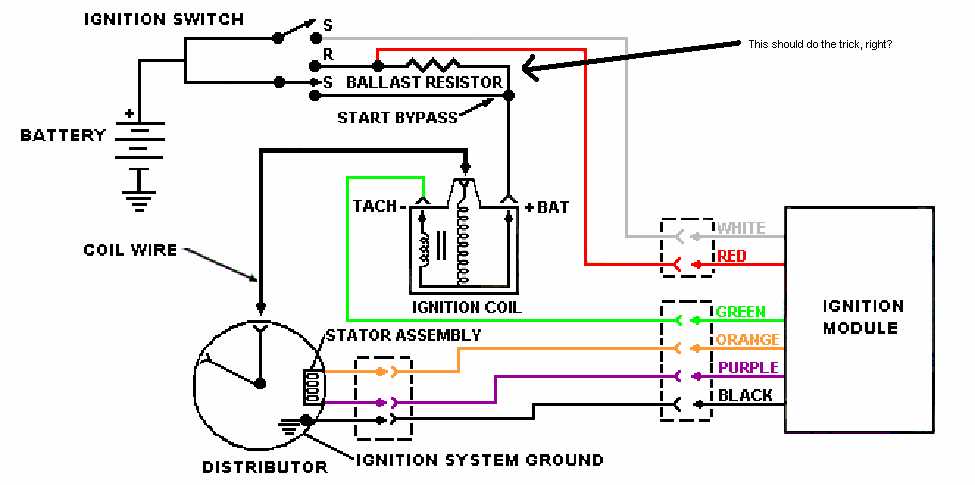
When it comes to the electrical system of a vehicle, one of the most important components is the ignition module. This module plays a crucial role in starting and running the engine smoothly. In the case of Ford vehicles, understanding the ignition module