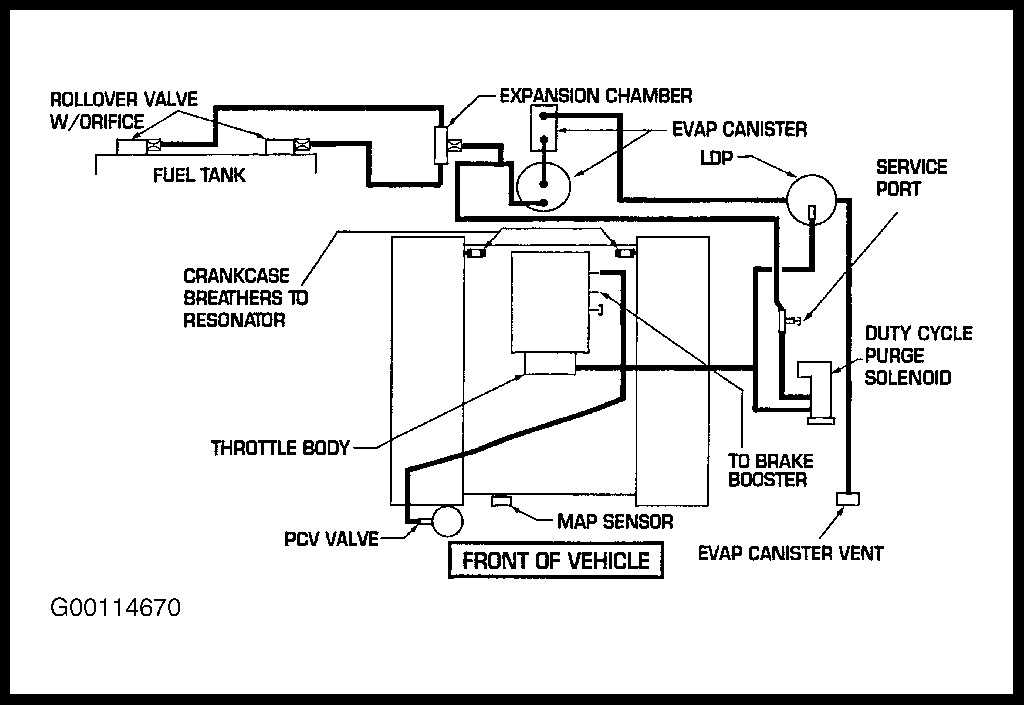
The Dodge Dakota vacuum diagram is an essential tool for understanding and maintaining your vehicle’s performance. The vacuum system plays a crucial role in various aspects of your Dakota’s operation, from fuel efficiency to engine performance. By understanding the vacuum diagram, you can identify potential issues, troubleshoot problems, and ensure that your Dakota is running at its best.
So, what exactly is a vacuum diagram? It is a schematic representation of the vacuum lines and components in your Dakota’s engine bay. These vacuum lines are responsible for carrying the negative pressure, or vacuum, created by the engine’s intake strokes. This vacuum is used to power various components, such as the brake booster, heating and cooling controls, emissions systems, and more.
Without a properly functioning vacuum system, your Dakota may experience a range of issues. For example, a vacuum leak can result in decreased engine performance, poor fuel efficiency, and even stalling. By referring to the vacuum diagram, you can identify the location of the vacuum lines and components, allowing you to inspect them for wear, damage, or leaks.
