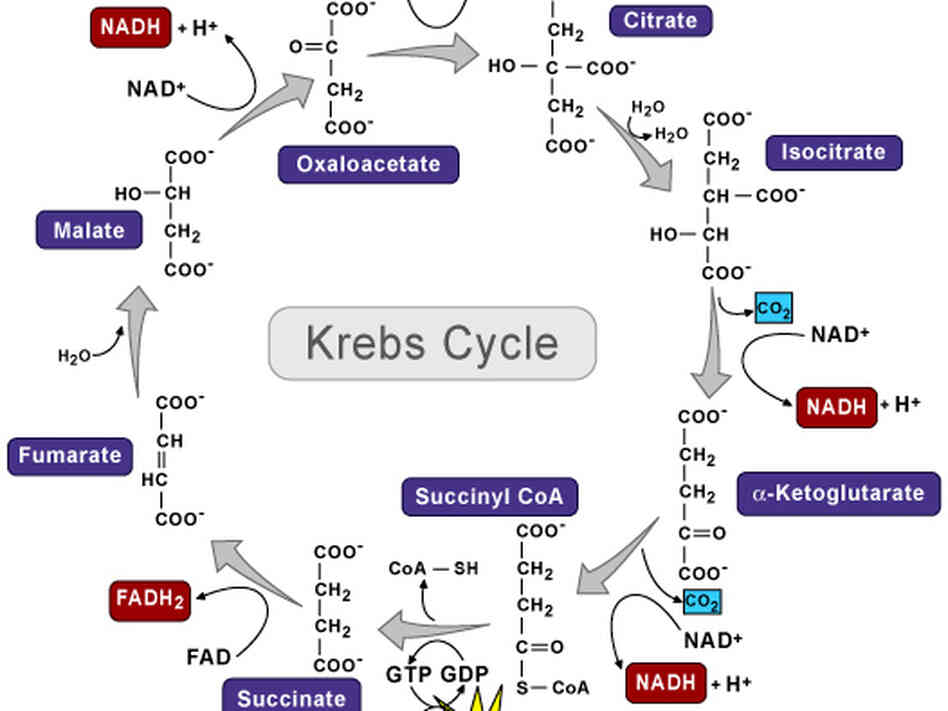
It is also known as TriCarboxylic Acid (TCA) cycle.
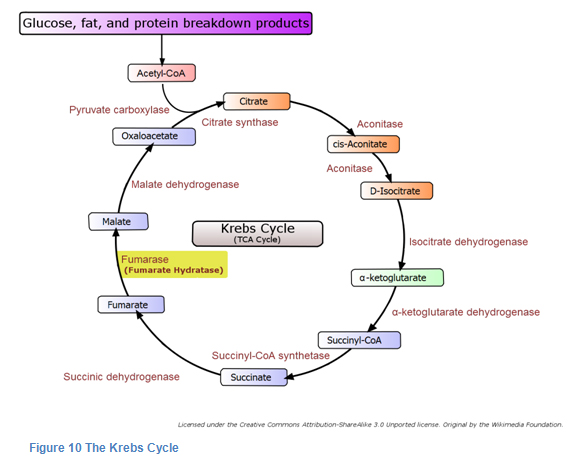
In prokaryotic cells, the citric acid cycle occurs in the cytoplasm; in eukaryotic cells, the citric. The Krebs cycle (named after Hans Krebs) is a part of cellular respiration.
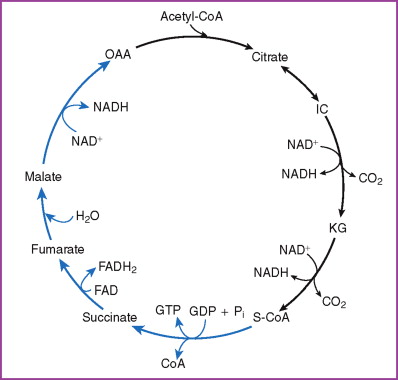
The diagram below shows how this part of respiration is an ever-repeating cycle. a) Krebs cycle ccurs in matrix of mitochondria. The diagram below is a very simple outline of the Krebs Cycle showing the removal of CO2, and the making of 3.