diagram is essential for proper troubleshooting and maintenance.
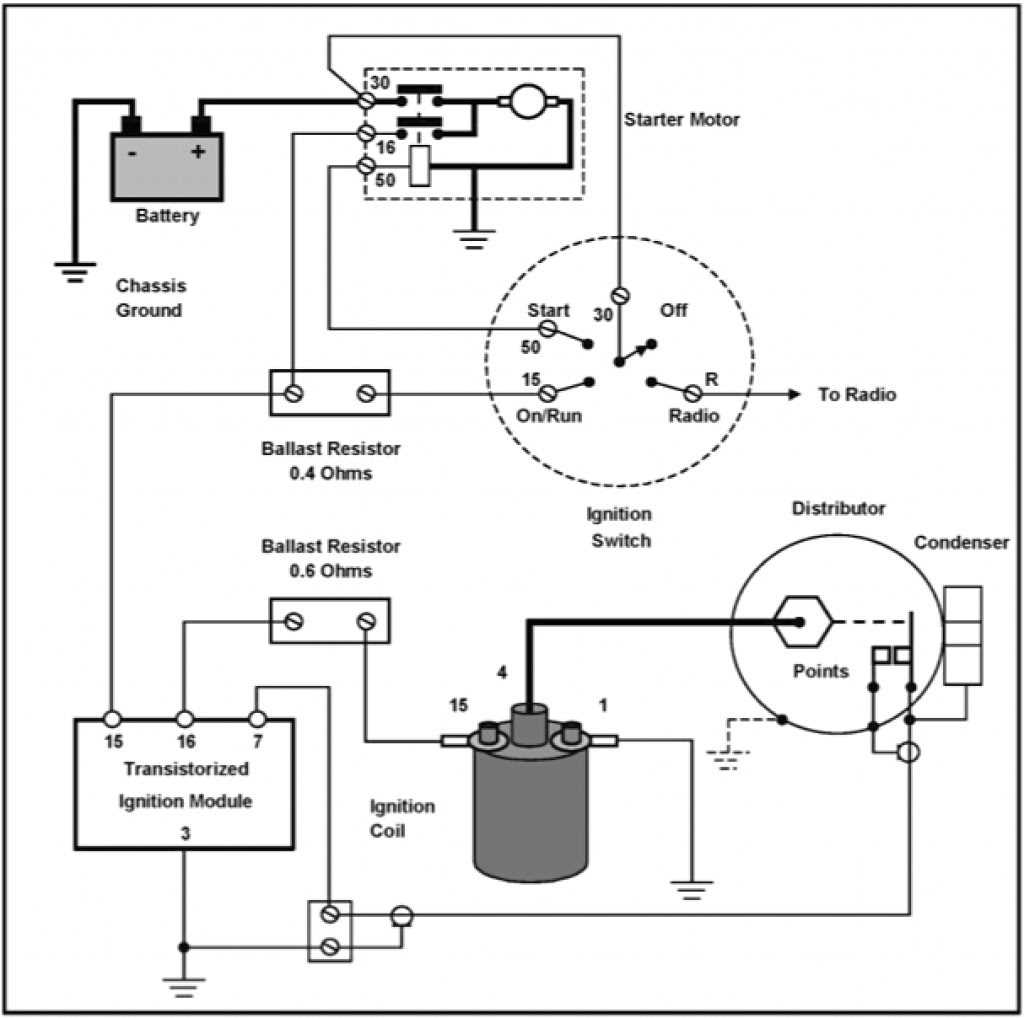
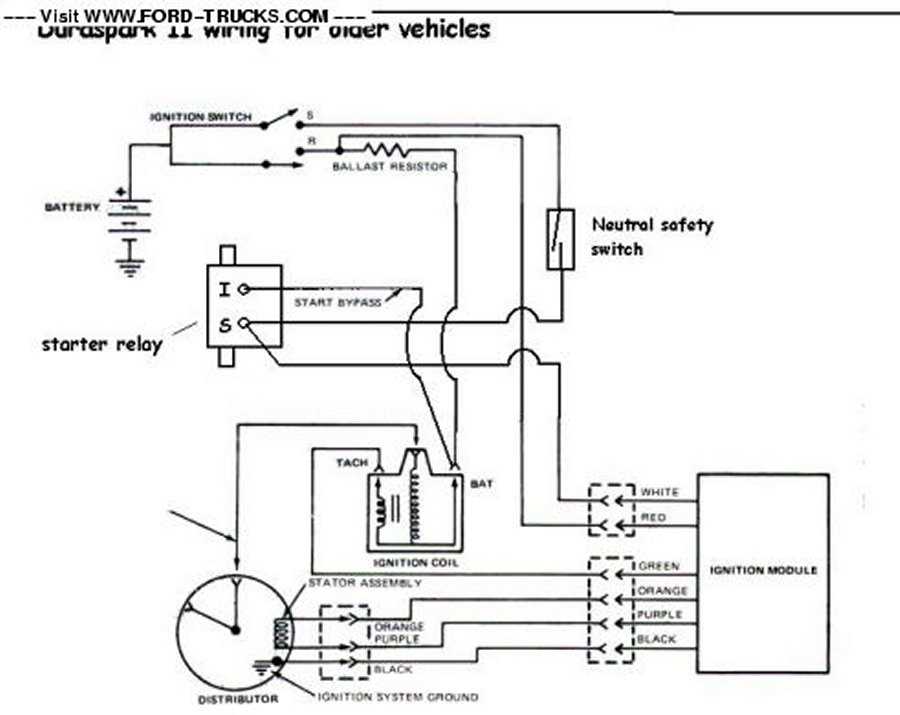
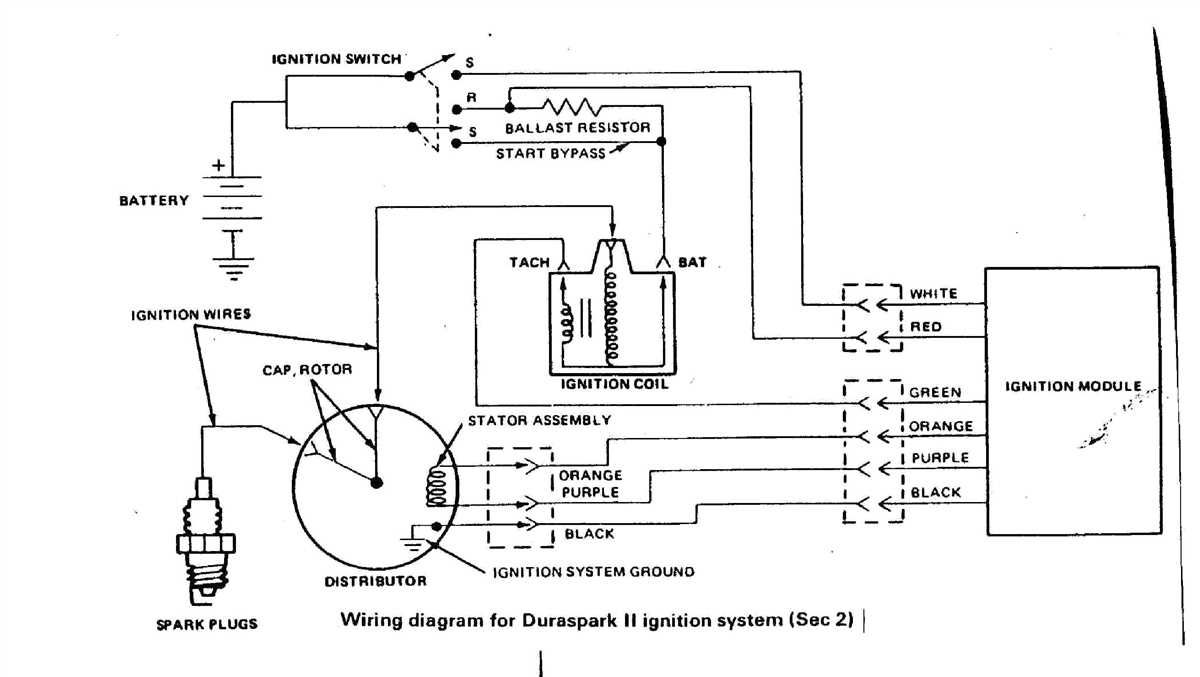
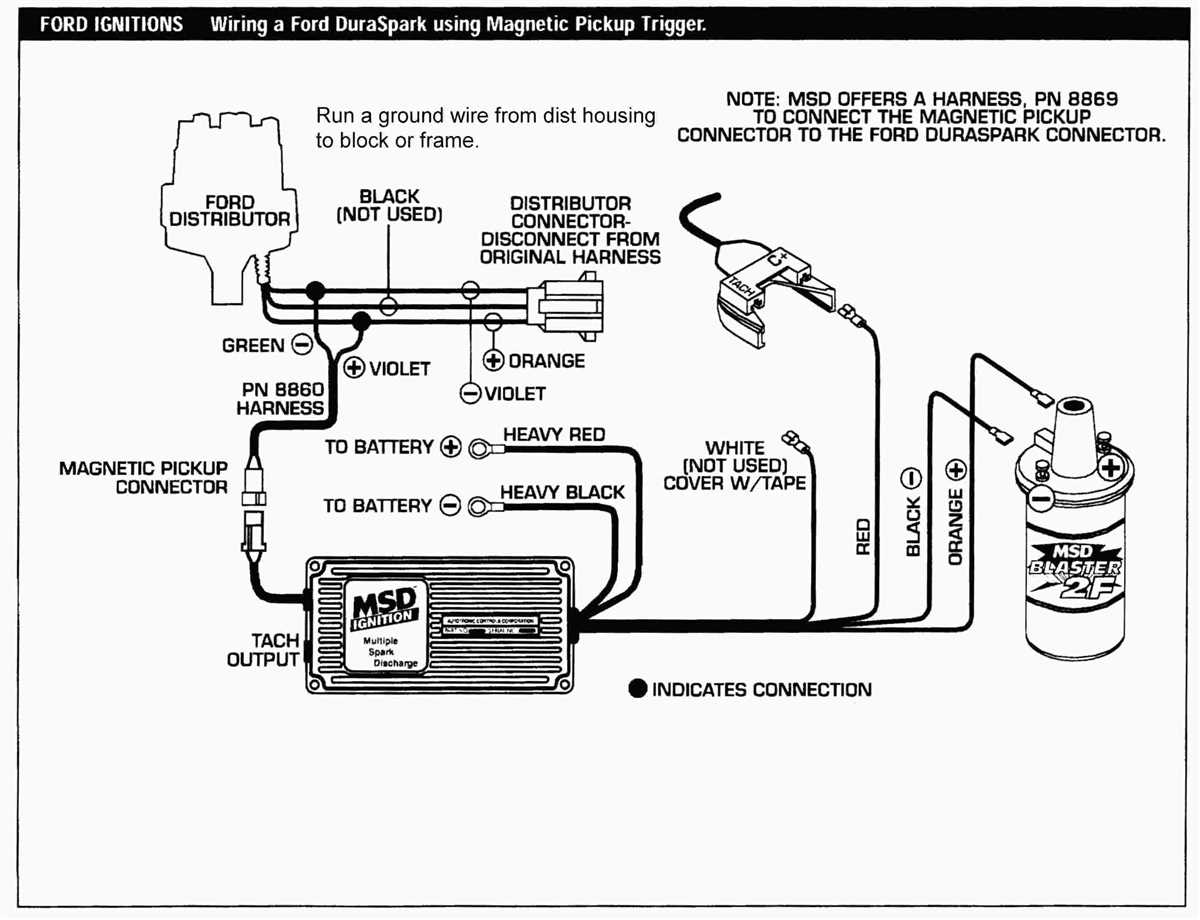
The ignition module diagram for Ford vehicles typically shows the various connections and components involved in the ignition system. This includes the ignition coil, distributor, spark plugs, and other related parts. By referring to this diagram, mechanics and DIY enthusiasts can easily identify and troubleshoot any issues that may arise in the ignition system.
