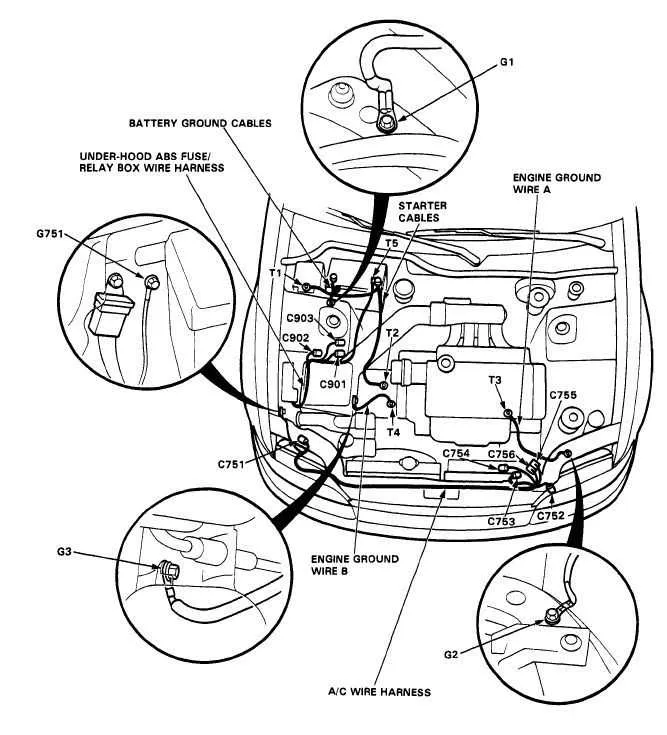
If you’re planning any maintenance or upgrades, it’s crucial to understand the engine compartment layout. Identifying key components will help you troubleshoot issues, replace parts, and optimize performance. This specific model’s layout reveals the precise location of critical systems such as the cooling mechanism, fuel delivery, and electrical connections.
Start by examining the engine block and its surrounding components, including the alternator, battery, and air intake system. Knowing where each part resides allows you to quickly locate and address potential problems, saving time and avoiding unnecessary disassembly.
Pay attention to the fuel system, including the fuel pump and fuel injectors. These parts require regular inspection to ensure smooth engine operation. A visual guide of this layout simplifies the identification of these crucial systems, streamlining the diagnostic process.
Equipped with this knowledge, you’ll have a clear roadmap for working on your engine’s components, making it easier to maintain and enhance the vehicle’s performance efficiently.
Engine Compartment Layout
To gain a deeper understanding of the engine bay, focus on key components that influence performance and maintenance. Here’s a breakdown of essential elements to check regularly:
- Power Unit: Usually located in the center, the main engine is the heart of any vehicle, with various systems surrounding it for optimal function.
- Air Filter: Positioned near the intake system, this component ensures clean airflow to the engine, which is crucial for performance and fuel efficiency.
- Battery: Typically found on one side, ensure the terminals are clean and connections tight to avoid electrical issues.
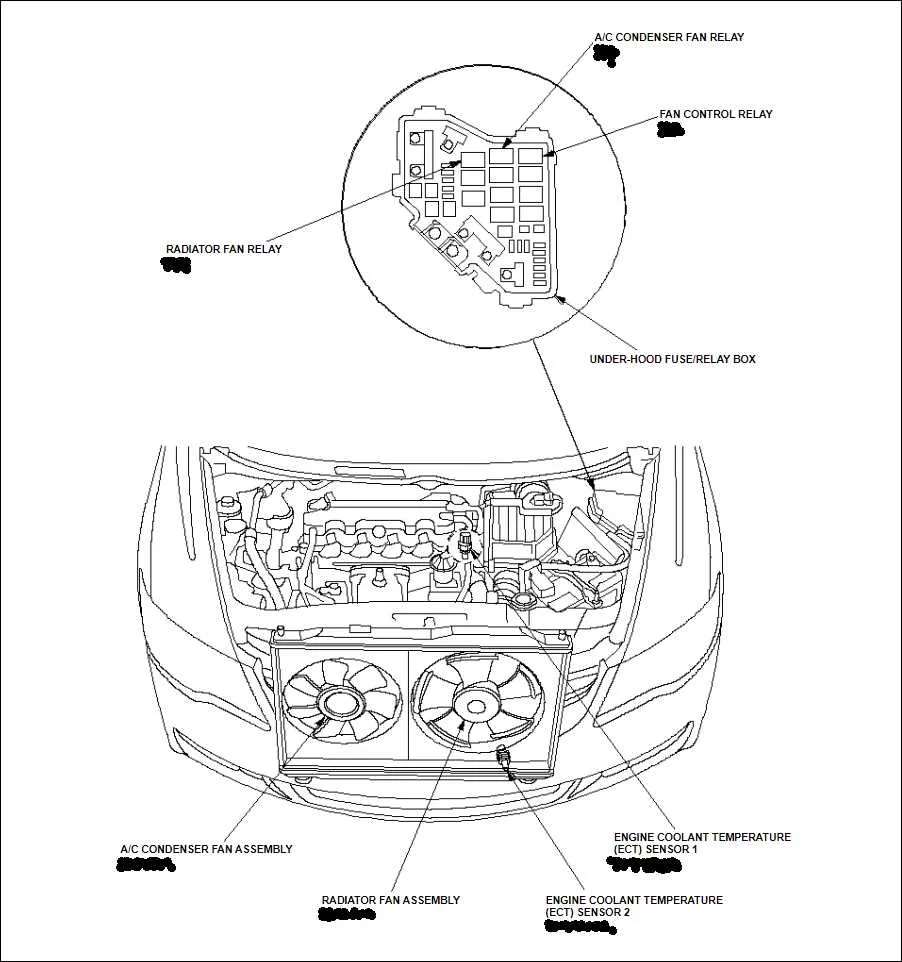
- Coolant Reservoir: Located near the radiator, regularly check fluid levels to avoid overheating, a critical aspect of engine longevity.
- Fuse Box: Usually on the driver’s side, fuses control electrical systems. Familiarize yourself with their layout for quick troubleshooting.
- Oil Cap: Typically on top, ensures proper lubrication of the engine. Change oil at recommended intervals to maintain engine health.
- Timing Belt: Located at the front of the engine, monitor wear and tear to prevent failure that could damage internal engine parts.
- Radiator: Positioned at the front, make sure the fins are clear of debris to ensure efficient cooling.
- Exhaust System: Check the exhaust manifold and surrounding parts for cracks or leaks that could compromise engine performance and emissions.
