The lobes of a p orbital disappear at the nucleus. What does this tell us about electrons in p orbitals? The probability of finding an electron at the nucleus is 0.
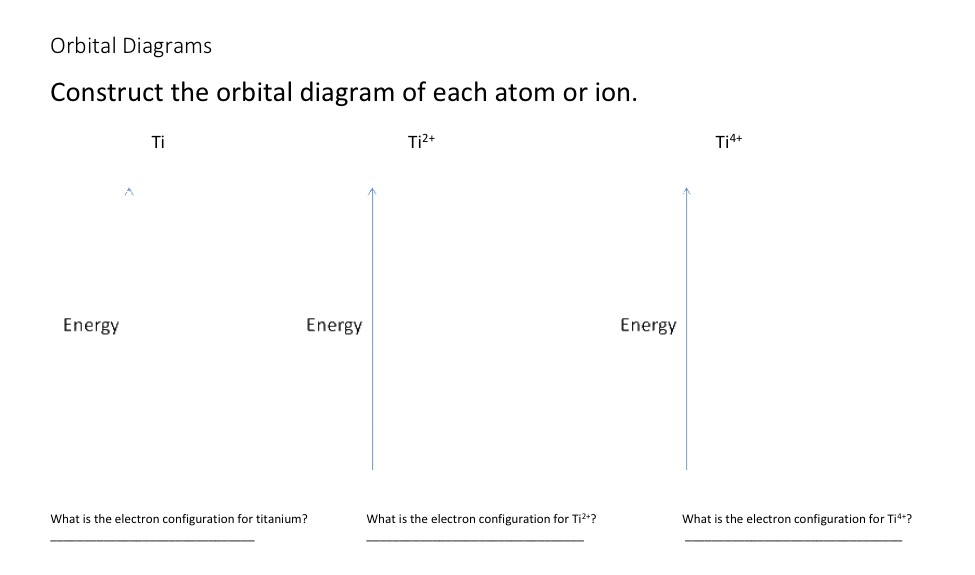
However, once the 4s orbital is filled, it becomes higher in energy than the 3d orbitals. This means that when titanium loses electrons, it does so. Answer to Construct the orbital diagram of each atom or ion.

Ti Ti2+ Ti4+. Which free ion has the greater number of unpaired d electrons, Ti2+ or Co2+? Draw the orbital diagram for the d orbitals in an octahedral complex containing.

Time-saving video by Brightstorm on Electron Configurations for Transition Metals and Their Ions Problem.The base expression (ground state; Ti0) is [Ar]3d24s2 so removal of 2 electrons to get the oxidation state of 2+ would result in the configuration of [Ar] 3d2. A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) molecular orbital method in particular.

What is the orbital diagram for Ti 2+? I got 1s two arrows, 2s two arrows, 2p 6 arrows, 3s two arrows, 3p six arrows, 4s two arrows but it is wrong. It said ions of d-block metals typically lack the outermost s electrons that are present in their neutral counterparts.

Draw the orbital diagram for the valence shell of Use an orbital diagram to describe the electron co Given the valence electron orbital level diagram a. Electron Configurations and Orbital Diagrams KEY Draw orbital diagrams for the following elements: 1. phosphorus ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑ ↑ ↑ 1s 2s 2p 3s 3p 4s 3d 4p.What is the electron configuration of “Ti”^(2+)?
| SocraticMolecular orbital diagram – Wikipedia