Sam Houston State University’s Department of Chemistry Web Page. Explanation of the physics of fluorescence, illustrated by the Jablonski diagram.
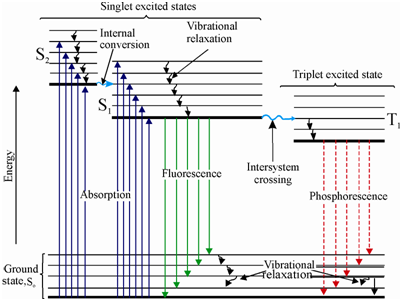
Download scientific diagram | Energy level diagram (Jablonski diagram) for visualization of fluorescence phenomena (see explanation in the text). from. The Jablonski diagram.
A, F, and P define the processes of photon absorption, fluorescence and phosphorescence emissions respectively. Singlet states are.
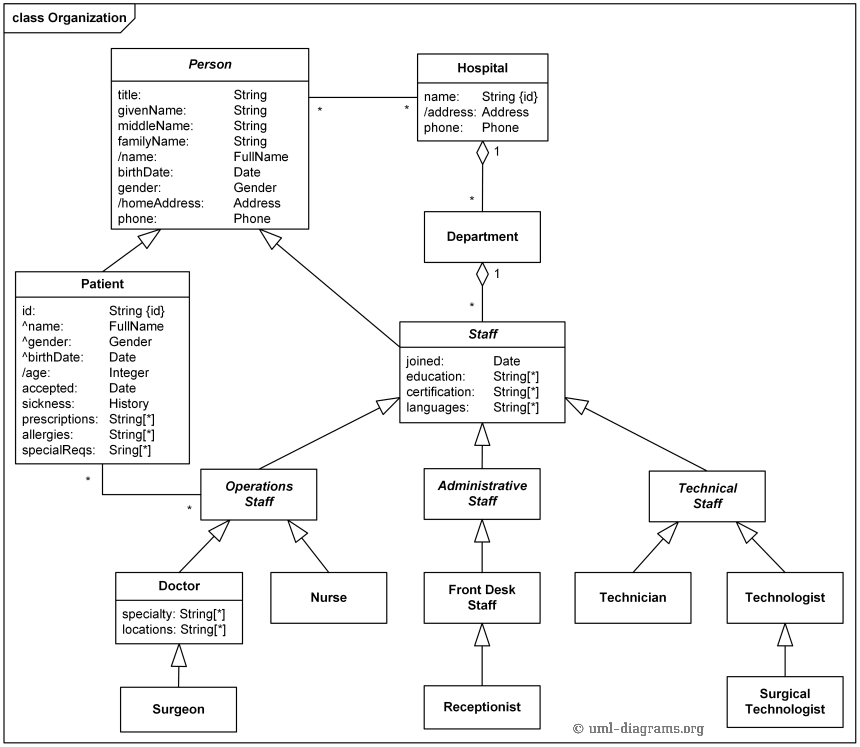
The various energy levels involved in the absorption and emission of light by a fluorophore are classically presented by a Jablonski energy diagram, named in.Absorbance. The first transition in most Jablonski diagrams is the absorbance of a photon of a particular energy by the molecule of interest.
This is indicated by a straight arrow pointing up. Jablonski diagram for fluorescence An excited-state electron rapidly (on the order of 10 seconds) loses its energy to vibration (heat), a process called internal conversion, and falls to the lowest level of the first (S 1) excited state.
The Jablonski diagram features the energy levels within a molecule where valence electrons could be excited. Light of specific wavelength interacts with an electron and causes its excitation to a higher-energy level.
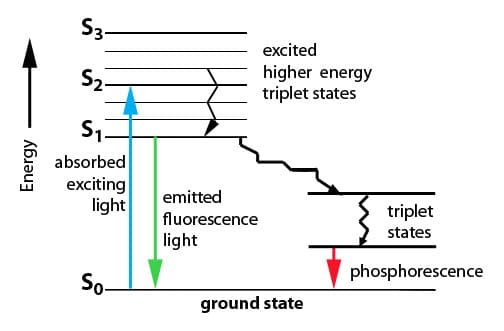
On this particular diagram. Interactive Tutorials Jablonski Energy Diagram.
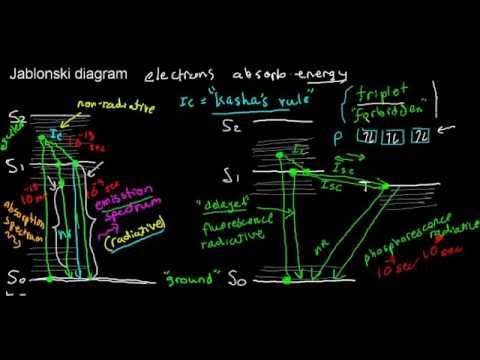
Fluorescence activity can be schematically illustrated with the classical Jablonski diagram, first proposed by Professor Alexander Jablonski in to describe absorption and emission of light. The Jablonski diagram is simple in nature, but powerful in terms of its practical takeaways.
Understanding the various characteristics of the diagram, including the quantum yield, extinction coefficient, and Stokes’ shift, will help you design better flow cytometry experiments.Jablonski diagram – WikipediaJablonski Energy Diagram – Java Tutorial