Dodge Dakota Vacuum Diagram
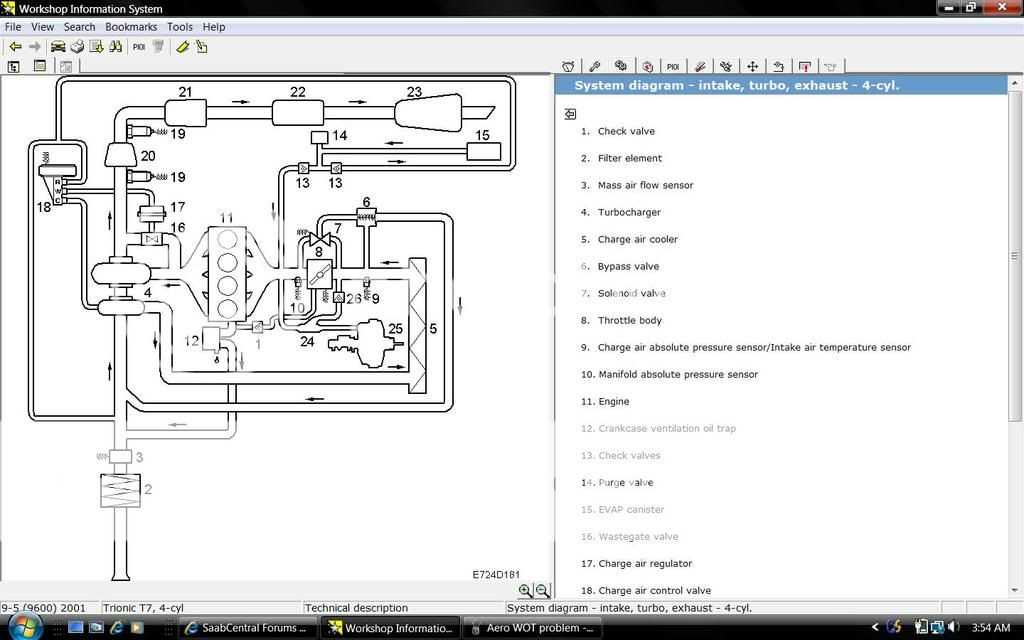
The Dodge Dakota is a popular mid-size pickup truck known for its durability and performance. Like any vehicle, it relies on a complex system of components to operate efficiently, including the vacuum system. Understanding the Dodge Dakota vacuum diagram is essential for troubleshooting and maintaining the truck’s performance.
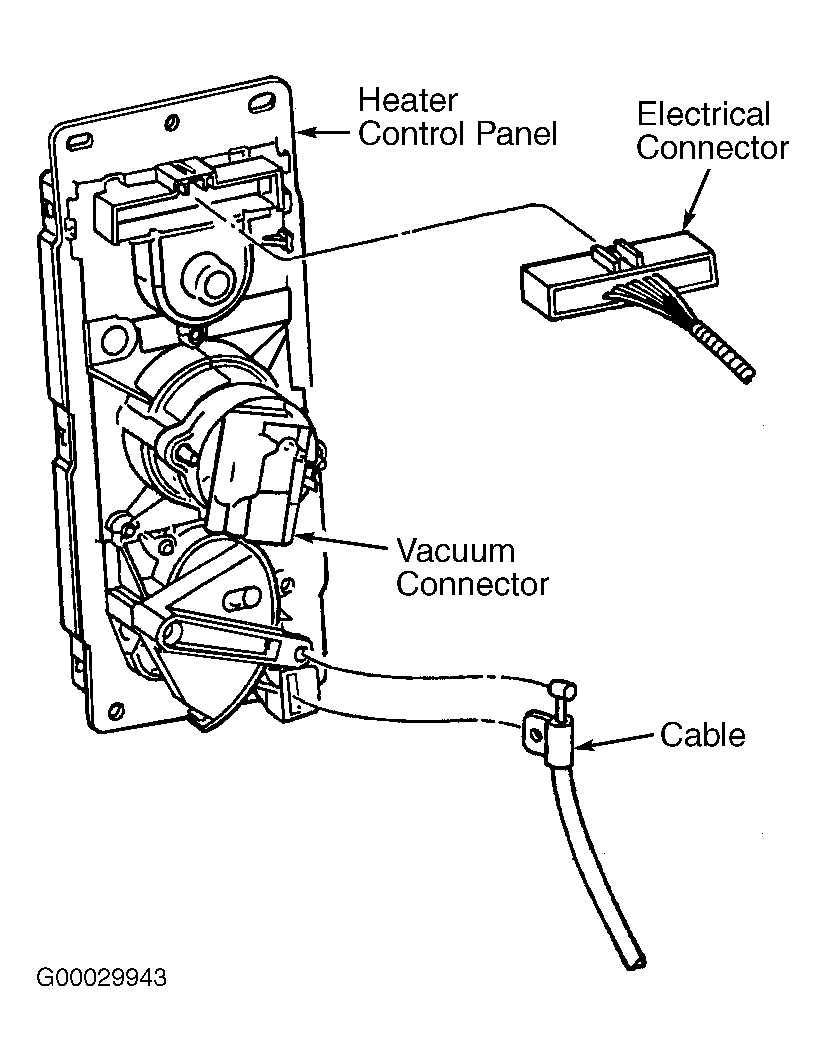
The vacuum diagram for a Dodge Dakota illustrates the various vacuum lines and their connections throughout the engine bay. These lines play a crucial role in several systems, including the brake booster, emissions control, and HVAC (heating, ventilation, and air conditioning).