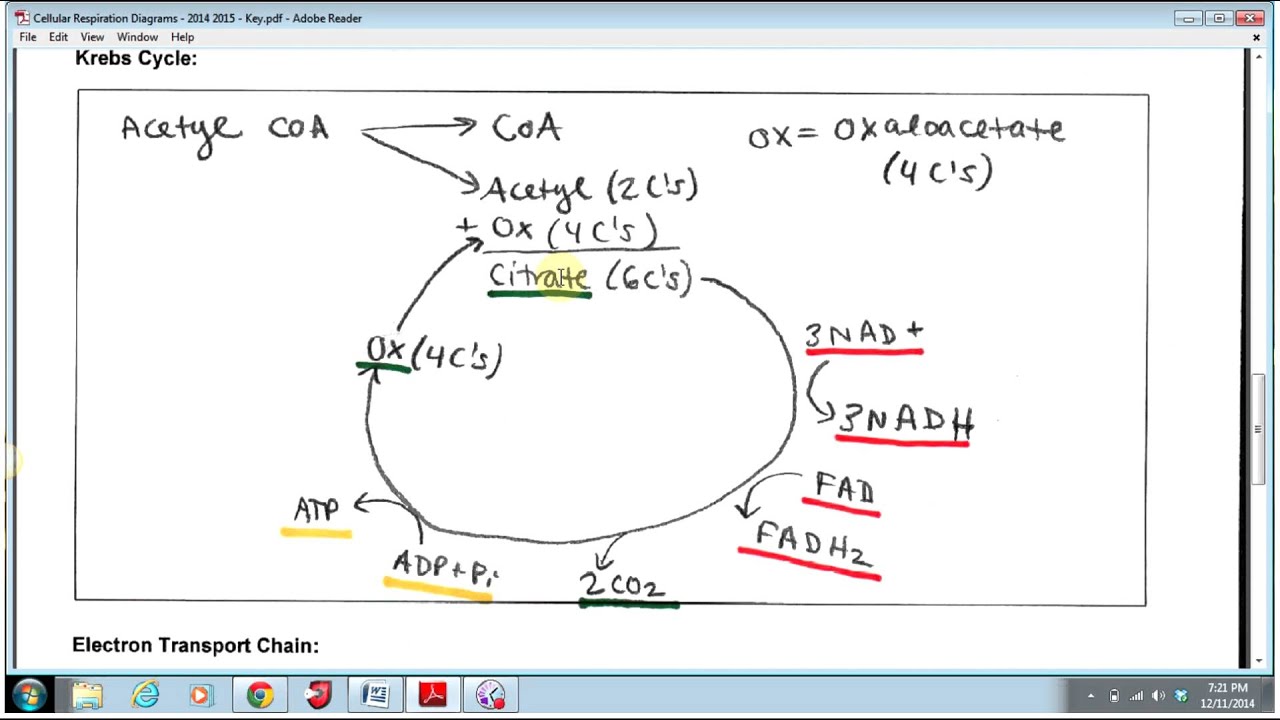
Overview and steps of the citric acid cycle, also known as the Krebs cycle or tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle. (TCA cycle).
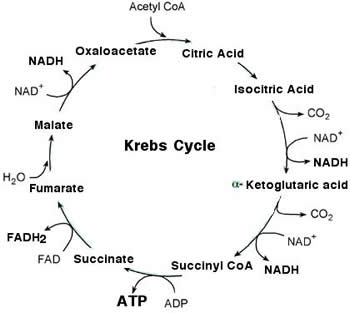
In this article we will discuss the TCA cycle (also known as Kreb’s cycle). Fig 1 – Diagram showing the steps of the TCA cycle.The Krebs cycle, also called the citric acid cycle or tricarboxylic cycle, is the first step of aerobic respiration in eukaryotic cells.
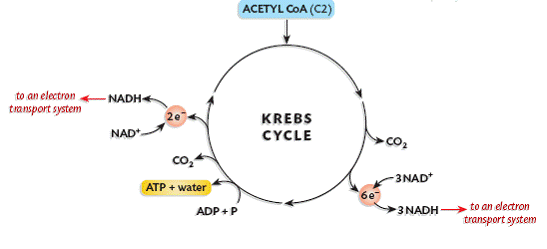
Its purpose is to collect high-energy electrons for use in the electron transport chain reactions. The Krebs cycle occurs in the mitochondrial matrix.
The oxidation of pyruvic acid into CO 2 and water is called Krebs cycle. This cycle is also citric acid cycle because the cycle begins with the formation of citric acid. Citric acid is .
Simplified diagram of the citric acid cycle. First, acetyl CoA combines with oxaloacetate, a four-carbon molecule, losing the CoA group and forming the six-carbon molecule citrate. After citrate undergoes a rearrangement step, it undergoes an oxidation reaction, transferring electrons to NAD+ to form NADH and releasing a molecule of carbon dioxide.
