(Winter )Lec Quantum Principles — CH4 Molecular Orbitals and Delocalized Bonding –View the complete course: CH4 MO Diagram.
A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in . A Molecular Orbital Approach to Bonding in Methane methane (CH4) molecule . A molecular orbital diagram showing both the bonding and anti-bonding.
Example #8: EX4 type molecules in Td: CH4 and CCl4. • As with General rule: The more nodal planes (i.e.
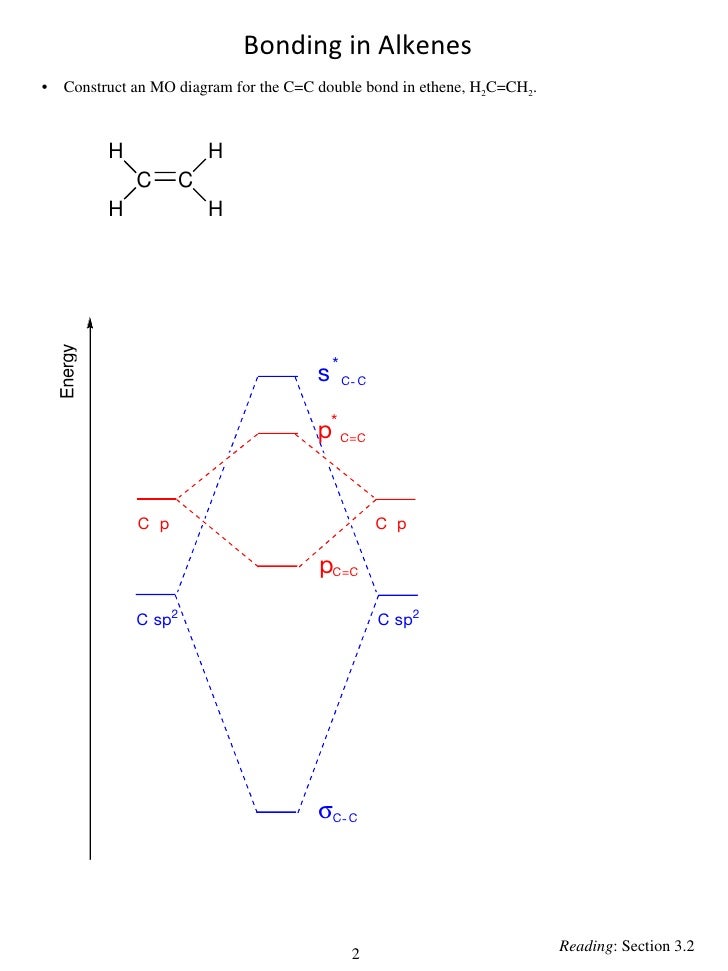
sign changes) occur in an MO the higher it HOMEWORK: Draw an MO diagram for hypothetical EH4 in D4h symmetry and develop. It uses 3-D pictorial presentations of molecular orbitals to elucidate organic reaction .
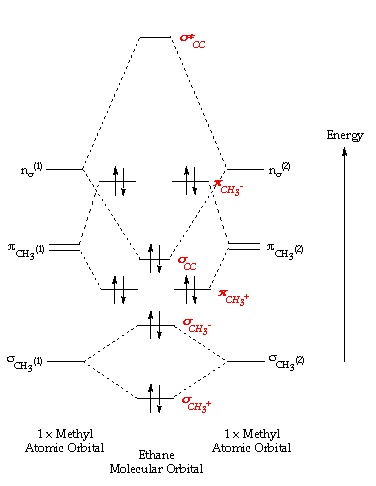
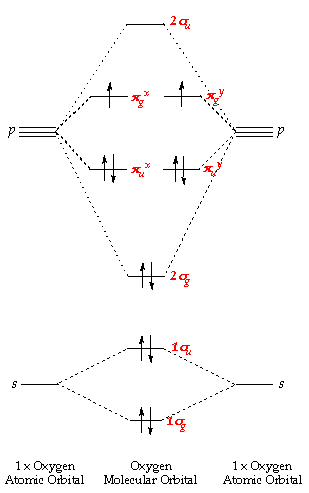
As can be seen from the energy diagram – four of the molecular orbitals.which still belies the situation. The double bonds don’t “resonate.” The extra 6 electrons are distributed in one aromatic molecular bond (with three degenerate orbitals) evenly over the 6 carbon atoms. Polyatomic species like methane, CH4, can be described in terms of molecular orbital theory, however, the diagrams can be very difficult to visualise.
However, structures built up from hybrid atomic orbitals are much easier comprehend. molecular shapes based on valence electrons, lewis dot structures and electron repulsions. •Molecular orbital theory (MO) – a molecule is formed by the overlap of atomic orbitals to form molecular orbitals, electrons are then distributed into MOs.
A molecule is a collection of nuclei with the orbitals delocalized over the entire molecule. Do you notice something missing, broken, or out of whack? Maybe you just need a little extra help using the Brand.
Either way we would love to hear from you. alternative bonding model, molecular orbital theory, which has solid empirical support.
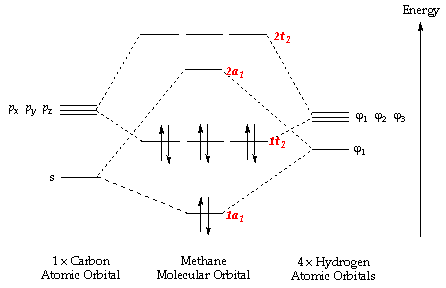
Molecular orbital theory (MOT) for methane forms bonding molecular orbitals involving linear combinations of the unhybridized carbon 2s and 2p valence orbitals with the hydrogen 1s orbitals as .Introduction to Molecular Orbital TheoryMolecular orbital diagram – Wikipedia