One of the key components in the vacuum system is the vacuum pump. It creates suction to power various accessories and systems that rely on vacuum pressure. The vacuum pump is usually driven by the engine’s accessory belt, ensuring it operates whenever the engine is running.
The Dodge Dakota vacuum diagram may show different colored lines or simply labeled with letters or numbers to indicate their purpose. Some diagrams may also include specific troubleshooting steps or guidelines for specific vacuum-related issues.
If you’re experiencing problems with your Dodge Dakota’s vacuum system, such as poor brake performance or issues with the HVAC system, referencing the vacuum diagram can often help pinpoint the issue. It is recommended to consult the vehicle’s manual or online resources to find the appropriate diagram for your specific model year.
Regular inspection and maintenance of the vacuum system, including checking for leaks or damaged lines, can help prevent potential issues and keep your Dodge Dakota operating at its best. Following the vacuum diagram and understanding how the system works can make troubleshooting and repairs easier.
What is a vacuum diagram?
A vacuum diagram is a visual representation of the vacuum system in a vehicle. The vacuum system plays an important role in the operation of various components in the engine, such as the brake booster, emissions control system, and HVAC system. A vacuum diagram shows the various hoses and connections that make up the vacuum system, as well as the direction of airflow and the components that are involved.
Components:
- Air filter
- Throttle body
- Vacuum reservoir
- Vacuum lines
- Vacuum check valve
- Vacuum actuator
Function:
The vacuum system in a vehicle helps to create a pressure differential that allows for the operation of different systems and components. It works by using the suction power generated by the engine to draw in air and create a vacuum. This vacuum is then used to power and control various components, such as the brake booster, which uses the vacuum to assist with braking, and the emissions control system, which relies on vacuum-operated valves to redirect exhaust gases.
Importance of a vacuum diagram:
A vacuum diagram is important because it provides a clear understanding of how the vacuum system in a vehicle is set up and how it functions. It helps technicians and mechanics identify potential issues with the system, such as leaks or blockages, and allows them to troubleshoot and repair the problem effectively. Without a vacuum diagram, it can be challenging to diagnose and fix problems related to the vacuum system, resulting in potential performance issues and increased emissions.
Why is the vacuum diagram important for a Dodge Dakota?
Understanding the vacuum diagram is crucial for maintaining and troubleshooting the Dodge Dakota’s engine performance. The vacuum diagram provides a visual representation of the engine’s intricate vacuum system, which plays a vital role in the vehicle’s overall operation.
Vacuum System Overview:
- The vacuum system in the Dodge Dakota helps control various components, such as the EGR valve, power brakes, climate control, and emission control systems.
- It works by utilizing vacuum pressure created by the engine to operate these systems and ensure their proper functioning.
- A vacuum diagram highlights the specific components connected by vacuum lines and illustrates their interconnections.
Importance of the Vacuum Diagram:
1. System Troubleshooting: The vacuum diagram acts as a guide for diagnosing and repairing any issues related to the vacuum system. By referring to the diagram, mechanics and vehicle owners can pinpoint the exact location of a broken or disconnected vacuum line, potentially saving time and money on troubleshooting.
2. Proper Component Connection: The vacuum diagram ensures that the various components connected by vacuum lines are correctly routed and interlinked. Improper connections can lead to inefficient system operation or even component failure. The diagram helps both professionals and DIY enthusiasts in ensuring that the vacuum lines are correctly installed.
3. Precision on System Operation: The vacuum diagram provides a clear understanding of how the vacuum-operated systems in the Dodge Dakota work together. It helps in grasping the functionality and interaction of different components, allowing for better optimization and performance.