Familiarity with this layout allows for efficient troubleshooting and maintenance, ensuring a smoother driving experience.
Identifying Key Engine Components in the Vehicle

Start by locating the engine block, a large metal component that forms the core of the powertrain system. It houses the cylinders where combustion occurs. The intake manifold, positioned above the engine block, channels air into the combustion chamber, while the exhaust manifold directs gases away from it.
The timing belt or chain controls the opening and closing of valves in synchronization with the crankshaft. Pay attention to the alternator, a crucial part for generating electrical power, typically located near the front of the engine. Next, identify the radiator, which helps cool the engine by circulating coolant through the system. A water pump, attached to the engine, pushes coolant through the radiator and engine block to maintain temperature balance.
The fuel injectors are responsible for delivering precise amounts of fuel into each cylinder. They are situated near the intake manifold. The air filter, often located near the engine’s intake system, ensures clean air flows into the engine, preventing contaminants from entering and damaging components.
The oil filter is essential for maintaining clean engine oil, ensuring proper lubrication and reducing wear on moving parts. The spark plugs, which are placed on top of the engine, ignite the fuel-air mixture inside the cylinders, enabling the combustion process.
Lastly, check the battery and starter motor, which work together to initiate the engine’s operation. The battery provides the necessary electrical energy, while the starter motor turns the engine over to begin its operation.
How to Read and Understand the Engine Compartment Layout
Start by identifying the key components such as the engine block, alternator, battery, and radiator. These parts are typically highlighted for easy reference. Focus on understanding how power flows from the engine to other systems like the cooling and electrical networks. Pay attention to symbols and labels near each component, which often provide crucial details like part numbers, voltage ratings, or fluid types.
Next, examine the lines connecting various elements–these may represent fuel, air, or coolant circulation. Look for color-coded lines that indicate different functions, such as red for fuel and blue for coolant. Understand the purpose of each line and how it integrates with the entire powertrain. These markings help avoid mistakes during maintenance or repairs.