One key aspect of the ignition module diagram is the wiring connections. Understanding how the wires are connected and where they lead can help in diagnosing problems such as poor spark or a complete loss of ignition. Additionally, the diagram may also include information about the ignition control module, which is responsible for controlling the timing and duration of the spark to each cylinder.
Ford Ignition Module Diagram: A Comprehensive Guide
The ignition module in a Ford vehicle is a crucial component of the ignition system. It plays a vital role in starting and generating power for the engine. Understanding the ignition module diagram can help in troubleshooting ignition system issues and making necessary repairs. In this comprehensive guide, we will examine the different parts and functions of the Ford ignition module.
1. Ignition Coil: The ignition coil is responsible for generating high voltage required to produce a spark at the spark plugs. It converts the low voltage from the battery into a high-voltage charge that is sent to the spark plugs.
2. Spark Plugs: The spark plugs are essential components of the ignition system. They create a spark that ignites the air-fuel mixture in the engine’s combustion chamber, resulting in the combustion process that generates power and drives the vehicle.
3. Distributor: In older Ford vehicles, the distributor is an integral part of the ignition system. It distributes the high-voltage charge from the ignition coil to the correct spark plug at the right time, ensuring optimal combustion and engine performance.
4. Ignition Control Module: The ignition control module, also known as the ignition control unit, is the main component of the Ford ignition module. It receives signals from various sensors and determines the timing and duration of the spark. It controls the ignition coil, spark plug firing sequence, and other ignition system functions.
5. Engine Control Unit (ECU): The engine control unit is responsible for controlling various aspects of the vehicle’s operation, including the ignition system. It receives input from sensors and uses this information to control the ignition timing and other engine functions. In some Ford vehicles, the ECU may integrate the functions of the ignition control module, eliminating the need for a separate ignition module.
Understanding the Ford ignition module diagram is essential for diagnosing and resolving ignition system issues. By familiarizing yourself with the different components and their functions, you can troubleshoot problems effectively and make necessary repairs or replacements. Remember to refer to the specific vehicle’s manual or consult a professional for accurate information and guidance.
What is an Ignition Module and How Does it Work?
An ignition module is a crucial component in a vehicle’s ignition system. Its main function is to control the timing and delivery of the ignition spark to the spark plugs, which is essential for starting the engine and keeping it running. The ignition module typically works in conjunction with the ignition coil and distributor to ensure proper ignition timing and reliable engine performance.
The ignition module contains various electronic components, including transistors, capacitors, and resistors, which work together to regulate the flow of electrical current and accurately time the ignition spark. The module receives signals from sensors, such as the crankshaft position sensor, to determine the engine’s position and speed. Based on this information, it sends a signal to the ignition coil to generate a high-voltage spark at the right moment.
The ignition module is usually mounted on or near the distributor for easy access and installation. It is powered by the vehicle’s battery and is grounded to the engine or chassis. When the ignition switch is turned on, the module receives power and begins its operation. It continuously monitors the engine’s speed and position to adjust the ignition timing accordingly.
The ignition module also has built-in protection mechanisms to prevent damage from voltage spikes or other electrical faults. For example, it may have overvoltage protection to safeguard against excessive voltage, or short-circuit protection to prevent damage in case of a short circuit. These safety features ensure the longevity and reliability of the ignition module.