4. Upgrading and Modification: For those looking to modify or upgrade their Dodge Dakota’s engine or vacuum-operated systems, the vacuum diagram is a crucial reference. It allows for proper planning and implementation of any modifications, ensuring that the new components or systems fit seamlessly into the existing vacuum system.
Overall, the vacuum diagram is an important tool for anyone working on or owning a Dodge Dakota. It provides valuable insights into the intricate vacuum system, ensuring optimal performance, and simplifying troubleshooting and repair processes.
Common Issues with the Vacuum System in a Dodge Dakota
In a Dodge Dakota, the vacuum system plays a crucial role in the proper operation of various components, including the brakes, ventilation, and 4-wheel drive system. However, over time, this system can develop issues that may affect the performance of the vehicle. Here are some common problems that Dodge Dakota owners may encounter with their vacuum systems:
Vacuum Leaks
Vacuum leaks occur when there is a break or gap in the vacuum lines or connections, allowing air to enter the system. This can lead to a loss of vacuum pressure, causing poor performance or erratic behavior of components that rely on vacuum, such as the brake booster or the HVAC system. Signs of a vacuum leak may include a hissing sound, fluctuating idle speed, or difficulty in engaging the 4-wheel drive system.
Defective Check Valves
Check valves are essential components in the vacuum system that prevent backflow or loss of vacuum pressure. If these valves become worn out or malfunctioning, it can lead to a loss of vacuum pressure and affect the performance of various components. Symptoms of faulty check valves may include a soft brake pedal, weak airflow from the vents, or difficulty in engaging the 4-wheel drive system.
Blocked or Clogged Vacuum Lines
Over time, the vacuum lines in a Dodge Dakota can become blocked or clogged with debris, preventing proper vacuum flow. This can result in poor performance or malfunctioning of components that rely on vacuum, such as the brake booster or the HVAC system. Signs of blocked or clogged vacuum lines may include a soft brake pedal, weak or no airflow from the vents, or difficulty in engaging the 4-wheel drive system.
Malfunctioning Vacuum Actuators
Vacuum actuators are responsible for controlling various functions in the vehicle, such as locking/unlocking the front hubs in a 4-wheel drive system. If these actuators become malfunctioning or fail, it can result in the improper operation of these functions. Signs of malfunctioning vacuum actuators may include difficulty in engaging or disengaging the 4-wheel drive system, or the inability to lock/unlock the front hubs.
In conclusion, the vacuum system in a Dodge Dakota can experience various issues over time, including vacuum leaks, defective check valves, blocked/clogged vacuum lines, and malfunctioning vacuum actuators. It is important to address these issues promptly to ensure the proper performance and functioning of the vehicle’s components.
How to read a vacuum diagram
A vacuum diagram is a schematic representation of the vacuum system in a vehicle. It shows how different components are connected and how the vacuum flows throughout the system. Understanding how to read a vacuum diagram is essential for diagnosing and troubleshooting issues related to the vacuum system.
Components: A vacuum diagram typically includes various components such as the intake manifold, throttle body, vacuum lines, vacuum switches, and vacuum reservoirs. Each component is represented by a specific symbol or label, making it easier to understand the connections.
Lines: Vacuum lines are represented by straight or curved lines in a vacuum diagram. The direction of the lines indicates the flow of vacuum, with arrows indicating the direction of airflow. Different line styles or colors may be used to differentiate between different types of vacuum lines.
Labels: Labels are used to identify different components or parts within the vacuum system. These labels typically include abbreviations or acronyms that represent specific parts. For example, “EGR” may indicate the exhaust gas recirculation valve.
Connections: The connections between components are shown using dots or circles on the vacuum diagram. These dots represent where the vacuum lines are connected to the corresponding components. Following the lines and connections can help identify any potential leaks or disconnected parts.
Notes: Some vacuum diagrams may include additional notes or information to provide more details about specific components or connections. These notes can be helpful for understanding the overall functioning of the vacuum system.
Using the diagram: To read a vacuum diagram, start by identifying the key components and their corresponding symbols or labels. Follow the vacuum lines and connections, paying attention to the direction of flow indicated by arrows. Cross-reference with any additional notes or information provided on the diagram to gain a comprehensive understanding of the vacuum system.
