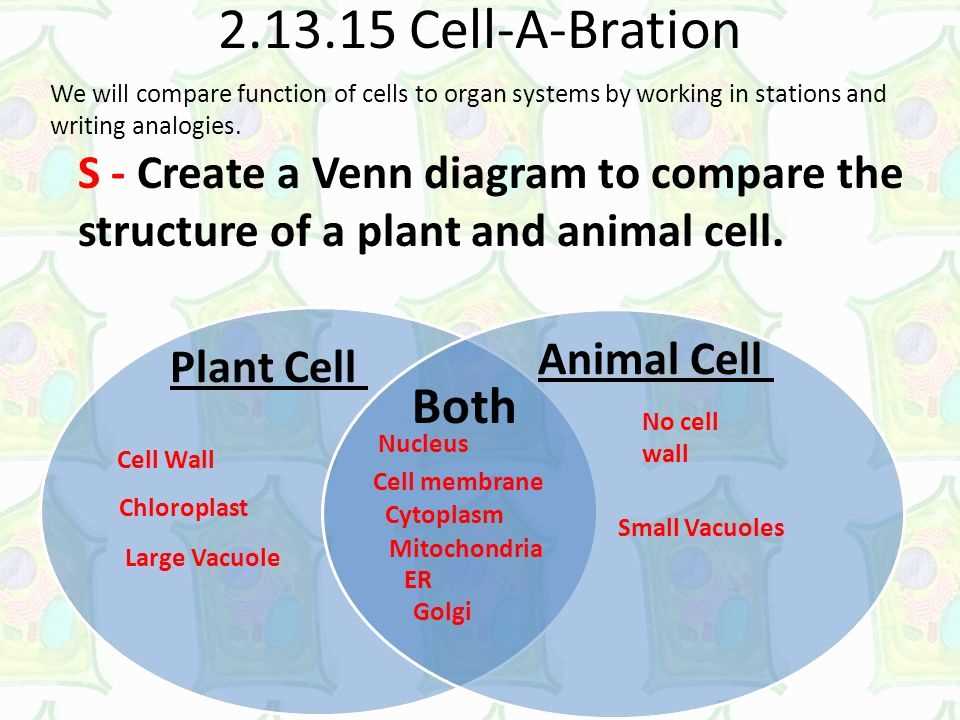
A Venn diagram is a visual representation that shows the similarities, differences, and overlaps between two or more categories or concepts. When it comes to the natural world, one popular Venn diagram compares plants and animals, highlighting their unique characteristics and traits.
Plants and animals are two distinct groups of living organisms, each with their own set of characteristics that define them. While both plants and animals are part of the larger classification of living organisms, there are several key differences between them.
Plants, for instance, are autotrophic organisms that make their own food through the process of photosynthesis. They have chloroplasts, structures that contain chlorophyll, which enables them to convert sunlight into energy. In contrast, animals are heterotrophic organisms that cannot produce their own food and rely on consuming other organisms to obtain energy.
Despite these differences, there are also many similarities between plants and animals. Both groups are made up of cells, have the ability to reproduce, and require certain conditions to survive. They also share a common evolutionary history, with evidence suggesting that plants and animals are descended from a common ancestor.
What is a Plant and Animal Venn Diagram?
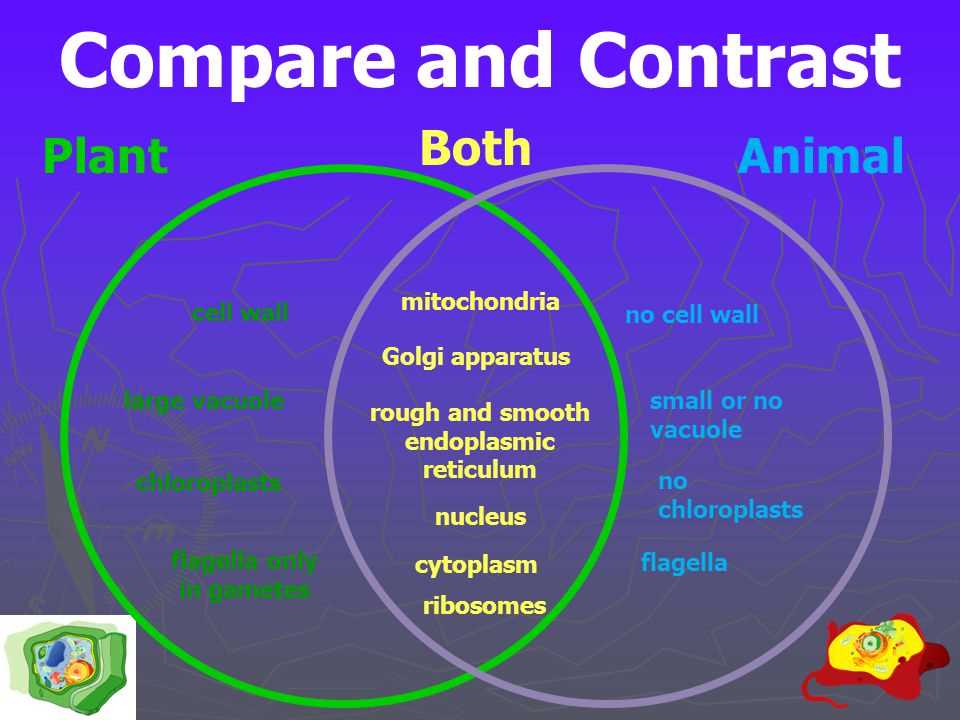
A plant and animal Venn diagram is a visual tool used to compare and contrast the characteristics of plants and animals. It is a diagram that consists of two overlapping circles, with one circle representing plants and the other circle representing animals. The areas where the circles overlap indicate shared characteristics between the two groups.