In summary, an ignition module is a vital component in a vehicle’s ignition system that controls the timing and delivery of the ignition spark. It works with other ignition system components to ensure proper engine performance. Understanding the role and functionality of the ignition module can help troubleshoot ignition system issues and maintain the overall health of the vehicle.
Understanding the Components of a Ford Ignition Module
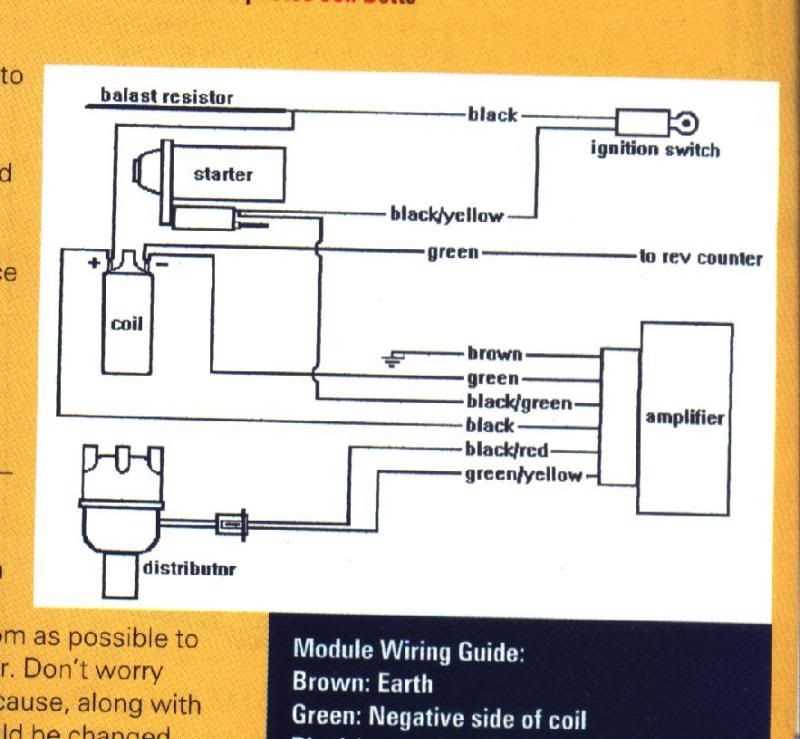
The Ford ignition module is a crucial component of the ignition system in Ford vehicles. It plays a key role in controlling the timing of the ignition spark and ensuring smooth engine operation. Understanding the components of the ignition module is essential for diagnosing and troubleshooting ignition-related issues.
Primary Components
The primary components of a Ford ignition module include:
- Power Supply: The ignition module receives power from the vehicle’s battery. It is essential for supplying the necessary voltage to operate the ignition system.
- Distributor: The distributor is responsible for distributing the high voltage from the ignition coil to each spark plug. It has a rotor that rotates and makes contact with the distributor cap, sending the spark to the correct cylinder.
- Ignition Coil: The ignition coil is responsible for generating a high voltage spark that ignites the fuel-air mixture in the combustion chamber. It converts low-voltage electricity from the battery into high-voltage electricity needed for the spark plugs.
- Control Module: The control module, also known as the ignition control module (ICM), is the brain of the ignition system. It receives signals from various sensors and determines the timing and duration of the spark. It controls the ignition timing based on engine speed and load conditions.
- Spark Plugs: The spark plugs are responsible for producing the actual spark that ignites the air-fuel mixture in the combustion chamber. They are located at the top of each cylinder and are essential for efficient and smooth engine operation.
These components work together to ensure proper ignition timing, reliable spark delivery, and efficient combustion. If any of these components malfunction or fail, it can lead to engine misfires, poor performance, and even engine damage. Regular maintenance and inspections are necessary to ensure the ignition module and its components are functioning correctly.
Common Symptoms of a Faulty Ignition Module
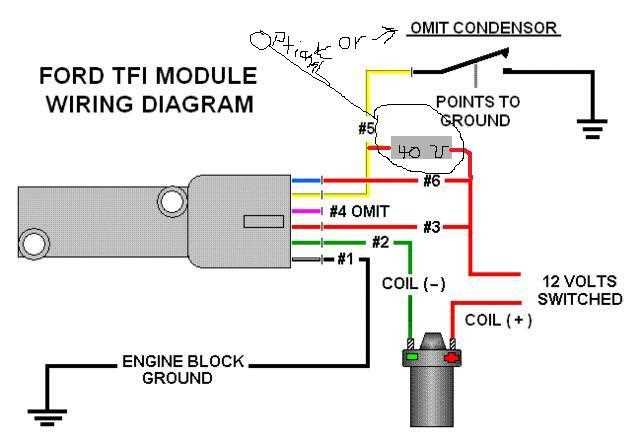
An ignition module is a key component in the ignition system of a vehicle, responsible for controlling the timing and operation of the ignition coils. When this module becomes faulty, it can result in a variety of symptoms that can affect the performance and reliability of the vehicle. Recognizing these symptoms can help diagnose and address the issue in a timely manner.