For safety and operational checks, inspect the location of sensors, fuses, and relays. They control engine performance and notify the driver of potential issues. Follow the wiring paths shown, as they often link critical components such as the ECU and ignition system. Be sure to understand where the grounding points are, as these ensure electrical stability.
Take note of any additional markings indicating recommended maintenance intervals or torque specifications for fasteners. These instructions help keep systems operating efficiently and prevent damage. Review each section carefully before performing any tasks to ensure you’re familiar with its specific features and functions.
Common Maintenance Areas Highlighted in the Engine Layout
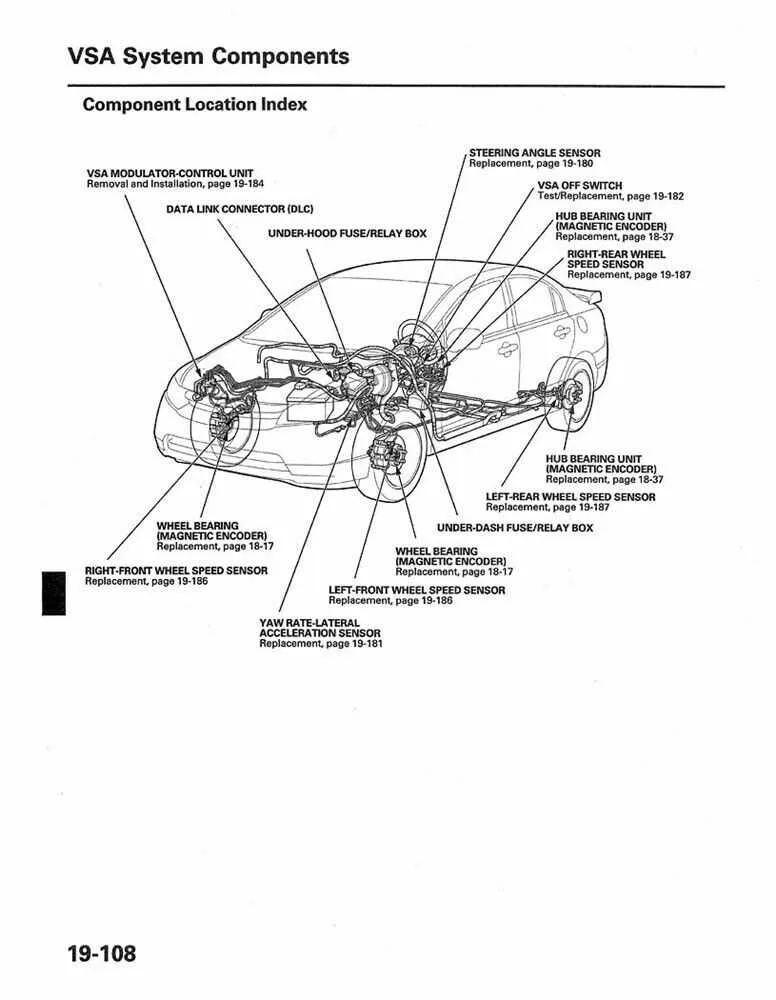
Focus on regular inspection of the air filter. A clogged filter reduces engine efficiency, so replace it every 15,000 to 30,000 miles, depending on driving conditions. Check the spark plugs as well, replacing them every 30,000 to 50,000 miles to ensure smooth ignition and optimal fuel consumption.
The timing belt should be replaced around the 60,000 to 100,000-mile mark to avoid potential engine damage. Always inspect the belt for cracks or wear, especially if it’s nearing its recommended replacement interval.
Monitor coolant levels and inspect hoses for signs of wear or leaks. Replace coolant every 2 to 3 years or as recommended by the manufacturer to maintain optimal engine temperature regulation.
Examine the exhaust system for rust, holes, or loose parts. A damaged exhaust can lead to reduced engine performance and fuel efficiency. Ensure the catalytic converter is clean and functioning properly to reduce harmful emissions.
Change the oil and replace the oil filter regularly, ideally every 3,000 to 5,000 miles. Keep an eye on oil levels, especially after long trips, to avoid engine strain.
Inspect belts and pulleys for signs of wear, cracking, or loosening. These components are crucial for driving multiple engine systems and should be replaced if damaged.
Ensure the battery terminals are clean and the battery itself is secure. A well-maintained battery contributes to reliable starting and overall electrical system performance.