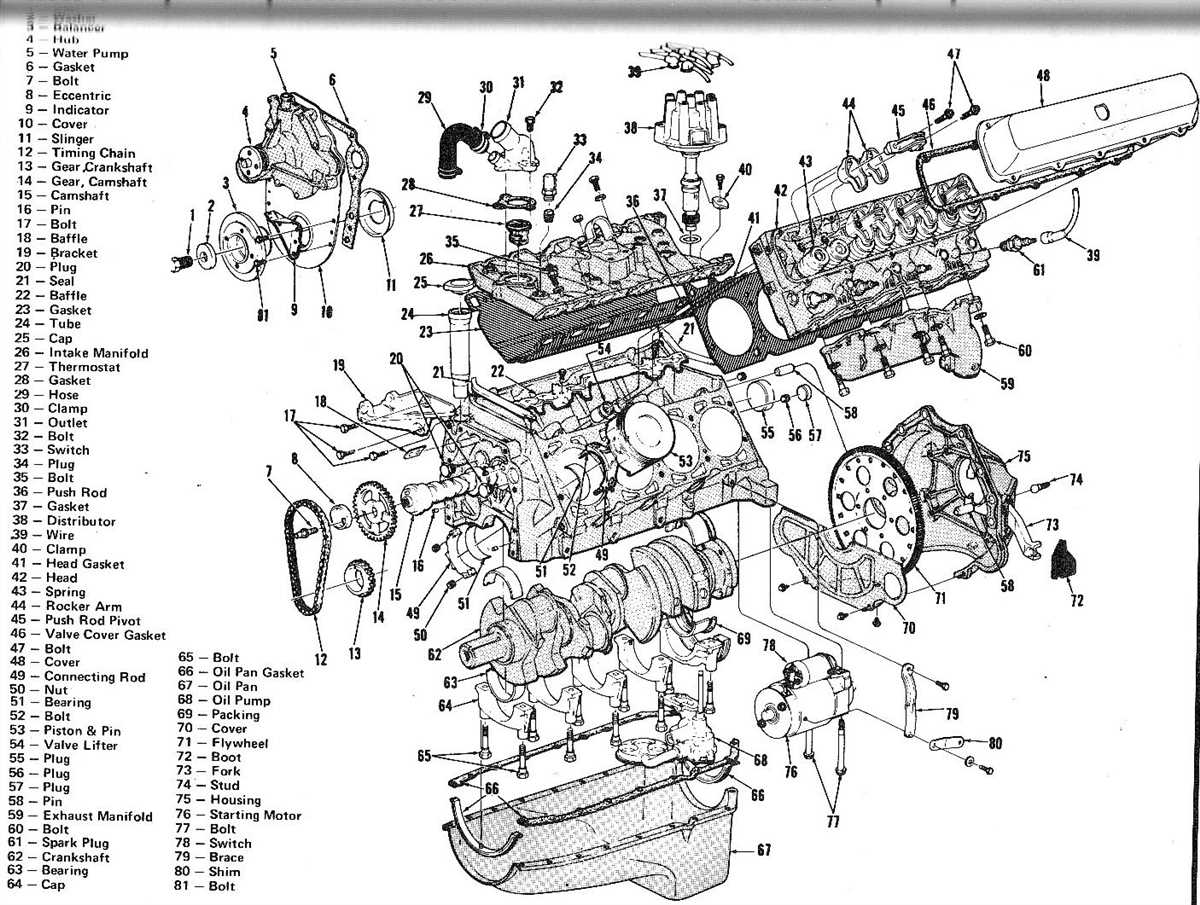
Fuel System
The fuel system is a crucial component of a diesel engine, responsible for delivering the required amount of fuel to the combustion chamber for the process of combustion. It consists of various parts and subsystems that work together to ensure efficient fuel delivery and combustion.
One of the main components of the fuel system is the fuel tank, which stores the diesel fuel. The fuel is then drawn from the tank by a fuel pump, which is usually electrically powered. The fuel pump pressurizes the fuel and delivers it to the fuel injectors.
Fuel Injectors
Fuel injectors are critical parts of the fuel system that directly inject the pressurized fuel into the combustion chamber. They are typically electronically controlled and operate based on signals from the engine control unit (ECU). The fuel injectors ensure precise fuel delivery and atomization, which is vital for efficient combustion and power generation.
Fuel Filters
Fuel filters are essential components in the fuel system that remove impurities and contaminants from the fuel before it reaches the combustion chamber. They prevent clogging of the fuel injectors and protect the engine from damage caused by dirty fuel. Regular maintenance and replacement of fuel filters are necessary to ensure the proper functioning of the fuel system.