1. Engine Misfires
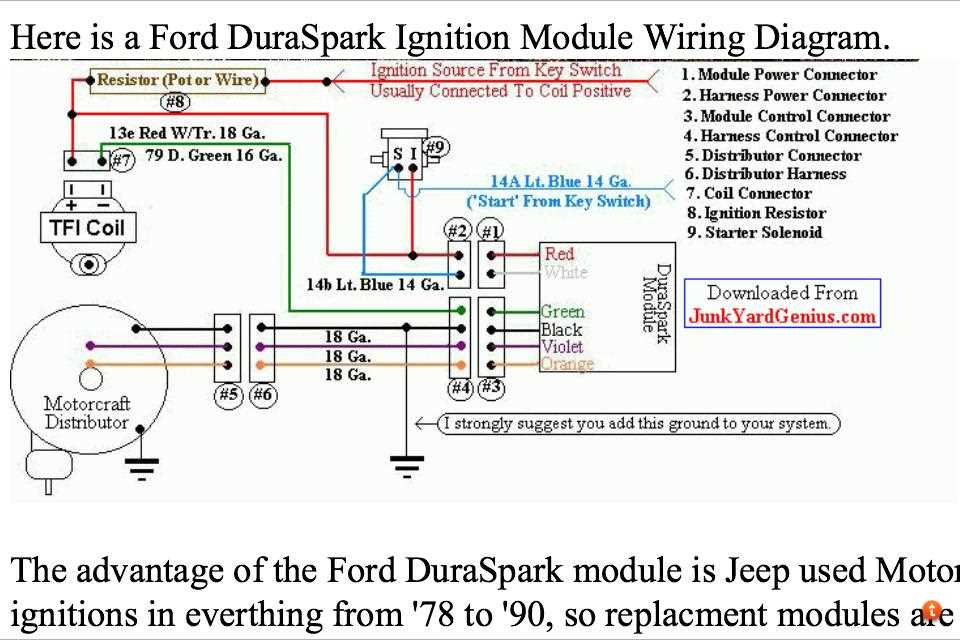
One of the most common symptoms of a faulty ignition module is engine misfires. If the module is not functioning properly, it may not send the correct signals to the ignition coils, causing them to fire at the wrong time. This can result in a misfire, causing the engine to run rough or sputter.
2. Stalling or Difficulty Starting
Another symptom of a faulty ignition module is stalling or difficulty starting the vehicle. When the module is malfunctioning, it may not provide the necessary spark to ignite the fuel mixture, leading to starting issues or even sudden stalling while driving.
3. Decreased Fuel Efficiency
A faulty ignition module can also lead to decreased fuel efficiency. If the module is not properly controlling the ignition timing, it can cause the engine to run inefficiently, resulting in poor fuel economy.
4. Engine Overheating
In some cases, a malfunctioning ignition module can cause the engine to overheat. If the ignition timing is not correct, it can result in an excessive build-up of heat in the engine, leading to overheating and potential damage.
5. Intermittent Loss of Power
A faulty ignition module may also cause intermittent loss of power while driving. This can manifest as a sudden drop in engine power or a hesitation when accelerating. These power losses can be dangerous, especially in situations that require immediate and consistent power, such as merging onto a highway or passing another vehicle.
Overall, a faulty ignition module can have a significant impact on the performance and reliability of a vehicle. Recognizing these symptoms and addressing any issues with the ignition module can help ensure the proper functioning of the ignition system and prevent further damage to the vehicle.
Testing and Troubleshooting Ford Ignition Module Issues
In autoignition systems, the ignition module plays a crucial role in controlling the ignition timing and firing the spark plugs. In Ford vehicles, the ignition module is an essential component that ensures smooth engine operation. However, like any electronic component, the ignition module can encounter issues that may affect the overall performance of the vehicle.