Plants: Plants are living organisms that belong to the kingdom Plantae. They are characterized by their ability to photosynthesize, meaning they can convert sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide into energy. Plants have cell walls made of cellulose, and they reproduce through seeds or spores. They also have roots, stems, and leaves, which are essential for their growth and survival.
Animals: Animals are multicellular organisms that belong to the kingdom Animalia. They are characterized by their ability to move and obtain energy by consuming other organisms. Unlike plants, animals do not have cell walls and are typically mobile. They have specialized sense organs, such as eyes and ears, and they reproduce sexually.
By using a plant and animal Venn diagram, one can identify the unique characteristics of plants and animals, as well as the similarities they share. This visual representation helps in understanding the diverse world of living organisms and their various adaptations to their environments.
Definition and Overview
In the study of biology, plants and animals are two major classifications of living organisms. While they share some similarities, there are also distinct differences between them. A Venn diagram is a useful tool to visually represent these similarities and differences, allowing for a better understanding of their characteristics.
Plants, also known as flora, refer to multicellular organisms that possess cell walls made of cellulose. They are capable of photosynthesis, which is the process of converting sunlight into energy. Plants play a vital role in the ecosystem as they are the primary producers, providing food and oxygen for other organisms. They can be found in various environments such as forests, grasslands, and aquatic habitats.
On the other hand, animals, also known as fauna, are multicellular organisms that lack cell walls and are heterotrophic, meaning they obtain their nutrients by consuming other organisms. Animals have complex body systems and are capable of movement. They can be further classified into different groups based on their characteristics, such as vertebrates (animals with a backbone) and invertebrates (animals without a backbone).
Despite their differences, plants and animals also share some common features. Both require water, nutrients, and sunlight to survive. They have cells, tissues, and organs that work together to carry out essential functions. Additionally, both plants and animals reproduce, although they may utilize different methods such as pollination in plants and sexual reproduction in animals.
In conclusion, plants and animals are two distinct classifications of living organisms. Plants are characterized by cell walls, photosynthesis, and their role as primary producers, while animals lack cell walls and obtain their nutrients by consuming other organisms. Understanding the similarities and differences between plants and animals is essential for studying their respective characteristics and roles in the ecosystem.
Key Similarities Between Plants and Animals
Plants and animals are two distinct categories of organisms that inhabit the Earth. While they have their own unique characteristics and functions, there are several key similarities between plants and animals that are worth exploring.
1. Cellular structure: Both plants and animals are composed of cells, which are the basic building blocks of life. These cells have similar components, such as a nucleus, cytoplasm, and organelles, which allow them to carry out various functions.
2. Need for energy: Both plants and animals require energy to survive and carry out their respective life processes. Plants obtain energy through photosynthesis, while animals acquire energy by consuming food. In both cases, energy is necessary for growth, reproduction, and other essential activities.
3. Reproduction: Both plants and animals have the ability to reproduce and ensure the survival of their species. Plant reproduction can occur through either sexual or asexual means, whereas animals typically reproduce sexually. Regardless of the method, the end goal is to pass on genetic material to the next generation.
4. Response to stimuli: Plants and animals both exhibit the ability to respond to external stimuli from their environment. For example, plants bend towards a light source, while animals may react to changes in temperature or movement. This ability to respond to stimuli is crucial for adaptation and survival.
5. Homeostasis: Both plants and animals have mechanisms in place to maintain a state of internal balance, known as homeostasis. This involves regulating factors such as temperature, pH levels, and nutrient concentrations to ensure optimal functioning of cells and overall well-being.
- Overall, while there are many differences between plants and animals, these key similarities highlight the fundamental aspects of life shared by both groups of organisms.