Overall, reading a vacuum diagram requires familiarity with the symbols, labels, and connections used in the diagram. With practice and knowledge of the specific vehicle model, understanding and interpreting vacuum diagrams becomes easier, enabling more effective troubleshooting and repair of vacuum system issues.
Steps to Diagnose and Repair Vacuum System Problems
When it comes to diagnosing and repairing vacuum system problems in a Dodge Dakota, it’s important to follow a step-by-step process to ensure accurate identification and effective resolution. Here are the steps to consider:
1. Visual Inspection
Start by conducting a visual inspection of the vacuum lines, hoses, and connections in the engine bay. Look for any signs of damage, cracks, or disconnected components. Pay close attention to the vacuum reservoir and check if it is securely attached.
2. Testing for Vacuum Leaks
One of the most common causes of vacuum system problems is a vacuum leak. To test for leaks, use a vacuum gauge or a smoke machine. Connect the gauge to a vacuum port on the intake manifold and observe the readings. If the gauge shows low or fluctuating vacuum levels, it may indicate a leak. Alternatively, you can use a smoke machine to introduce smoke into the vacuum system and look for any visible leaks.
3. Check Valve Functionality
The vacuum system relies on various check valves to control the flow of air and maintain proper vacuum levels. Inspect these valves and ensure they are working correctly. Test them by applying suction or blowing air through them and checking for any obstructions or improper functioning.
4. Check Vacuum Pump or Vacuum Source
If your Dodge Dakota is equipped with a vacuum pump or another dedicated vacuum source, check its functionality. Ensure that it is properly connected and supplying sufficient vacuum to the system. Test it by using a vacuum gauge to measure the vacuum levels it generates.
5. Replace Faulty Components
If you have identified any damaged or malfunctioning components during the inspection and testing process, it’s time to replace them. Replace any cracked or disconnected hoses, faulty check valves, or malfunctioning vacuum pump. Ensure that the replacement parts are compatible with your Dodge Dakota model and follow proper installation procedures.
6. Retest and Verify Results
After replacing any faulty components, retest the vacuum system to ensure proper functionality. Use a vacuum gauge or smoke machine again to check for leaks and verify that vacuum levels are within the acceptable range. Make any necessary adjustments or additional repairs if needed.
Following these steps can help you diagnose and repair vacuum system problems in your Dodge Dakota effectively. Remember to always consult the vehicle’s service manual or seek professional assistance if needed.
Tips for maintaining the vacuum system in a Dodge Dakota
Maintaining the vacuum system in your Dodge Dakota is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and reliability of your vehicle. Here are some tips to help you keep the vacuum system in top condition:
1. Regularly check for leaks
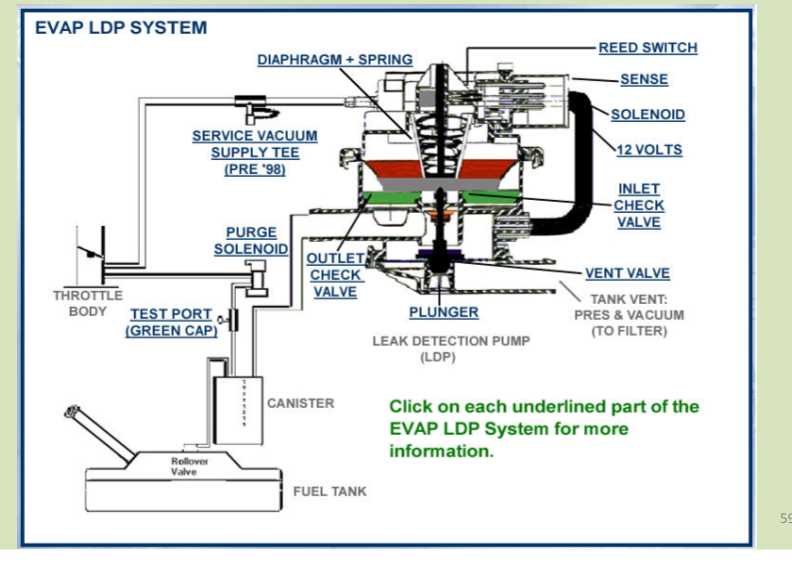
Inspect the vacuum lines and connections for any signs of leaks. Leaks can result in loss of vacuum pressure, leading to poor engine performance and reduced fuel efficiency. Use a vacuum gauge to check the system and repair any leaks promptly.