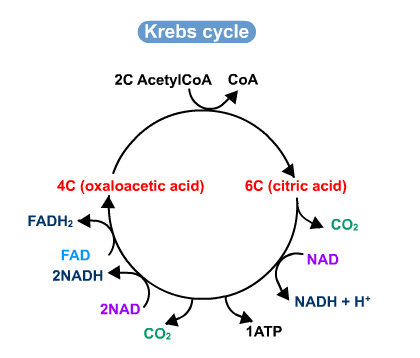
The citric acid cycle (CAC) – also known as the TCA cycle (tricarboxylic acid cycle) or the Krebs cycle – is a series of chemical reactions used by all aerobic organisms to release stored energy through the oxidation of acetyl-CoA derived from carbohydrates, fats, and proteins into adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and carbon dioxide. Dec 28, · The Krebs cycle, also known as the Citric Acid cycle, is a very important process in cellular respiration.
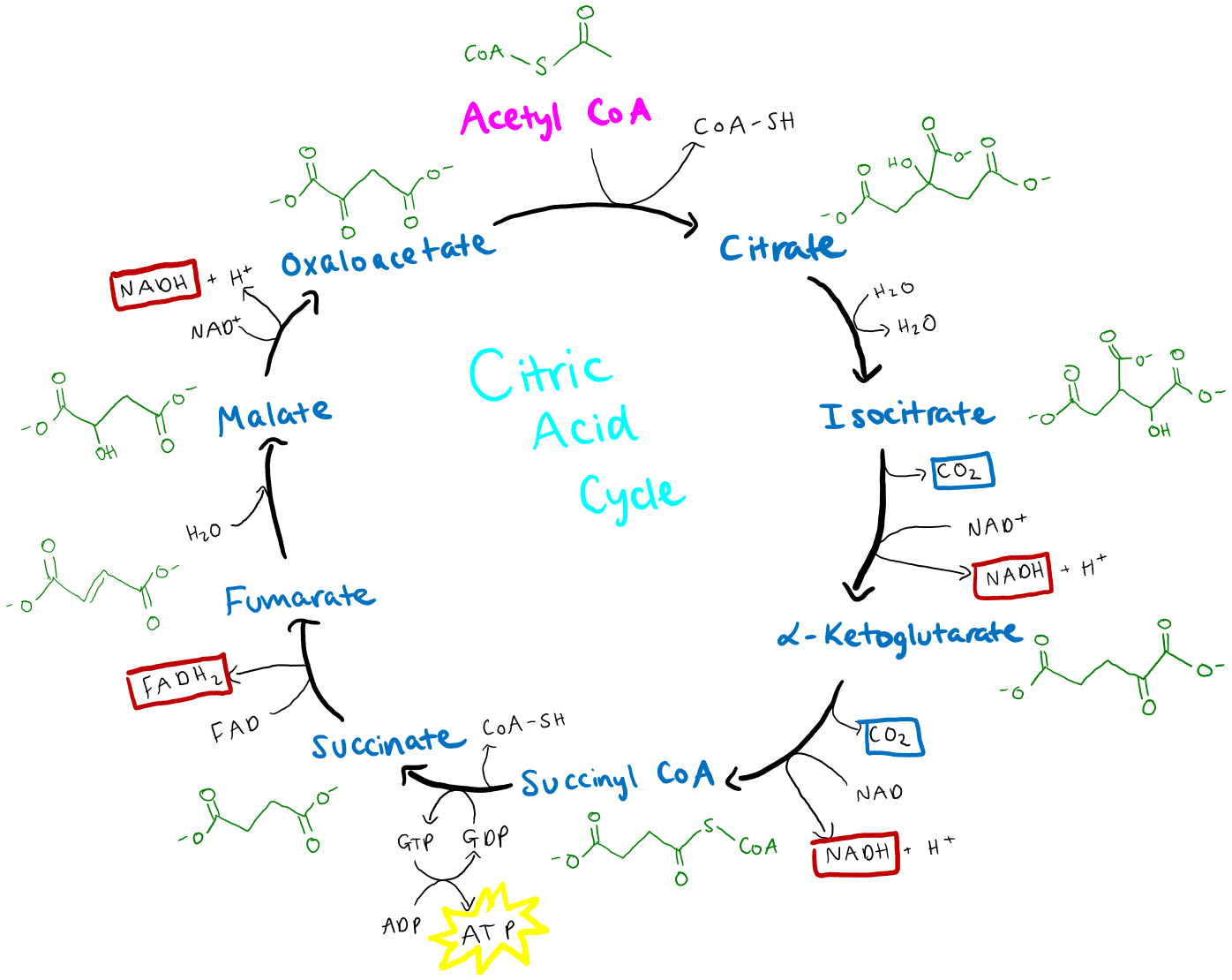
Without this portion, respiration would not be possible. This is because the Krebs cycle uses the pyruvate molecules from glycolysis to produce high energy molecules essential for the electron transport chain (ETC) which follows soon after.Krebs (Citric Acid) Cycle Steps by Steps Explanation – Microbiology schematron.orgBiology Made Simple: Krebs Cycle Broken Down