Key Differences Between Plants and Animals
Plants and animals are two diverse forms of life on Earth, each with their own unique characteristics and adaptations. Understanding the key differences between them is essential for studying biology and ecology. Below are some of the key differences that distinguish plants from animals:
Cell Structure and Organization:
- Plants: Plants are multicellular organisms with a well-defined cell wall made of cellulose. They have specialized cell types, such as parenchyma, collenchyma, and sclerenchyma, which contribute to their structural support.
- Animals: Animals are also multicellular but lack a cell wall. Instead, they have a plasma membrane that encloses the cells. Animal cells have various organelles, including mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, and lysosomes.
Nutrition and Energy Source:
- Plants: Plants are autotrophic organisms that produce their own food through photosynthesis. They absorb sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide to synthesize glucose, which is used as a source of energy.
- Animals: Animals are heterotrophic organisms that obtain their food by consuming other organisms. They require complex organic molecules, such as carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids, for energy and survival.
Mobility:
- Plants: Plants are generally immobile or sessile organisms. They obtain nutrients through their roots and are rooted firmly in the ground. Some plants, however, show limited movement, such as the bending of stems towards sunlight.
- Animals: Animals are highly mobile organisms. They exhibit various modes of locomotion, including walking, crawling, swimming, and flying. Mobility allows animals to search for food, mates, and suitable habitats.
Reproduction:
- Plants: Plants exhibit both sexual and asexual reproduction. Sexual reproduction involves the fusion of male and female gametes, while asexual reproduction involves vegetative propagation through structures like rhizomes, bulbs, or runners.
- Animals: Animals primarily reproduce sexually, with the union of male and female gametes. However, some animals can also reproduce asexually through methods such as budding, fragmentation, or parthenogenesis.
These are just a few of the key differences between plants and animals. By exploring these distinctions, scientists can gain a deeper understanding of the intricate mechanisms and adaptations that have evolved in these two remarkable forms of life.
Examples of Plants
There are millions of different plant species on Earth, ranging from tiny mosses to towering trees. Plants play a crucial role in the ecosystem, providing food, shelter, and oxygen for other living organisms. Here are a few examples of plants:
- Rose: Roses are beautiful flowering plants that belong to the family Rosaceae. They are known for their fragrant and colorful petals, which come in a variety of shades, including red, pink, yellow, and white. Roses are often cultivated for their ornamental purposes and are common in gardens.
- Palm Tree: Palm trees are tall, tropical plants that are commonly found in coastal regions. They have a distinctive appearance, with a long, slender trunk and a crown of large, fan-shaped leaves. Palm trees are known for their ability to withstand strong winds and are often associated with beach landscapes.
- Wheat: Wheat is a cereal grain that is widely cultivated for its edible seeds. It is a staple food in many parts of the world and is used to make a variety of products, including bread, pasta, and cereals. Wheat plants have long, slender stalks with clusters of small flowers at the top.
- Sunflower: Sunflowers are large, vibrant plants that belong to the family Asteraceae. They are known for their tall stalks and large, yellow flower heads that follow the movement of the sun throughout the day. Sunflower seeds are popular snacks and are also used to extract oil.
These are just a few examples of the incredible diversity of plants that exist on our planet. Each plant has its own unique characteristics and adaptations that allow it to survive and thrive in different environments. Whether it’s providing us with food, shelter, or simply adding beauty to our surroundings, plants are an essential part of our lives.
Examples of Animals
Animals are a diverse group of living organisms that inhabit the Earth. They come in various shapes, sizes, and habitats. Here are some examples of animals:
- Mammals: Mammals are warm-blooded vertebrates that typically have hair or fur and produce milk to nourish their young. Examples include dogs, cats, elephants, and dolphins.
- Birds: Birds are warm-blooded vertebrates characterized by their feathers and beaks. They are known for their ability to fly. Examples include eagles, sparrows, penguins, and flamingos.
- Reptiles: Reptiles are cold-blooded vertebrates with dry, scaly skin. They lay eggs and have lungs for breathing. Examples include snakes, crocodiles, turtles, and lizards.
- Amphibians: Amphibians are cold-blooded vertebrates that undergo metamorphosis from aquatic larvae to terrestrial adults. They have moist skin and lay eggs in water. Examples include frogs, toads, salamanders, and newts.
- Fish: Fish are cold-blooded vertebrates that live in water and have gills for breathing. They come in various shapes and sizes. Examples include goldfish, sharks, trout, and clownfish.
These are just a few examples of the wide variety of animals that exist on our planet. Each species has its unique characteristics and plays a vital role in maintaining the balance of ecosystems. Animals are not only fascinating to study but also essential for the well-being of our planet.
By appreciating and understanding the diversity of animal life, we can work towards preserving their habitats and ensuring a sustainable future for all living creatures.