2. Replace worn-out hoses and connections
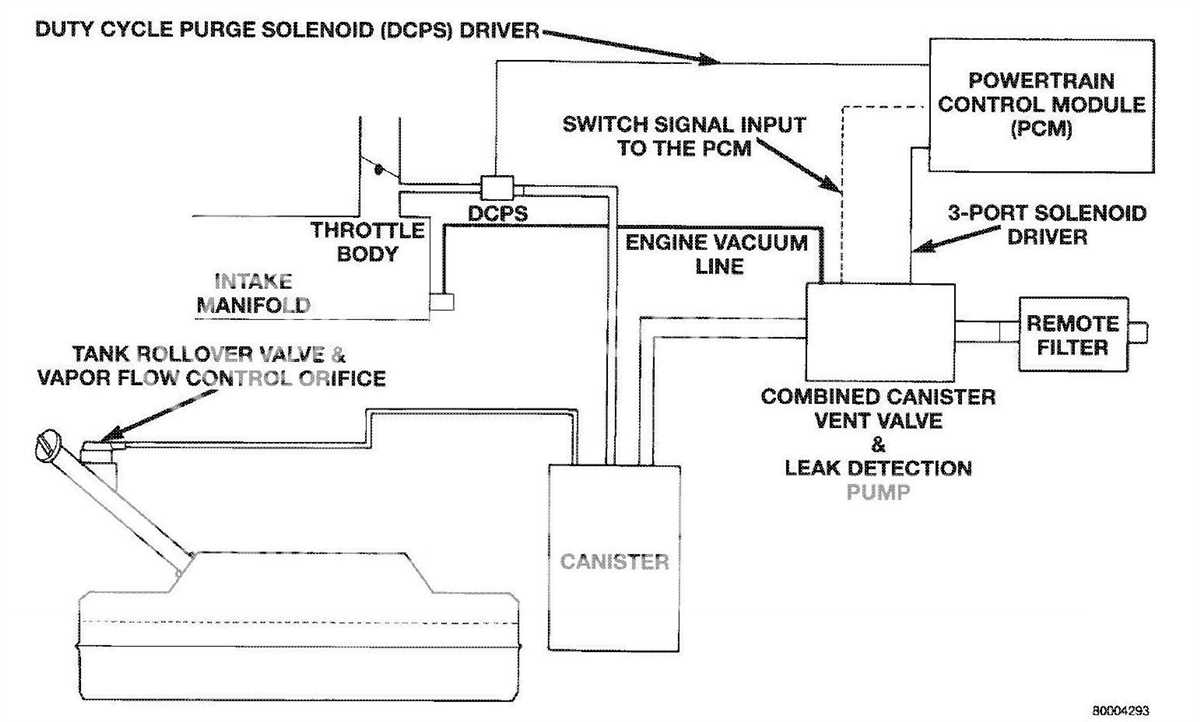
Over time, vacuum hoses can become brittle and develop cracks or leaks. Inspect the hoses for any signs of wear and replace them if necessary. Also, check the connections for any signs of damage or looseness. Secure or replace any damaged connections to maintain proper vacuum flow.
3. Keep the vacuum reservoir clean
The vacuum reservoir stores vacuum pressure for use during high-demand situations. It is important to keep it clean and free from debris or contaminants that can interfere with vacuum flow. Regularly inspect the reservoir and clean it if needed.
4. Follow recommended maintenance intervals
Refer to your vehicle’s owner’s manual for the recommended maintenance intervals for the vacuum system. This may include inspecting and replacing components such as the vacuum pump or check valve. Adhering to these intervals will help prevent unexpected vacuum system failures.
5. Avoid excessive strain on the vacuum system
Avoid situations that put excessive strain on the vacuum system, such as towing heavy loads or driving in harsh terrain. These conditions can cause the vacuum system to work harder and increase the risk of damage or failure. Use caution and drive responsibly to minimize the strain on the vacuum system.
By following these tips, you can ensure that your Dodge Dakota’s vacuum system remains in optimal condition, promoting better vehicle performance and longevity.