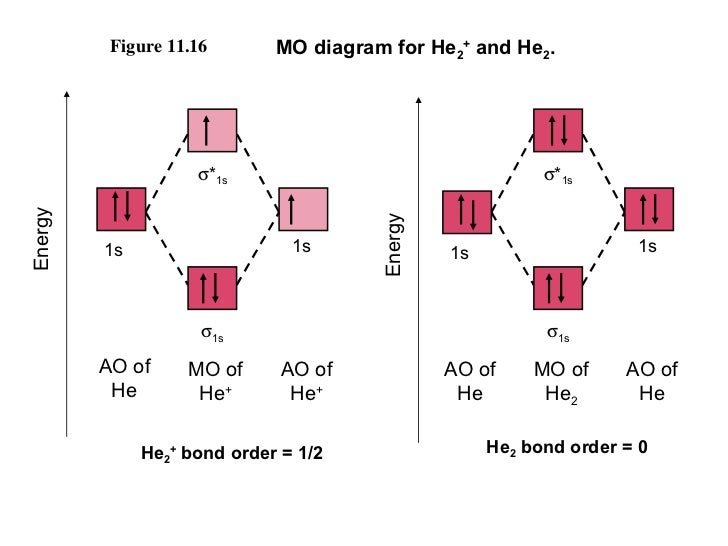
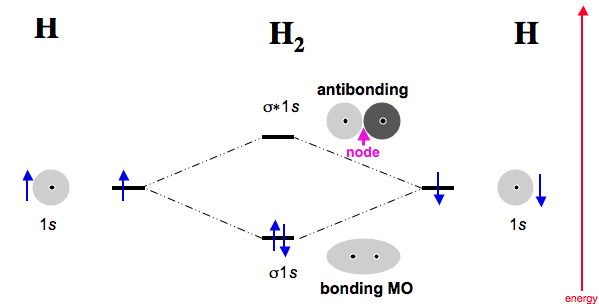
The molecular orbital energy-level diagram, which is a diagram that shows the relative energies of molecular orbitals, for the H2 molecule is shown in Figure Answer to Construct MO diagrams for He2 and [He2]1and rationalize why the former is not known but the latter may be detected. According to the molecular orbital theory, in a supposed He2 molecule, both the bonding and the antibonding orbitals will have 2 electrons each.
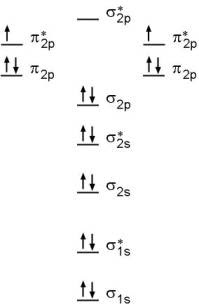
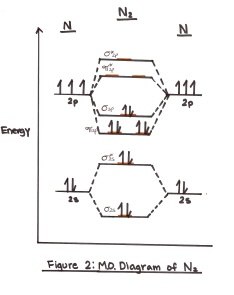
And so, the. Molecular orbital theory (MO theory) provides an explanation of chemical bonding that accounts for the paramagnetism of the oxygen molecule.
It also explains. Molecular orbital theory (MO theory) provides an explanation of chemical bonding that accounts for the paramagnetism of the oxygen molecule.
It also explains.© Prof Adam J Bridgeman | close windowProf Adam J Bridgeman | close window. Question: Construct the molecular orbital diagram for He2 and then identify the bond order.
Bond order: Cli Bond order: Cli Show transcribed image text Construct the molecular orbital diagram for He2 and then identify the bond order%(16). Sep 25, · According to the molecular orbital theory, in a supposed He2 molecule, both the bonding and the antibonding orbitals will have 2 electrons each.
And so, the bond order (half the difference in the numbers of bonding and antibonding electrons) for such a diatomic entity is zero. Aug 26, · After a preliminary check with He2 and He2+, self‐consistent field calculations have been carried out for the nitrogen and carbon monoxide molecules and some of their positive ions for the range of internuclear distances from about times equilibrium down to bohr. To adequately describe the passage from the separated to the united atom limits, basis sets comprised of even‐tempered.
The molecular orbital energy-level diagram, which is a diagram that shows the relative energies of molecular orbitals, for the H 2 molecule is shown in Figure b: MO theory of bonding in H₂⁺ – Chemistry LibreTextsDiatomic Species | MO theory | Chemogenesis