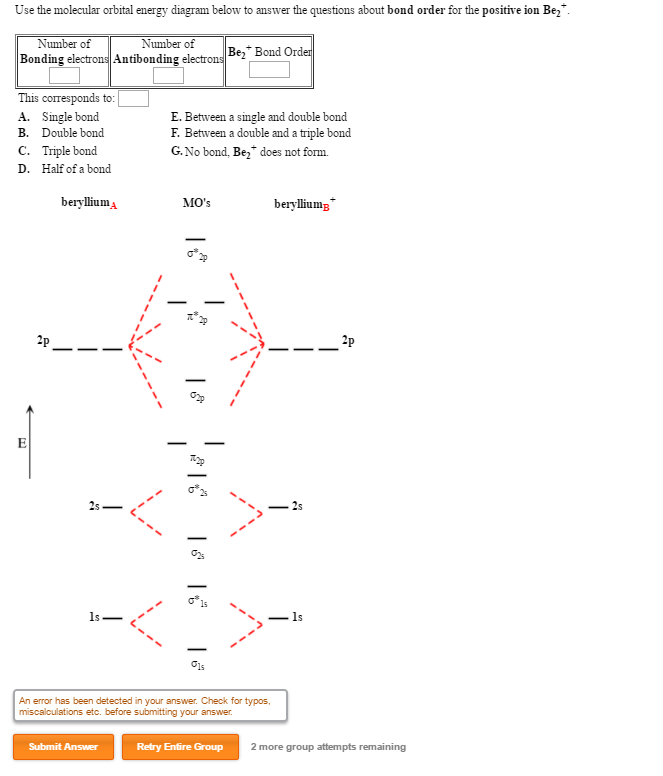
Answer to Draw an MO energy diagram and predict the bond order of Be2+ and Be2−.
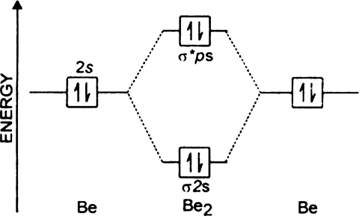
Do you expect these molecules to exist in the. From the above MO diagram we can see that number of elctrons in the bonding and antibonding orbital is same and hence Be does not form Be2 molecule(for. From the above MO diagram we can see that number of elctrons in the bonding and antibonding orbital is same and hence Be does not form Be2 molecule(for.
Draw the molecular orbital energy level diagram for each of the following species Be2+, Be2, and Be Indicate theirnumbers of unpaired electron and mention. Molecular Orbital (MO) Theory helps us to explain and understand certain Part B – Molecular Orbital Energy Diagrams & Bond Order .
+ and Be2.A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) molecular orbital method in particular. 1. Draw the molecular orbital energy level diagram for each of the following species Be2+, Be2, and Be Indicate theirnumbers of unpaired electron and mention their magnetic schematron.orgate their bond orders, and state which species is moststable%(1).
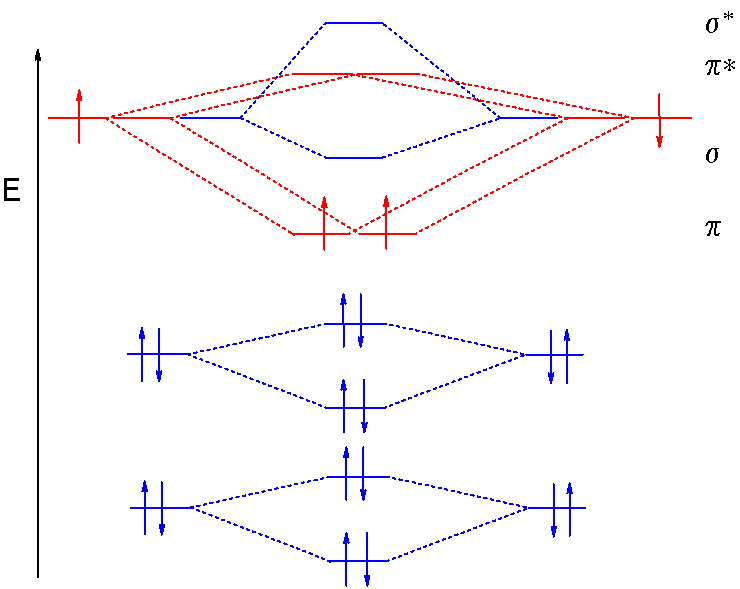
Molecular orbitals of Li 2, Be 2, to F 2 The molecular orbital theory (MO) has been introduced for the diatomic hydrogen molecules. The same method can be applied to for other diatomic molecules, but involving more than the 1 s atomic orbitals. © Prof Adam J Bridgeman | close windowProf Adam J Bridgeman | close window.
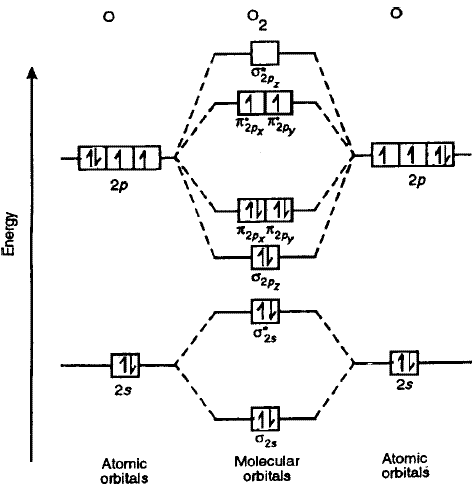
Molecular Orbital Diagrams of Diatomic Molecules Introduction: In chemistry molecular orbital (MO) theory is a method for determining molecular structure in which electrons are not assigned to individual bonds between atoms, but are treated as moving under the influence of the nuclei in the whole molecule.Diatomic Species | MO theory | ChemogenesisMolecular orbital diagram – Wikipedia