- Fuel Lines: The fuel lines transport the pressurized fuel from the fuel pump to the fuel injectors. They need to be made of durable materials and properly sealed to prevent any leakage.
- Fuel Pressure Regulator: The fuel pressure regulator maintains a constant fuel pressure in the system by regulating the flow of fuel. This ensures the optimal functioning of the fuel injectors and prevents fuel starvation or flooding.
- Fuel Rail: The fuel rail is a tube that connects the fuel injectors and delivers the pressurized fuel to them. It serves as a manifold for fuel distribution and plays a crucial role in maintaining consistent fuel pressure.
In summary, the fuel system of a diesel engine includes the fuel tank, fuel pump, fuel injectors, fuel filters, fuel lines, fuel pressure regulator, and fuel rail. These components work together to deliver the required amount of fuel to the combustion chamber, ensuring efficient combustion and power generation.
Cooling System
The cooling system in a diesel engine is crucial for maintaining the optimal operating temperature. It helps prevent overheating and ensures that the engine runs efficiently. The cooling system consists of several key components that work together to dissipate heat generated during combustion. These components include the radiator, water pump, thermostat, and cooling fan.
The radiator is responsible for cooling the engine coolant. It is typically located at the front of the vehicle to maximize airflow. The radiator has a series of small tubes that allow the coolant to flow through and be cooled by the surrounding air. The hot coolant enters the radiator from the engine, and as it flows through the tubes, heat is transferred to the air, cooling the coolant. The cooled coolant then returns to the engine to absorb more heat.
The water pump plays a crucial role in circulating the coolant through the engine and radiator. It is driven by a belt connected to the engine’s crankshaft and pumps the coolant from the engine to the radiator and back. The water pump ensures a continuous flow of coolant, preventing hot spots and maintaining a consistent temperature throughout the engine.
The thermostat is a temperature-sensitive valve that regulates the flow of coolant through the engine. It remains closed when the engine is cold to allow it to warm up quickly. Once the engine reaches its optimal operating temperature, the thermostat opens, allowing coolant to flow through the engine and radiator. This helps maintain a constant temperature and prevent overheating.
The cooling fan is responsible for creating airflow through the radiator when the vehicle is not moving or when additional cooling is required. It is typically driven by an electric motor and is controlled by the engine’s cooling system. When the engine temperature rises above a certain threshold, the cooling fan is activated to draw air through the radiator, dissipating heat and cooling the coolant.
Exhaust System
The exhaust system is an essential component of a diesel engine, responsible for removing the harmful gases produced during the combustion process. It plays a crucial role in maintaining the engine’s performance, efficiency, and overall environmental impact.
The main parts of the exhaust system include:
- Exhaust manifold: This component collects the waste gases from each cylinder and directs them into the exhaust pipe.
- Exhaust pipe: It carries the gases from the manifold to the catalytic converter or muffler.
- Catalytic converter: This device is responsible for reducing the pollutants in the exhaust gases by converting them into less harmful substances through chemical reactions.
- Muffler: It reduces the noise produced by the engine by using sound-absorbing materials and exhaust baffles.
- Tailpipe: This is the final part of the exhaust system, through which the cleaned exhaust gases are released into the atmosphere.
The exhaust system plays a vital role in maintaining the overall performance and longevity of a diesel engine. By efficiently removing the waste gases, it helps to optimize the engine’s combustion process and reduce power loss. Additionally, the catalytic converter helps to minimize the emission of harmful pollutants, making the diesel engine more environmentally friendly.
It is important to ensure that the exhaust system is regularly inspected and maintained to prevent any leaks or blockages that could affect the engine’s performance and increase emissions. Regular maintenance and timely replacement of worn-out components are necessary to ensure the proper functioning of the exhaust system and the diesel engine as a whole.
Q&A:
What is an exhaust system?
An exhaust system is a system in a vehicle that carries exhaust gases away from the engine and releases them into the atmosphere.
What are the components of an exhaust system?
The components of an exhaust system include the exhaust manifold, catalytic converter, muffler, and tailpipe.
What is the purpose of the exhaust manifold?
The exhaust manifold collects gases from each cylinder in the engine and directs them into the exhaust system.
What does the catalytic converter do?
The catalytic converter is responsible for reducing harmful emissions by converting toxic gases into less harmful substances.
Why is a muffler used in an exhaust system?
A muffler is used to reduce the noise produced by the exhaust gases as they flow through the system.
What is an exhaust system?
An exhaust system is a series of pipes and components that are designed to direct exhaust gases away from the engine and out of the vehicle.