When troubleshooting Ford ignition module issues, it is important to first diagnose the problem accurately. One common symptom of a faulty ignition module is engine misfires or stalling. If the engine runs rough, lacks power, or has trouble starting, it could be due to a malfunctioning ignition module. It is also worth noting that some Ford vehicles have a separate ignition control module, while others have it integrated into the powertrain control module (PCM).
To test the ignition module, begin by checking for any visible damage, such as burnt or corroded connectors or wires. If any issues are detected, they should be repaired or replaced immediately. Next, use a digital multimeter to measure the voltage at the ignition module’s terminals. Compare the readings to the specifications provided by the manufacturer. Any significant deviations could indicate a faulty module.
Another method to test the ignition module is by performing an ignition coil output test. This involves disconnecting the ignition coil wire and attaching a spark tester to the coil output. Start the engine and observe the spark tester for a consistent, strong spark. If the spark is weak or inconsistent, it may suggest a faulty ignition module.
In some cases, it is also recommended to perform an output test on the ignition module using an oscilloscope. This test can help identify any irregularities in the ignition module’s waveform pattern, which may indicate a problem with the module’s internal circuitry.
Overall, testing and troubleshooting Ford ignition module issues require a systematic approach and the appropriate tools. If unsure about performing the tests or diagnosing the problem, it is recommended to consult a professional automotive technician. They will have the expertise and resources to accurately diagnose and resolve any ignition module issues for optimal vehicle performance.
How to Replace an Ignition Module on a Ford Vehicle
The ignition module in a Ford vehicle is responsible for controlling the ignition spark and timing. Over time, this module can wear out or fail, resulting in engine performance issues. If you suspect that your Ford vehicle’s ignition module is faulty, it is important to replace it as soon as possible to prevent further damage to the engine.
Before replacing the ignition module, ensure that you have the correct replacement part for your specific Ford vehicle model and year. Refer to the owner’s manual or consult a professional mechanic for assistance in identifying the correct ignition module.
Here is a step-by-step guide on how to replace an ignition module on a Ford vehicle:
- Make sure the engine is cool and the ignition is turned off.
- Locate the ignition module, which is typically mounted on the engine block near the distributor.
- Disconnect the negative battery terminal to prevent any accidental electrical discharge.
- Remove any components or wires that may be obstructing access to the ignition module.
- Using the appropriate tools, gently remove the mounting bolts or screws that secure the ignition module in place.
- Carefully disconnect the wiring harness or connector from the ignition module.
- Remove the old ignition module from the engine.
- Install the new ignition module in the same position as the old module.
- Reconnect the wiring harness or connector to the new ignition module.
- Secure the ignition module in place by tightening the mounting bolts or screws.
- Reconnect the negative battery terminal.
- Start the engine and test the new ignition module to ensure proper functionality.
It is important to note that replacing the ignition module in a Ford vehicle may require some technical expertise. If you are not confident in your abilities, it is recommended to seek the assistance of a professional mechanic to perform the replacement.
Tips for Preventing Ignition Module Failure in Ford Vehicles
In order to prevent ignition module failure in Ford vehicles, it is important to follow some key tips and maintenance practices. By taking these steps, you can help ensure the longevity and reliability of your ignition module, avoiding potential issues and costly repairs.
Regularly Check and Clean Connections
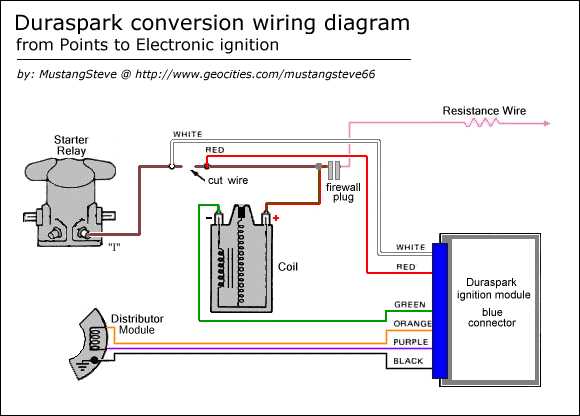
One of the most basic, yet effective, ways to prevent ignition module failure is to regularly check and clean the connections. Over time, dirt, corrosion, and moisture can accumulate on the connections, leading to poor electrical conductivity and potential module failure. By inspecting and cleaning the connections on a regular basis, you can prevent these issues and maintain optimal performance.
Use High-Quality Ignition Components
Using high-quality ignition components, such as spark plugs, spark plug wires, and ignition coils, can significantly reduce the risk of ignition module failure. Cheap or low-quality components may not provide the necessary voltage and current levels, putting additional strain on the ignition module. Investing in premium components that are compatible with your Ford vehicle can help ensure proper operation and reduce the likelihood of module failure.
Avoid Overworking the Ignition System
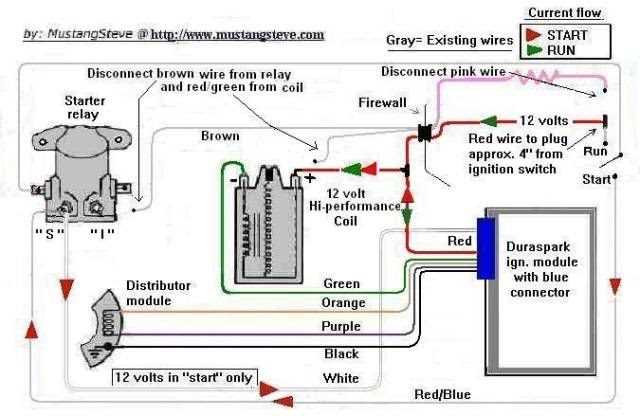
Avoiding overworking the ignition system can go a long way in preventing module failure. Excessive starting attempts, extended periods of idling, or frequent engine misfires can all put additional strain on the ignition module, increasing the risk of failure. By following the manufacturer’s recommendations for maintenance and operation, such as avoiding excessive cranking or idle periods, you can help extend the lifespan of your ignition module.
Properly Maintain the Cooling System
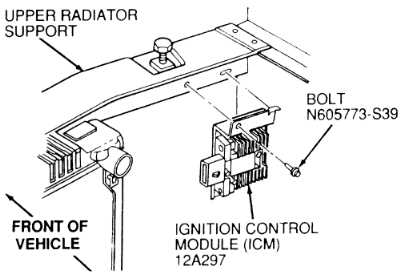
Another important aspect of preventing ignition module failure is to properly maintain the cooling system of your Ford vehicle. Excessive heat can damage the ignition module and other ignition components, leading to failure. Regularly check the coolant level, ensure proper coolant circulation, and address any cooling system issues promptly. Additionally, consider using a coolant with a higher boiling point to better protect the ignition system from overheating.
Consider Using a Voltage Stabilizer
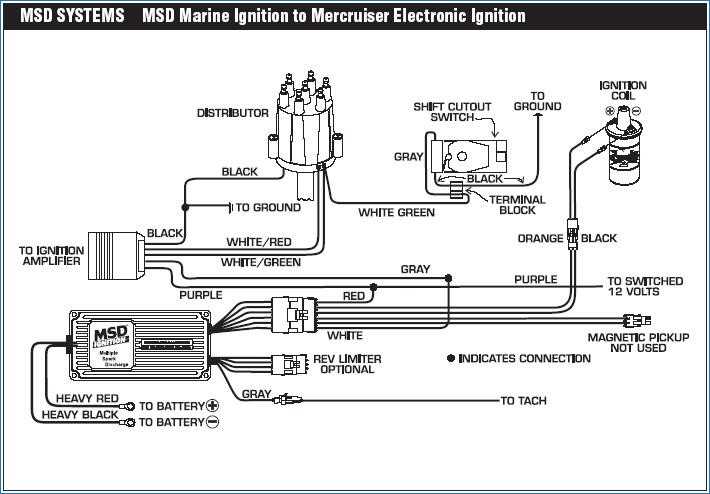
In some cases, using a voltage stabilizer can help protect the ignition module from voltage fluctuations and spikes, which can lead to premature failure. A voltage stabilizer can regulate the voltage supplied to the ignition module, providing a stable and consistent power source. Consult your vehicle’s manual or a trusted mechanic to determine if using a voltage stabilizer is recommended for your specific Ford vehicle.
- Regularly check and clean connections
- Use high-quality ignition components
- Avoid overworking the ignition system
- Properly maintain the cooling system
- Consider using a voltage stabilizer
By following these tips and being proactive in the maintenance of your Ford vehicle’s ignition system, you can minimize the risk of ignition module failure and ensure reliable performance for years to come.